Abstract
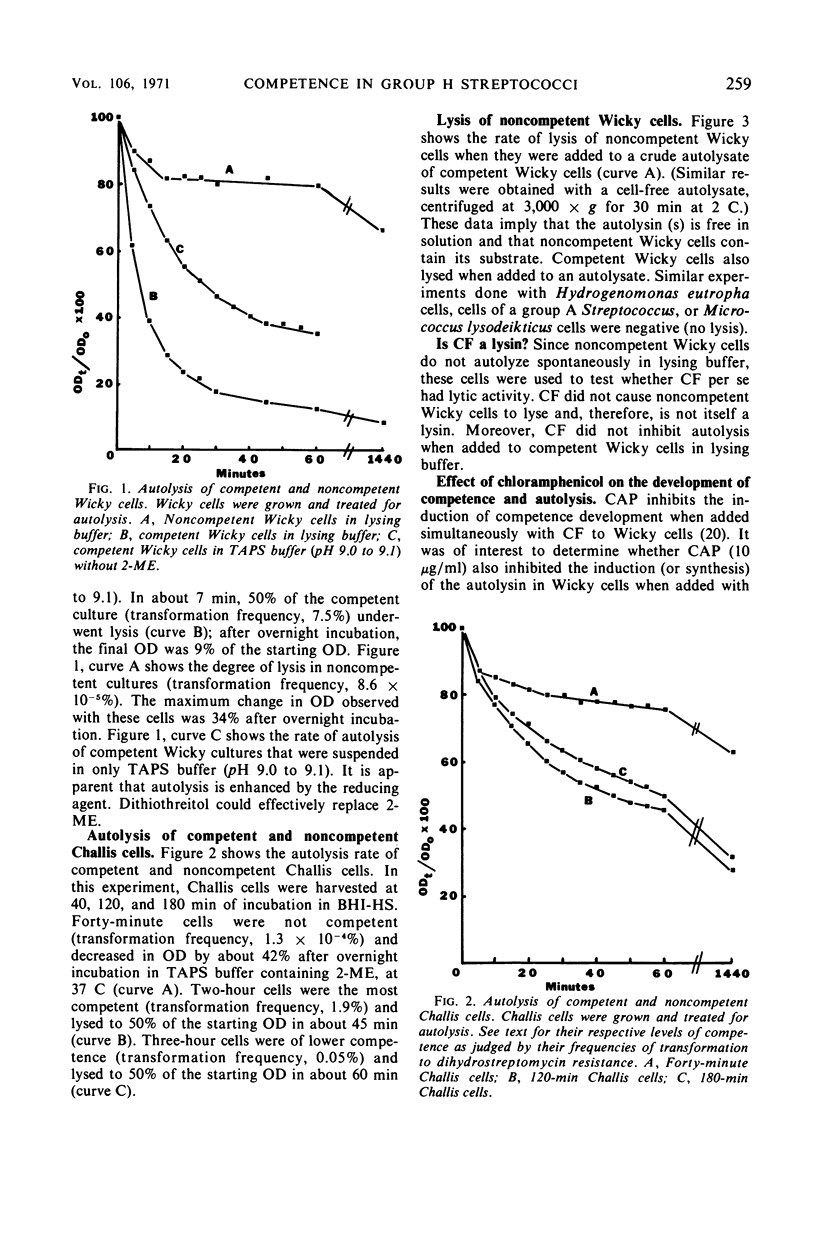
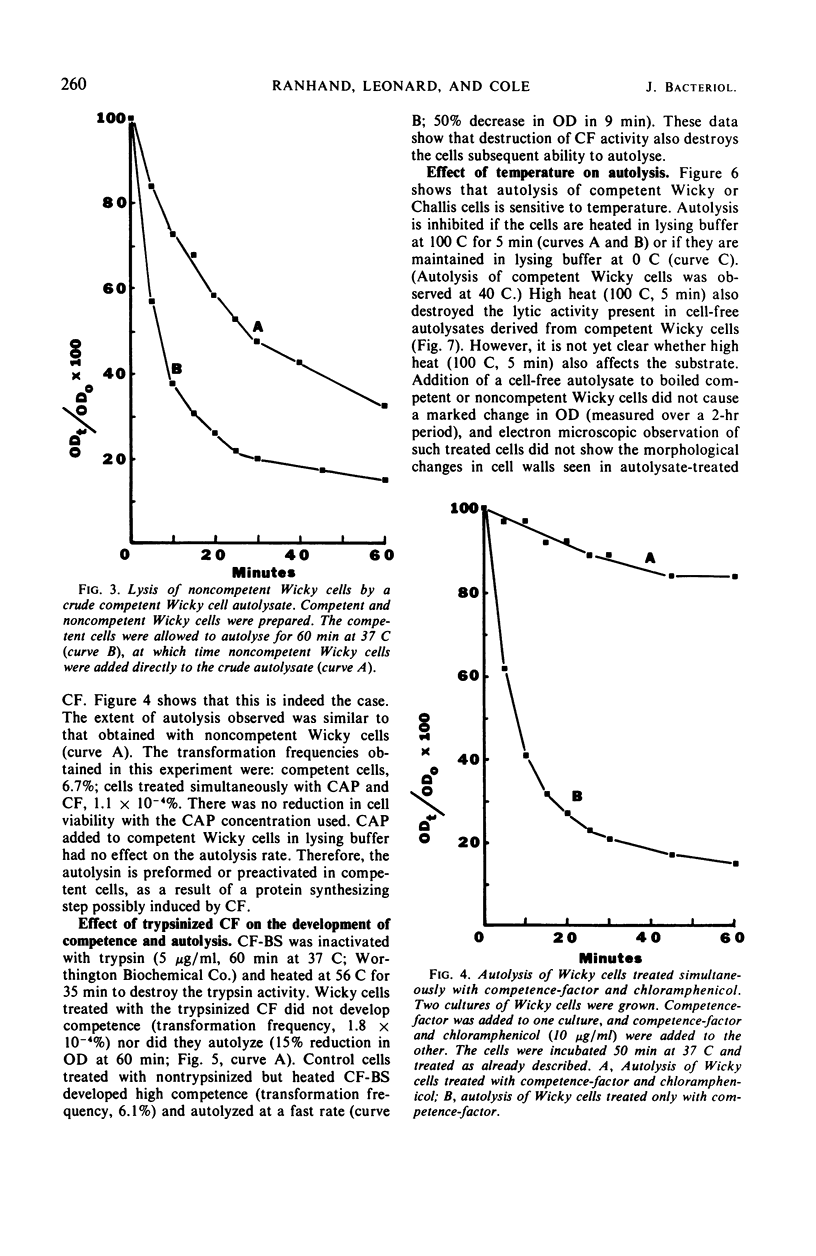
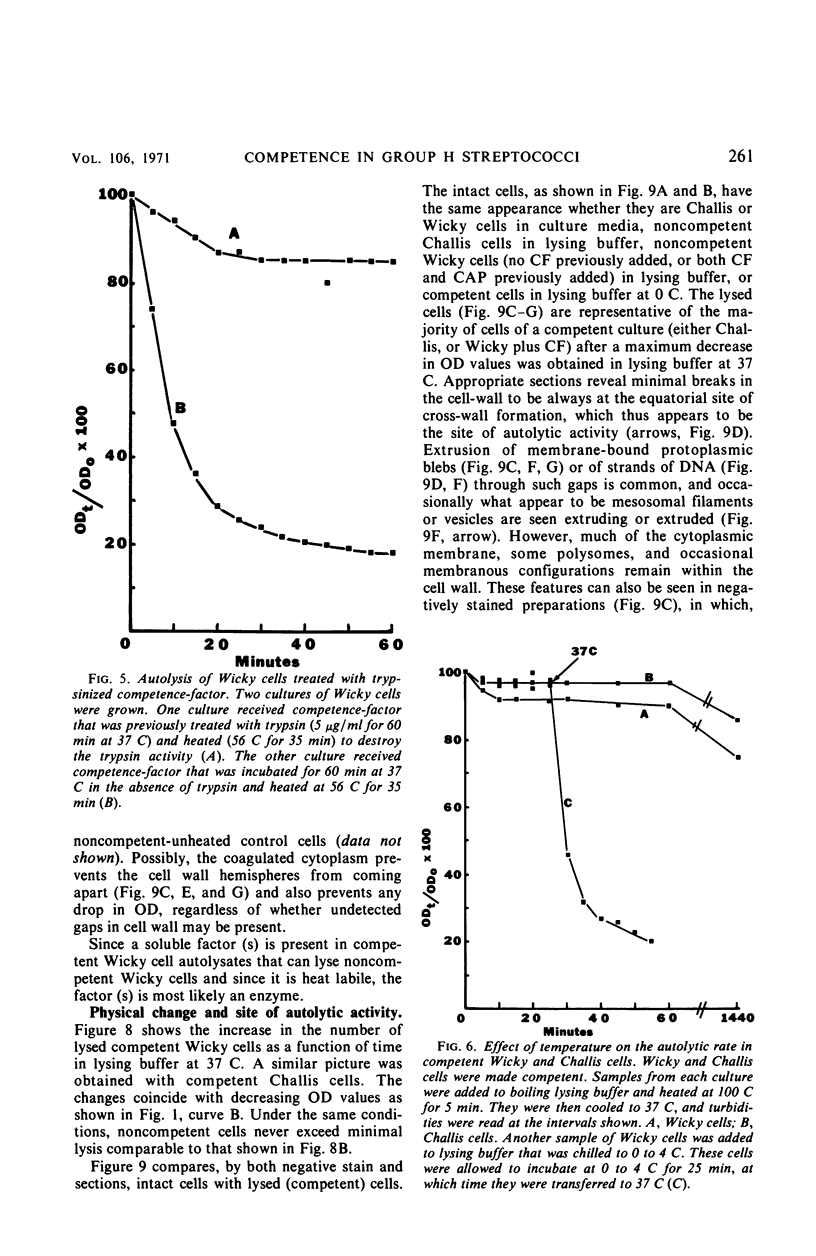
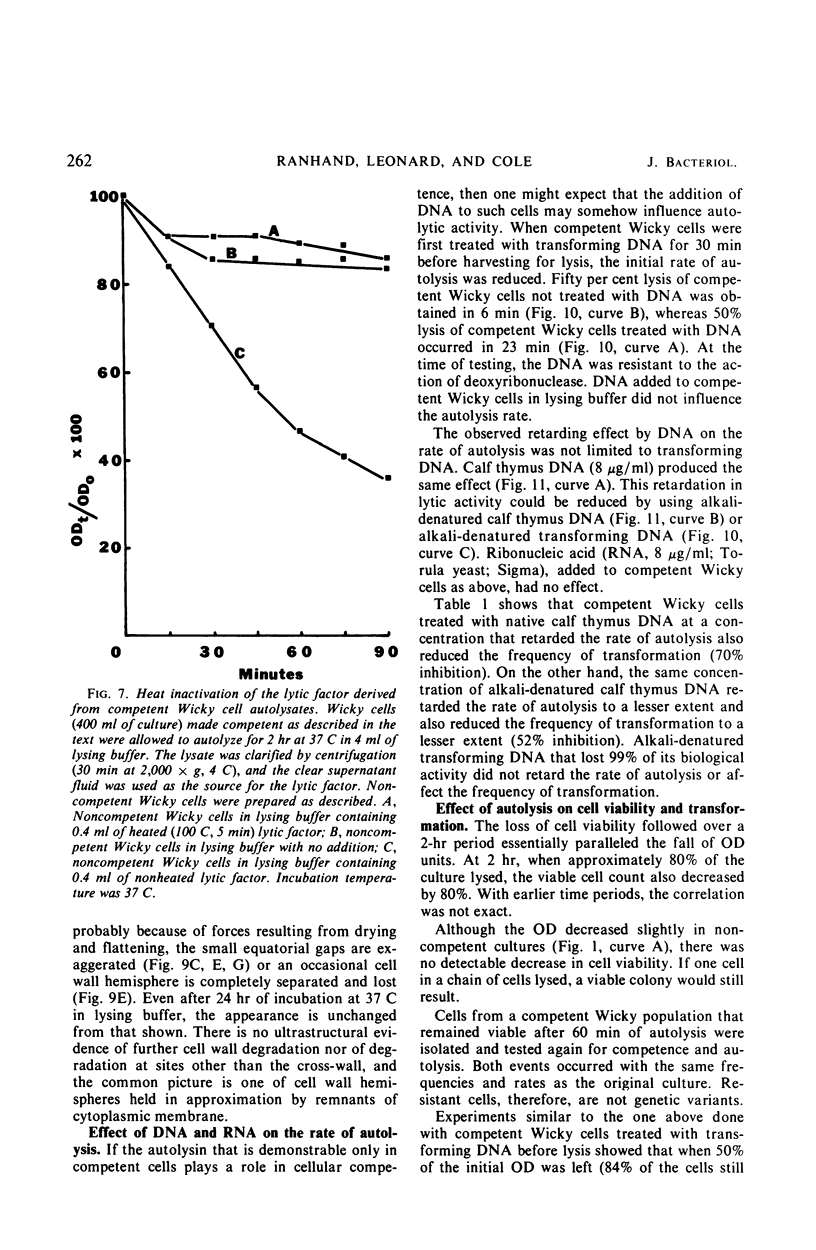
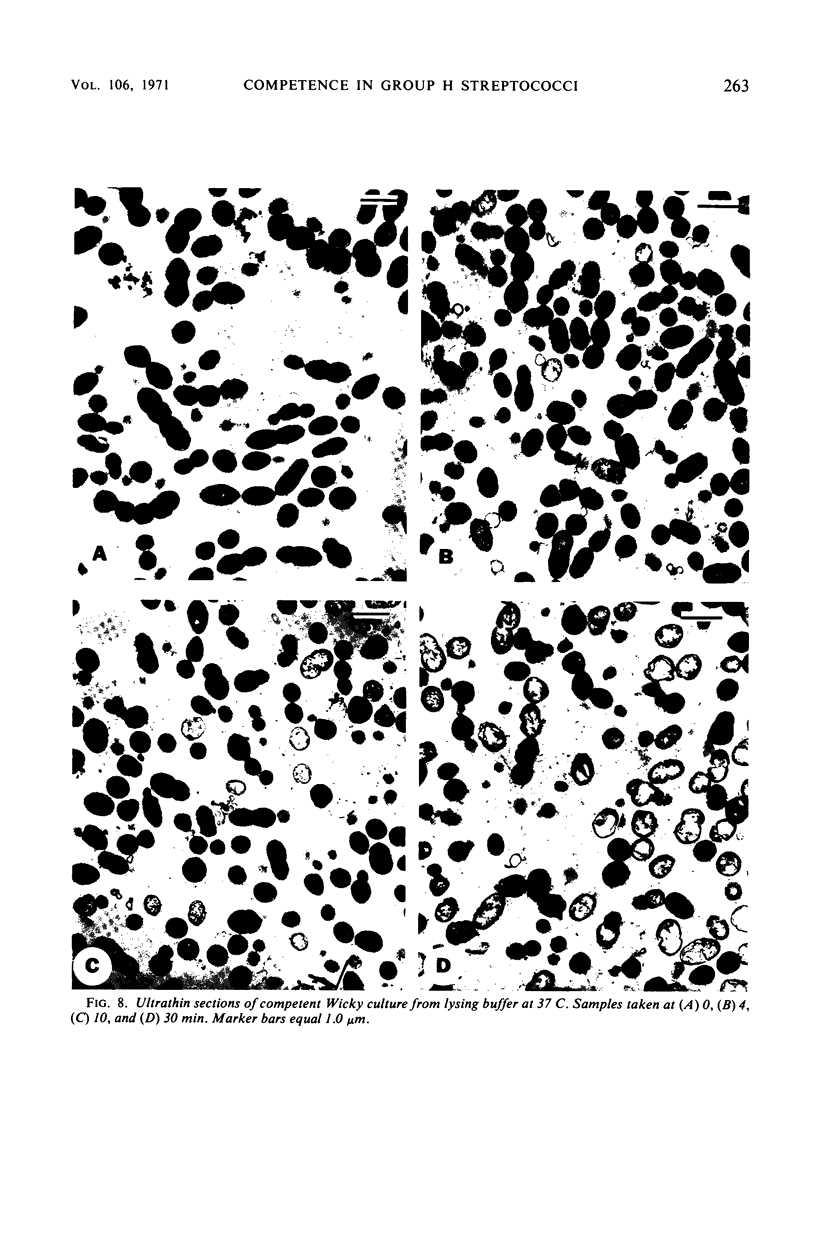
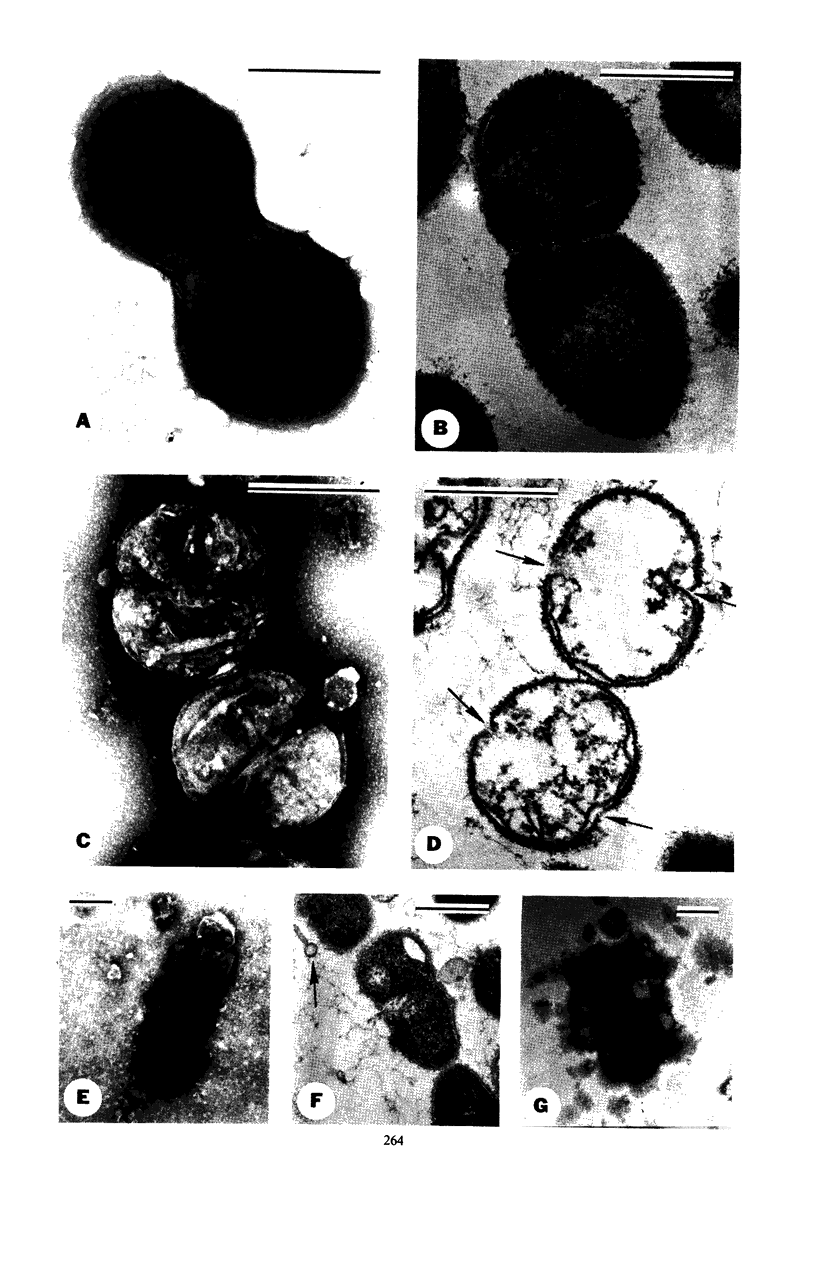
Competent cells of group H streptococci strains Wicky and Challis autolyzed markedly when placed at 37 C in 0.05 m tris(hydroxymethyl)methyl-amino-propane sulfonic acid buffer (pH 9.0 to 9.1) containing 0.02 m 2-mercaptoethanol, whereas noncompetent cells autolyzed slightly. Autolysis of competent Wicky cells did not occur at 0 C or after the cells were heated at 100 C for 5 min. Culture fluids derived from strain Challis that contained competence factor (CF) activity did not contain lytic activity. Addition of native deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) to competent Wicky cells caused a retardation in the rate of autolysis; ribonucleic acid and alkali-denatured DNA had less of an effect. Supernantant fluids derived from competent cell lysates lysed noncompetent Wicky cells but were inactive against cells of Hydrogenomonas eutropha, a group A Streptococcus, and against a commercial lysozyme substrate (Micrococcus lysodeikticus). This lytic activity was inactivated by heat (5 min at 100 