Abstract
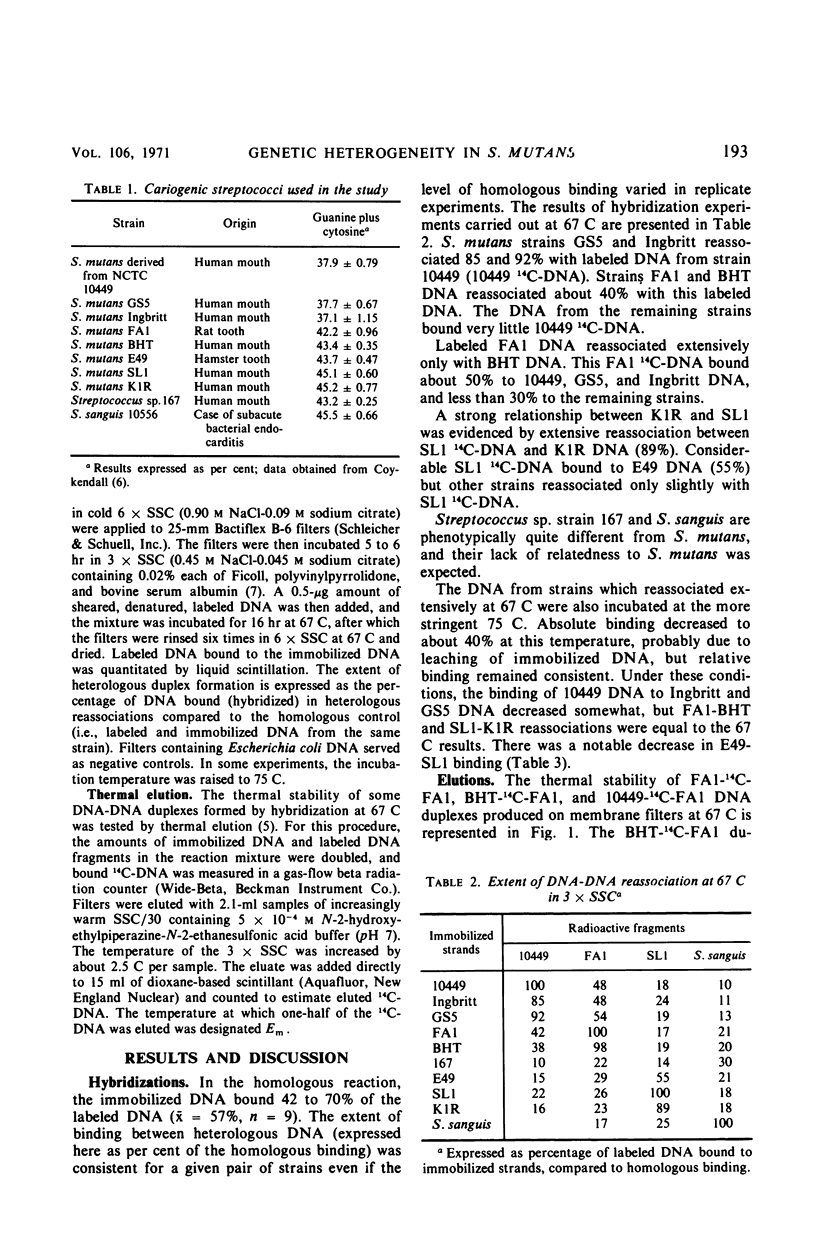
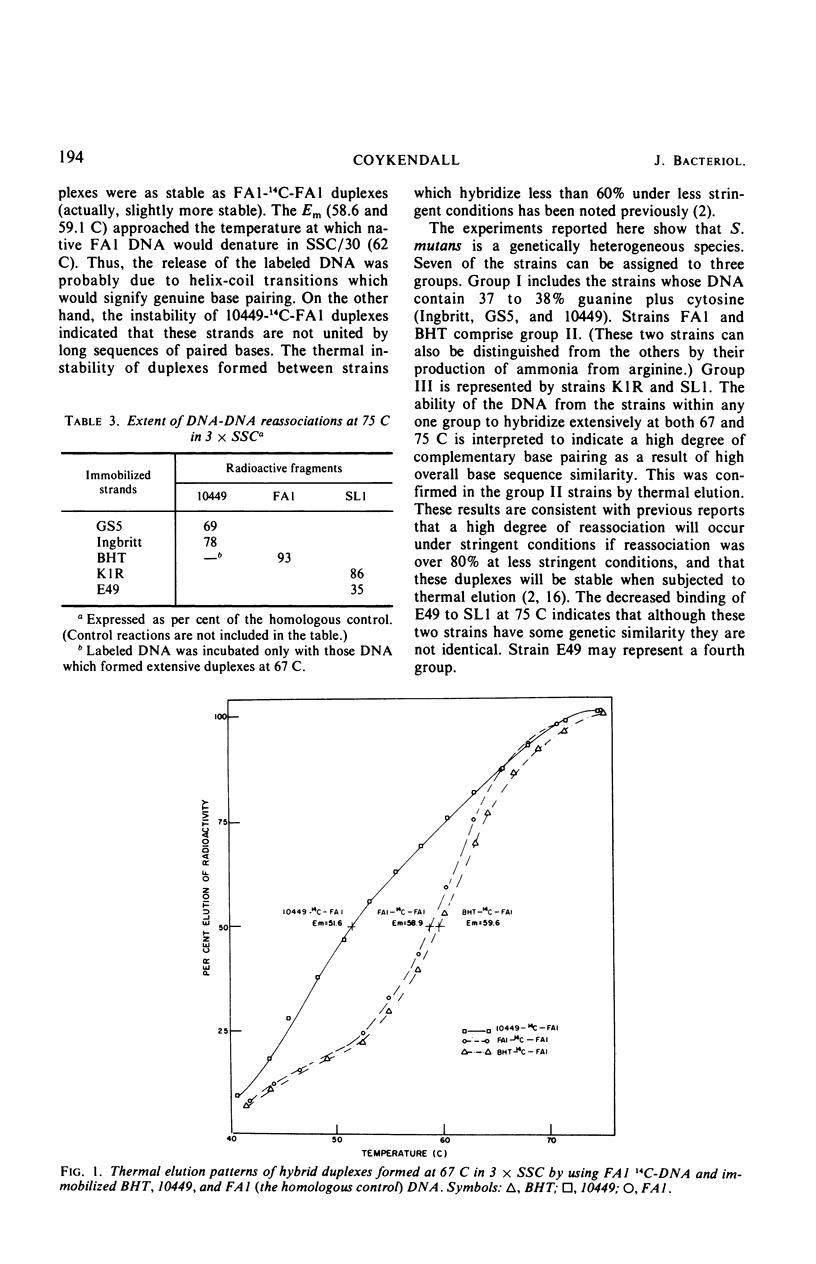
The genetic homogeneity among eight cariogenic strains of Streptococcus mutans was assessed by deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)-DNA reassociation experiments. DNA species were extracted from strains GS5, Ingbritt, 10449, FAl, BHT, E49, SLl, and KlR. Labeled DNA (14C-DNA) was extracted from strains 10449, FAl, and SLl. Denatured 14C-DNA fragments were allowed to reassociate, i.e., form hybrid duplexes, with denatured DNA immobilized on membrane filters incubated in 0.45 m NaCl-0.045 m sodium citrate at 67 or 75 C. At 67 C, 10449 14C-DNA reassociated extensively only with GS5 and Ingbritt DNA. FAl 14C-DNA hybridized extensively only with BHT DNA, and SLl 14C-DNA reassociated with KlR and E49 DNA. DNA which hybridized extensively at 67 C also reassociated to a high degree at 75 C. Thermal elution of 14C-FAl-BHT duplexes showed that the hybrid duplexes were thermostable. The results indicate that S. mutans is a genetically heterogeneous species. The strains studied can be divided into three (possibly four) genetic groups, and these groups closely parallel antigenic groups.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bratthall D. Demonstration of five serological groups of streptococcal strains resembling Streptococcus mutans. Odontol Revy. 1970;21(2):143–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. J., Fanning G. R., Johnson K. E., Citarella R. V., Falkow S. Polynucleotide sequence relationships among members of Enterobacteriaceae. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):637–650. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.637-650.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson J. A numerical taxonomic study of human oral streptococci. Odontol Revy. 1968;19(2):137–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowie D. B., Szafranski P. Thermal chromatography of DNA-DNA reactions. Biophys J. 1967 Sep;7(5):567–584. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(67)86607-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coykendall A. L. Base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid isolated from cariogenic streptococci. Arch Oral Biol. 1970 Apr;15(4):365–368. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(70)90063-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drucker D. B., Melville T. H. Computer classification of streptococci, mostly of oral origin. Nature. 1969 Feb 15;221(5181):664–664. doi: 10.1038/221664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwardsson S. Characteristics of caries-inducing human streptococci resembling Streptococcus mutans. Arch Oral Biol. 1968 Jun;13(6):637–646. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(68)90142-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FITZGERALD R. J., KEYES P. H. Demonstration of the etiologic role of streptococci in experimental caries in the hamster. J Am Dent Assoc. 1960 Jul;61:9–19. