Abstract
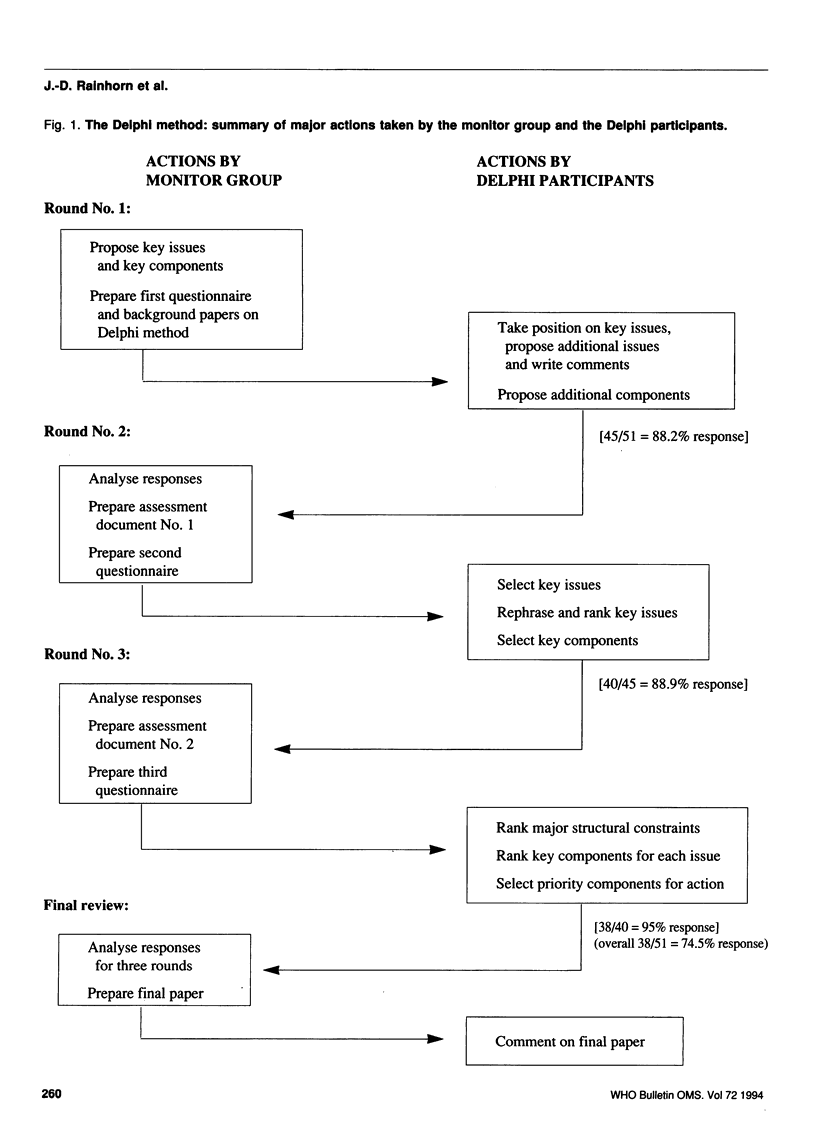
The use of the Delphi method as a systematic and logical approach to establishing consensus among international experts on the priorities for interventions in national drug policies in developing countries is described. The Delphi survey showed a high degree of reliability, as evidenced by the high response rate, the quality of respondents, and the high standard for consensus. In addition to creating consensus on key issues and key components for priority intervention, the study identified six components that could constitute a basic framework for designing drug policy in developing countries. The study's conclusions have important implications for decision-makers within international development agencies and national governments.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Farrell P., Scherer K. The Delphi technique as a method for selecting criteria to evaluate nursing care. Nurs Pap. 1983 Spring;15(1):51–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink A., Kosecoff J., Chassin M., Brook R. H. Consensus methods: characteristics and guidelines for use. Am J Public Health. 1984 Sep;74(9):979–983. doi: 10.2105/ajph.74.9.979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourley D. R., Hadsall R. S., Gourley G., Fine D. J., Wiener M. ASHP members' concepts of institutional pharmacy in the year 2000. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1985 Jan;42(1):96–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldi R. C., Steindler E. M., Wilford B. B., Goodwin D. Clarification and standardization of substance abuse terminology. JAMA. 1988 Jan 22;259(4):555–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohatgi K., Rohatgi P. K. A delphi study on health in future India. J Sci Ind Res (India) 1980 Jul;39(7):359–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soumerai S. B., McLaughlin T. J., Avorn J. Improving drug prescribing in primary care: a critical analysis of the experimental literature. Milbank Q. 1989;67(2):268–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson D. F., Heflin N. R. Frequency and appropriateness of drug prescribing for unlabeled uses in pediatric patients. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1987 Apr;44(4):792–794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