C). Electron microscopic observations of autolyzed cells showed that autolysis occurs only at the site of cross-wall formation. A close relationship between the development of competence and autolysis is suggested by the fact that certain conditions that prevent the establishment of the competent state in Wicky populations (such as no CF, addition of CF simultaneously with chloramphenicol, and addition of trypsin-inactivated CF) also prevent autolysis. This observation emphasizes the indirect or inductive nature of CF on these processes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akrigg A., Ayad S. R., Blamire J. Uptake of DNA by competent bacteria--a possible mechanism. J Theor Biol. 1969 Sep;24(3):266–272. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(69)80051-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akrigg A., Ayad S. R. Studies on the competence-inducing factor of Bacillus subtilis. Biochem J. 1970 Apr;117(2):397–403. doi: 10.1042/bj1170397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARKULIS S. S., SMITH C., BOLTRALIK J. J., HEYMANN H. STRUCTURE OF STREPTOCOCCAL CELL WALLS. IV. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF STREPTOCOCCAL PHAGE MURALYSIN. J Biol Chem. 1964 Dec;239:4027–4033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRUMFITT W., WARDLAW A. C., PARK J. T. Development of lysozyme-resistance in Micrococcus lysodiekticus and its association with an increased O-acetyl content of the cell wall. Nature. 1958 Jun 28;181(4626):1783–1784. doi: 10.1038/1811783a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLE R. M., HAHN J. J. Cell wall replication in Streptococcus pyogenes. Science. 1962 Mar 2;135(3505):722–724. doi: 10.1126/science.135.3505.722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins M. L., Pooley H. M., Shockman G. D. Site of initiation of cellular autolysis in Streptococcus faecalis as seen by electron microscopy. J Bacteriol. 1970 Aug;103(2):504–512. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.2.504-512.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins M. L., Shockman G. D. Early changes in the ultrastructure of Streptococcus faecalis after amino acid starvation. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jul;103(1):244–253. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.1.244-253.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins M. L., Shockman G. D. Model for cell wall growth of Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1970 Feb;101(2):643–648. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.2.643-648.