Abstract
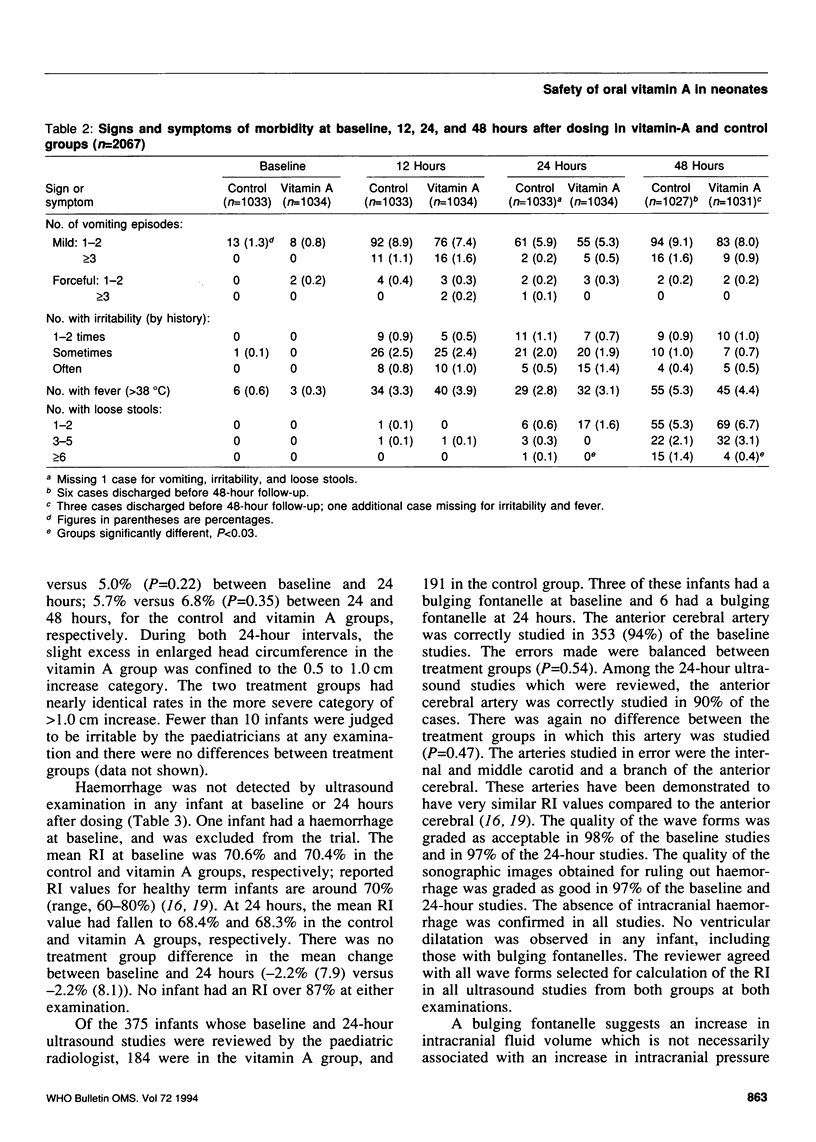
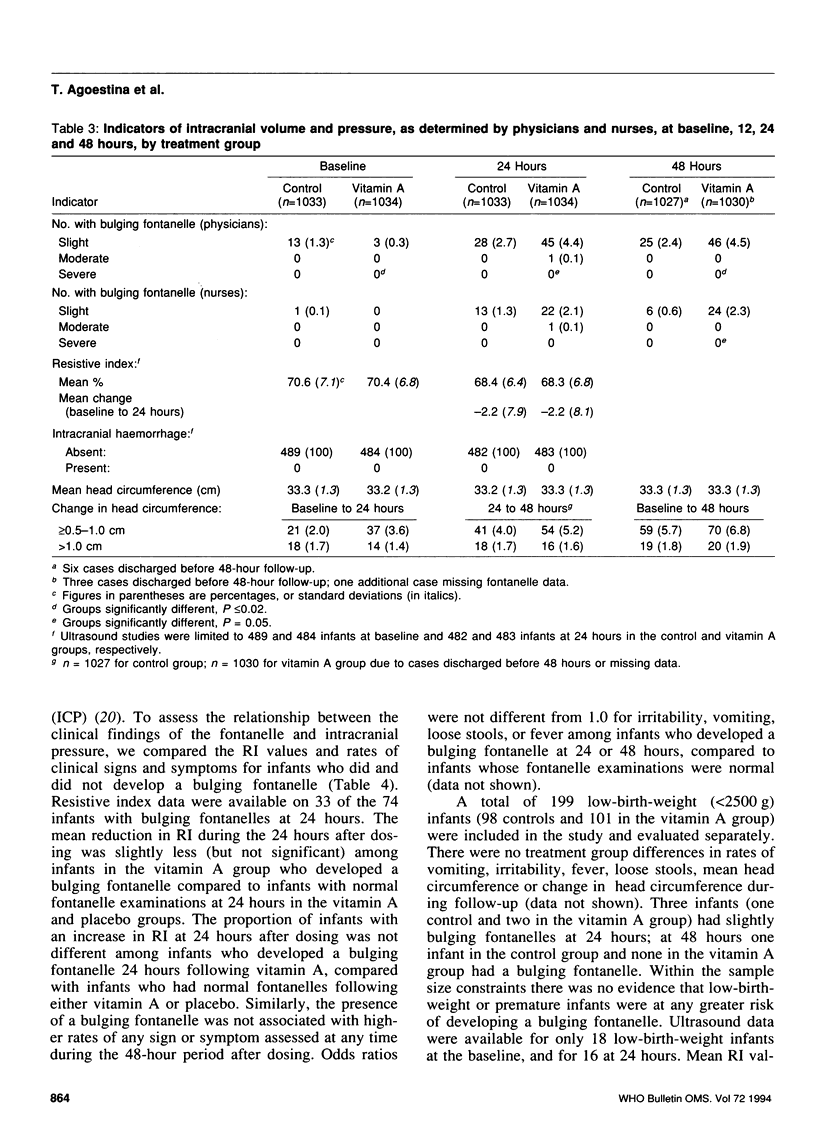
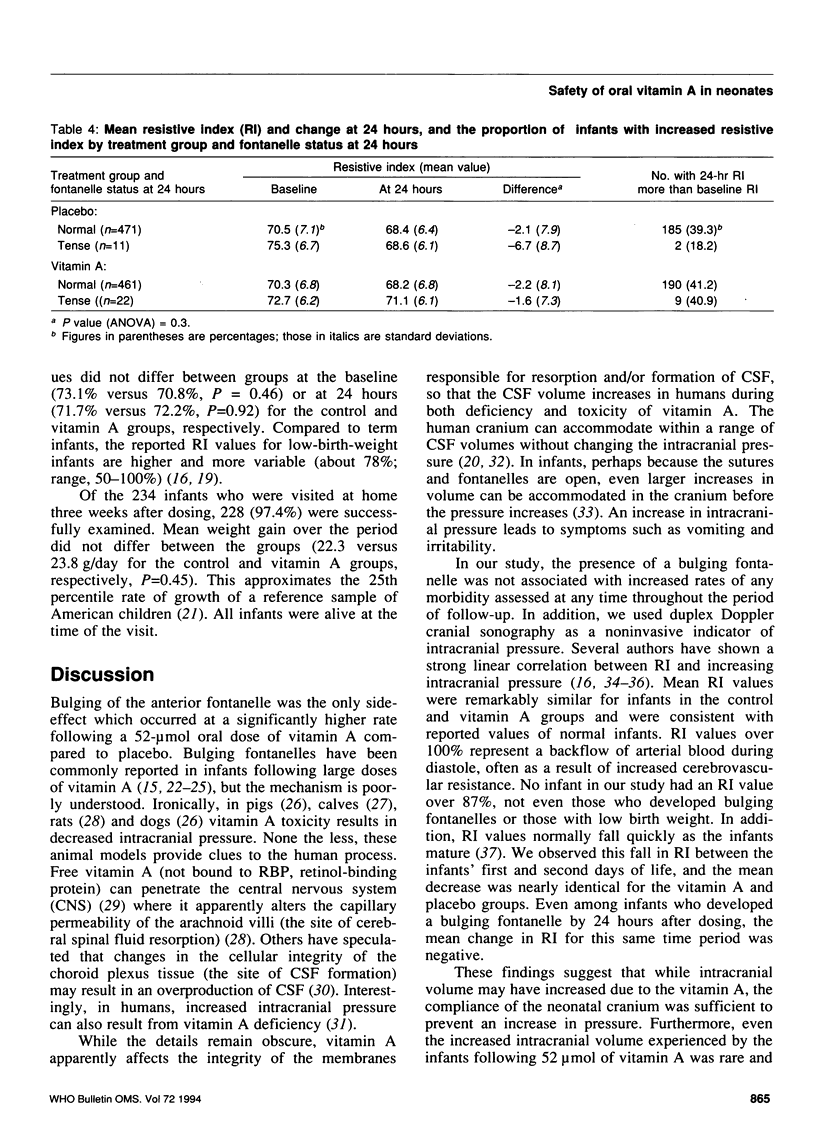
A placebo-controlled trial was carried out among 2067 Indonesian neonates to assess the safety of administering one oral 52-mumol (50,000 IU) dose of vitamin A. Infants were assessed for potential acute side-effects before and throughout 48 hours after the dose. The first 965 infants were examined by cranial ultrasound before and at 24 hours after dosing to rule out intracranial haemorrhage and determine the resistive index (RI) of the anterior cerebral artery using duplex Doppler. Groups were comparable at the baseline. A bulging fontanelle occurred in the control and vitamin A groups, respectively, among 2.7% and 4.6% of the infants at 24 hours, and 2.4% and 4.5% of the infants at 48 hours. The groups did not differ in any other sign or symptom assessed. No infant developed intracranial haemorrhage. Mean RI values were normal and not different between groups at baseline or at 24 hours. Mean RI fell during the 24 hours, as normally occurs; the mean decrease was nearly identical in the two groups. A bulging fontanelle was not associated with increased rates of any sign or symptom or with an increase in RI. The 52-mumol dose of oral vitamin A may cause a small increase in intracranial volume in a small proportion of infants, but no increase in intracranial pressure. Acute side-effects following this intervention were rare and mild.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BECKER N. H., SUTTON C. H. PATHOLOGIC FEATURES OF THE CHOROID PLEXUS. 1. CYTOCHEMICAL EFFECTS OF HYPERVITAMINOSIS A. Am J Pathol. 1963 Dec;43:1017–1030. