Abstract
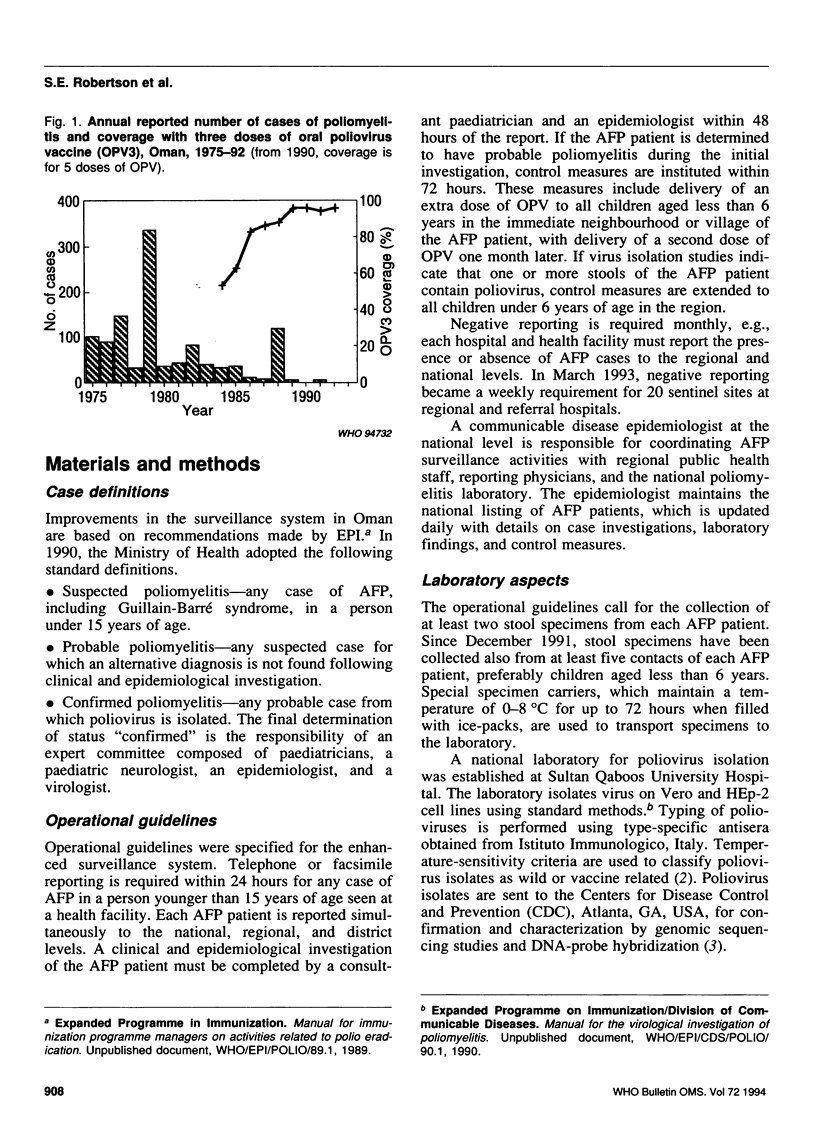
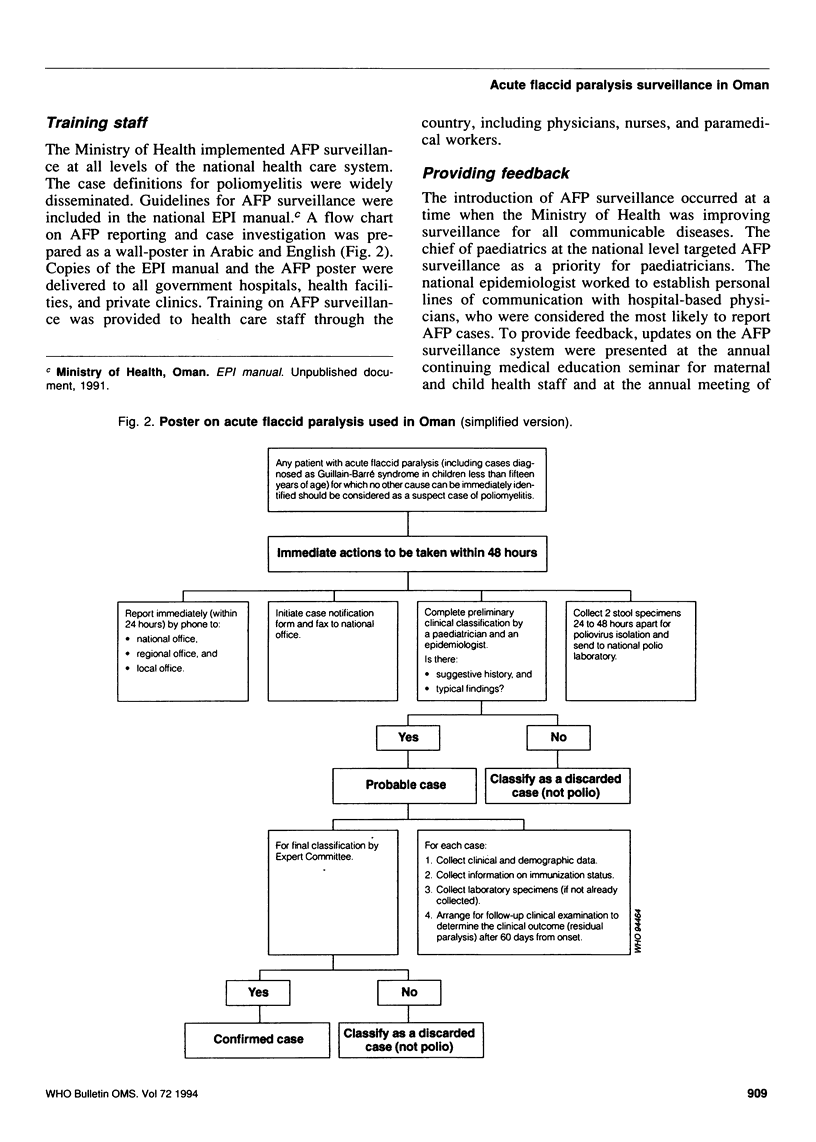
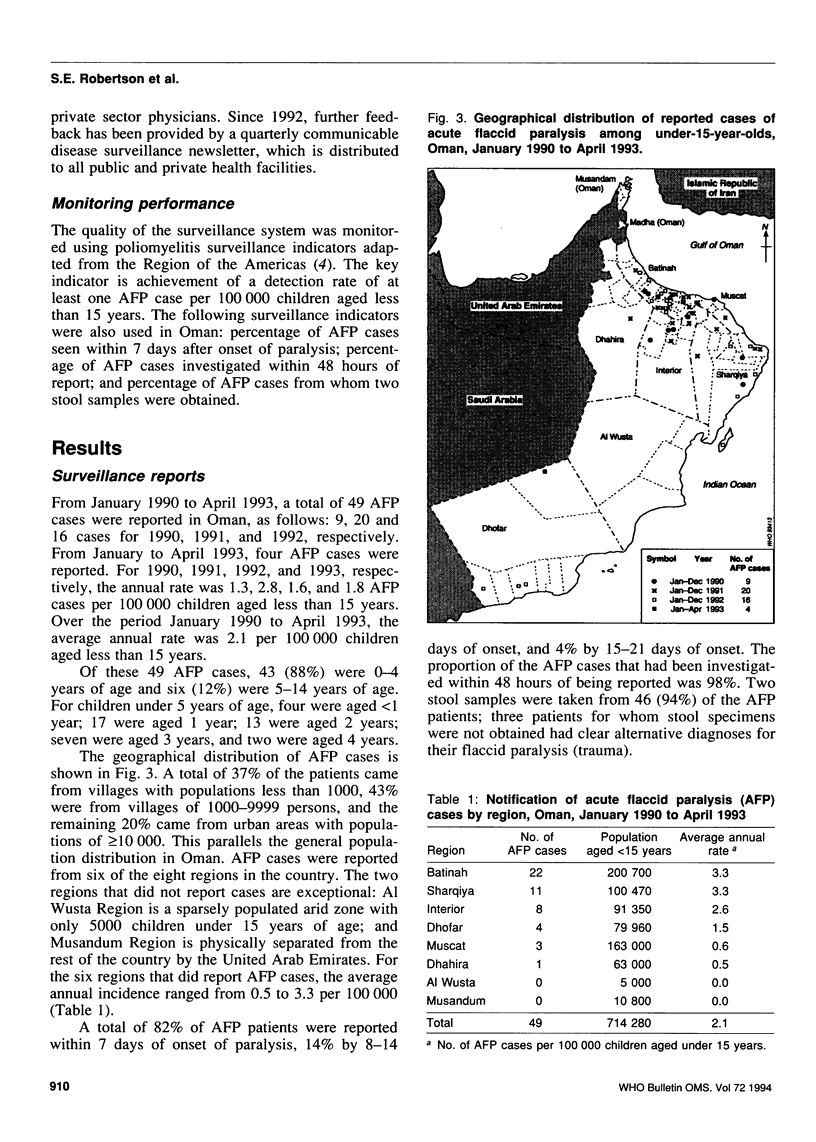
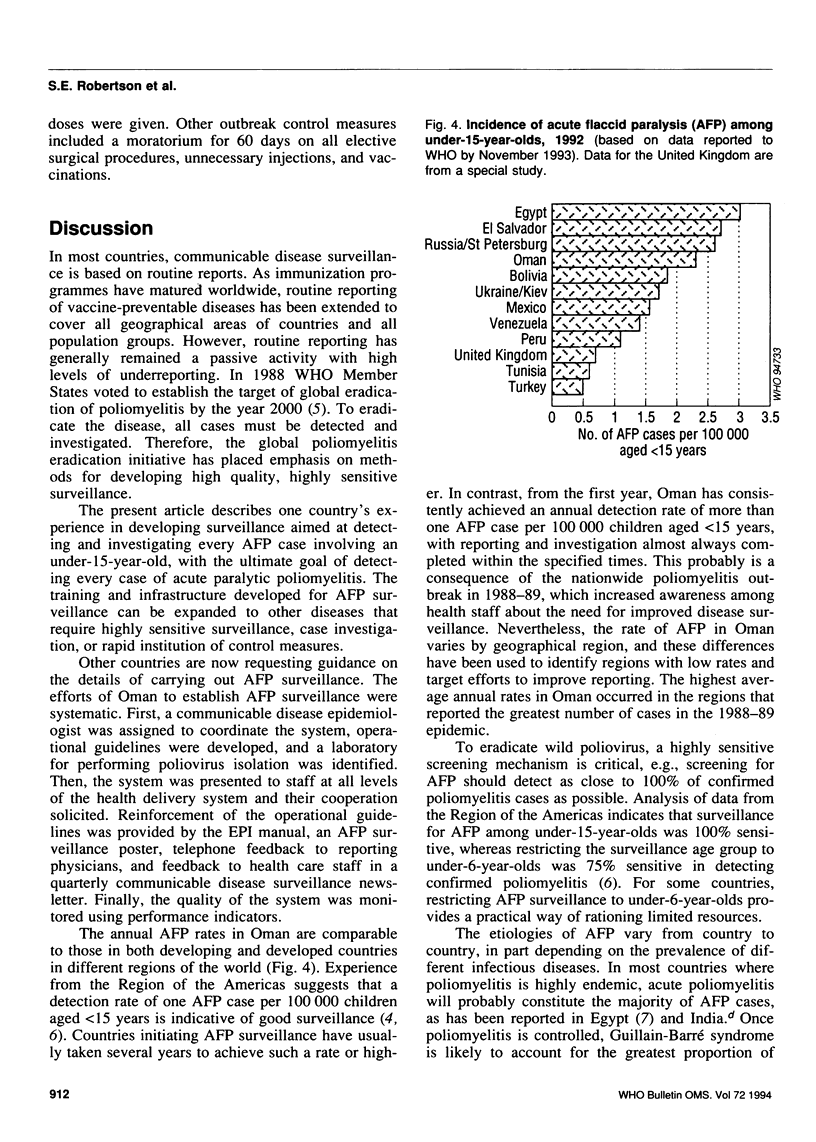
Countries are increasingly requesting guidance on carrying out acute flaccid paralysis (AFP) surveillance, aimed at detecting and confirming all cases of acute paralytic poliomyelitis. The experience of Oman provides many lessons in this respect. AFP surveillance in Oman was established systematically. First, an epidemiologist was assigned to coordinate surveillance, and a laboratory for performing polio-virus isolation was identified. Next, operational guidelines for AFP surveillance were developed and widely promoted among health staff. The quality of the system has been monitored for more than 3 years with selected performance indicators. From January 1990 to April 1993, 49 AFP cases were reported, corresponding to an average annual rate of 2.1 AFP cases per 100,000 children aged less