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAUSE R. M. Studies on the bacteriophages of hemolytic streptococci. II. Antigens released from the streptococcal cell wall by a phage-associated lysin. J Exp Med. 1958 Dec 1;108(6):803–821. doi: 10.1084/jem.108.6.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S. Mutants of Diplococcus pneumoniae that lack deoxyribonucleases and other activities possibly pertinent to genetic transformation. J Bacteriol. 1970 Feb;101(2):373–383. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.2.373-383.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard C. G., Corley D. C., Cole R. M. Transformation of streptococci in chemically defined media. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Jan 23;26(2):181–186. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90231-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard C. G., Ranhand J. M., Cole R. M. Competence factor production in chemically defined media by noncompetent cells of group H Streptococcus strain Challis. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):674–683. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.674-683.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAXTED W. R. The active agent in nascent phage lysis of streptococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Jun;16(3):584–595. doi: 10.1099/00221287-16-3-584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL P., MOYLE J. Autolytic release and osmotic properties of protoplasts from Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Feb;16(1):184–194. doi: 10.1099/00221287-16-1-184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAKULA R., CYBULSKA J., WALCZAK W. THE EFFECT OF ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS ON TRANSFORMABILITY OF A STREPTOCOCCUS. Acta Microbiol Pol. 1963;12:245–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pakula R. Production of competence-provoking factor and development of competence of a transformable streptococcus in serum-free media. Can J Microbiol. 1965 Oct;11(5):811–822. doi: 10.1139/m65-110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pooley H. M., Shockman G. D. Relationship between the location of autolysin, cell wall synthesis, and the development of resistance to cellular autolysis in Streptococcus faecalis after inhibition of protein synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1970 Aug;103(2):457–466. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.2.457-466.