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chadduck W. M., Seibert J. J., Adametz J., Glasier C. M., Crabtree M., Stansell C. A. Cranial Doppler ultrasonography correlates with criteria for ventriculoperitoneal shunting. Surg Neurol. 1989 Feb;31(2):122–128. doi: 10.1016/0090-3019(89)90324-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daulaire N. M., Starbuck E. S., Houston R. M., Church M. S., Stukel T. A., Pandey M. R. Childhood mortality after a high dose of vitamin A in a high risk population. BMJ. 1992 Jan 25;304(6821):207–210. doi: 10.1136/bmj.304.6821.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djunaedi E., Sommer A., Pandji A., Kusdiono, Taylor H. R. Impact of vitamin A supplementation on xerophthalmia. A randomized controlled community trial. Arch Ophthalmol. 1988 Feb;106(2):218–222. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1988.01060130228033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florentino R. F., Tanchoco C. C., Ramos A. C., Mendoza T. S., Natividad E. P., Tangco J. B., Sommer A. Tolerance of preschoolers to two dosage strengths of vitamin A preparation. Am J Clin Nutr. 1990 Oct;52(4):694–700. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/52.4.694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gangemi M., Maiuri F., Di Martino L., Pettoello M. Intracranial hypertension due to acute vitamin A intoxication. Acta Neurol (Napoli) 1985 Feb;7(1):27–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goh D., Minns R. A., Hendry G. M., Thambyayah M., Steers A. J. Cerebrovascular resistive index assessed by duplex Doppler sonography and its relationship to intracranial pressure in infantile hydrocephalus. Pediatr Radiol. 