than 15 years. A total of 98% of the AFP cases were investigated within 48 hours of being reported; two stool samples were obtained from 94% of the cases. Following complete investigation, nearly a third of the reported AFP cases were classified as being clinically compatible with Guillain-Barré syndrome. Four AFP cases, all reported in 1991, were confirmed to be due to wild type 3 poliovirus. Because AFP surveillance detected these cases rapidly, Oman was able to carry out outbreak control measures promptly and more than 350,000 extra doses of oral poliovirus vaccine were delivered to children under 6 years of age.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alcalá H. Diagnóstico diferencial de la poliomielitis y otras parálisis flácidas agudas. Bol Med Hosp Infant Mex. 1993 Feb;50(2):136–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrus J. K., de Quadros C., Olivé J. M., Hull H. F. Screening of cases of acute flaccid paralysis for poliomyelitis eradication: ways to improve specificity. Bull World Health Organ. 1992;70(5):591–596. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiba Y., Xu A., Li L., Liu G., Takezaki T., Urabe D., Yamamoto T., Minami R., Hagiwara A., Yoneyama T. Outbreaks of paralytic poliomyelitis and polio surveillance in Shandong province of China. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1992 Oct-Dec;45(5-6):255–266. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.45.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Quadros C. A., Andrus J. K., Olivé J. M., Da Silveira C. M., Eikhof R. M., Carrasco P., Fitzsimmons J. W., Pinheiro F. P. Eradication of poliomyelitis: progress in the Americas. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1991 Mar;10(3):222–229. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199103000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson S. E., Chan C., Kim-Farley R., Ward N. Worldwide status of poliomyelitis in 1986, 1987 and 1988, and plans for its global eradication by the year 2000. World Health Stat Q. 1990;43(2):80–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter R. W., Patriarca P. A., Brogan S., Malankar P. G., Pallansch M. A., Kew O. M., Bass A. G., Cochi S. L., Alexander J. P., Hall D. B. Outbreak of paralytic poliomyelitis in Oman: evidence for widespread transmission among fully vaccinated children. Lancet. 1991 Sep 21;338(8769):715–720. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)91442-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter R. W., Patriarca P. A., Suleiman A. J., Pallansch M. A., Zell E. R., Malankar P. G., Brogan S., al-Ghassani A. A., el-Bualy M. S. Paralytic poliomyelitis in Oman: association between regional differences in attack rate and variations in antibody responses to oral poliovirus vaccine. Int J Epidemiol. 1993 Oct;22(5):936–944. doi: 10.1093/ije/22.5.936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