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYTER A., KELLENBERGER E., BIRCHANDERSEN A., MAALOE O. Etude au microscope électronique de plasmas contenant de l'acide désoxyribonucliéique. I. Les nucléoides des bactéries en croissance active. Z Naturforsch B. 1958 Sep;13B(9):597–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranhand J. M., Theodore T. S., Cole R. M. Protein difference between competent and noncompetent cultures of a group H Streptococcus. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):360–362. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.360-362.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABATINI D. D., BENSCH K., BARRNETT R. J. Cytochemistry and electron microscopy. The preservation of cellular ultrastructure and enzymatic activity by aldehyde fixation. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:19–58. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shockman G. D., Martin J. T. Autolytic enzyme system of Streptococcus faecalis. IV. Electron microscopic observations of autolysin and lysozyme action. J Bacteriol. 1968 Nov;96(5):1803–1810. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.5.1803-1810.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shockman G. D. Symposium on the fine structure and replication of bacteria and their parts. IV. Unbalanced cell-wall synthesis: autolysis and cell-wall thickening. Bacteriol Rev. 1965 Sep;29(3):345–358. doi: 10.1128/br.29.3.345-358.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart C. R., Marmur J. Increase in lytic activity in competent cells of Bacillus subtilis after uptake of deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1970 Feb;101(2):449–455. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.2.449-455.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A. Biological consequences of the replacement of choline by ethanolamine in the cell wall of Pneumococcus: chanin formation, loss of transformability, and loss of autolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jan;59(1):86–93. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.1.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUNG F. E., SPIZIZEN J. BIOCHEMICAL ASPECTS OF COMPETENCE IN THE BACILLUS SUBTILIS TRANSFORMATION SYSTEM. II. AUTOLYTIC ENZYME ACTIVITY OF CELL WALLS. J Biol Chem. 1963 Sep;238:3126–3130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young F. E. Autolytic enzyme associated with cell walls of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 10;241(15):3462–3467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]