1992;22(4):246–250. doi: 10.1007/BF02019849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goh D., Minns R. A., Pye S. D., Steers A. J. Cerebral blood flow velocity changes after ventricular taps and ventriculoperitoneal shunting. Childs Nerv Syst. 1991 Dec;7(8):452–457. doi: 10.1007/BF00263188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant E. G., White E. M., Schellinger D., Choyke P. L., Sarcone A. L. Cranial duplex sonography of the infant. Radiology. 1987 Apr;163(1):177–185. doi: 10.1148/radiology.163.1.3547492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill A., Volpe J. J. Normal pressure hydrocephalus in the newborn. Pediatrics. 1981 Nov;68(5):623–629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horgan J. G., Rumack C. M., Hay T., Manco-Johnson M. L., Merenstein G. B., Esola C. Absolute intracranial blood-flow velocities evaluated by duplex Doppler sonography in asymptomatic preterm and term neonates. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1989 May;152(5):1059–1064. doi: 10.2214/ajr.152.5.1059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurt H. D., Eaton H. D., Rousseau J. E., Jr, Hall R. C., Jr Rates of formation and absorption of cerebrospinal fluid in chronic bovine hypervitaminosis A. J Dairy Sci. 1967 Dec;50(12):1941–1947. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(67)87751-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalin J. R., Wells M. J., Hill D. L. Disposition of 13-cis-retinoic acid and N-(2-hydroxyethyl)retinamide in mice after oral doses. Drug Metab Dispos. 1982 Jul-Aug;10(4):391–398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keating J. P., Feigin R. D. Increased intracranial pressure associated with probable vitamin A deficiency in cystic fibrosis. Pediatrics. 1970 Jul;46(1):41–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddux G. W., Foltz F. M., Nelson S. R. Effect of vitamin A intoxication on intracranial pressure and brain water in rats. J Nutr. 1974 Apr;104(4):478–482. doi: 10.1093/jn/104.4.478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney C. P., Margolis M. T., Knauss T. A., Labbe R. F. Chronic vitamin A intoxication in infants fed chicken liver. Pediatrics. 