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.1960.0138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser F., Mandel M. Deoxyribonucleic acid base composition of the genus Lactobacillus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):580–588. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.580-588.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser F., Mandel M., Rogosa M. Lactobacillus jensenii sp.nov., a new representative of the subgenus Thermobacterium. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Aug;62(2):219–222. doi: 10.1099/00221287-62-2-219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guggenheim B. Streptococci of dental plaques. Caries Res. 1968;2(2):147–163. doi: 10.1159/000259553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer B. H., McCullough N. B. Homologies of deoxyribonucleic acids from Brucella ovis, canine abortion organisms, and other Brucella species. J Bacteriol. 1968 Nov;96(5):1783–1790. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.5.1783-1790.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JORDAN H. V., FITZGERALD R. J., BOWLER A. E. Inhibition of experimental caries by sodium metabisulfite and its effect on the growth and metabolism of selected bacteria. J Dent Res. 1960 Jan-Feb;39:116–123. doi: 10.1177/00220345600390010501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. L., Ordal E. J. Deoxyribonucleic acid homology in bacterial taxonomy: effect of incubation temperature on reaction specificity. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):893–900. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.893-900.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A., 3rd, Sandine W. E., Elliker P. R. Deoxyribonucleic acid base composition of lactobacilli determined by thermal denaturation. J Bacteriol. 1970 Apr;102(1):278–280. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.1.278-280.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niven C. F., Smiley K. L., Sherman J. M. The Hydrolysis of Arginine by Streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1942 Jun;43(6):651–660. doi: 10.1128/jb.43.6.651-660.1942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E., Schramek S., Wilson N. N., Newman L. W. Deoxyribonucleic Acid Heterogeneity Between Human and Murine Strains of Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1970 Jul;2(1):24–28. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.1.24-28.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZINNER D. D., JABLON J. M., ARAN A. P., SASLAW M. S. EXPERIMENTAL CARIES INDUCED IN ANIMALS BY STREPTOCOCCI OF HUMAN ORIGIN. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Mar;118:766–770. doi: 10.3181/00379727-118-29964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinner D. D., Jablon J. M. Cariogenic streptococci in infants. Arch Oral Biol. 1969 Dec;14(12):1429–1431. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(69)90260-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