1980 May;65(5):893–897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERSSON B., TUNELL R., EKENGREN K. CHRONIC VITAMIN A INTOXICATION DURING THE FIRST HALF YEAR OF LIFE; DESCRIPTION OF 5 CASES. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1965 Jan;54:49–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1965.tb06345.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahmathullah L., Underwood B. A., Thulasiraj R. D., Milton R. C., Ramaswamy K., Rahmathullah R., Babu G. Reduced mortality among children in southern India receiving a small weekly dose of vitamin A. N Engl J Med. 1990 Oct 4;323(14):929–935. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199010043231401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seibert J. J., McCowan T. C., Chadduck W. M., Adametz J. R., Glasier C. M., Williamson S. L., Taylor B. J., Leithiser R. E., Jr, McConnell J. R., Stansell C. A. Duplex pulsed Doppler US versus intracranial pressure in the neonate: clinical and experimental studies. Radiology. 1989 Apr;171(1):155–159. doi: 10.1148/radiology.171.1.2648468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro K., Fried A., Marmarou A. Biomechanical and hydrodynamic characterization of the hydrocephalic infant. J Neurosurg. 1985 Jul;63(1):69–75. doi: 10.3171/jns.1985.63.1.0069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel N. J., Spackman T. J. Chronic hypervitaminosis A with intracranial hypertension and low cerebrospinal fluid concentration of protein. Two illustrative cases. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1972 Oct;11(10):580–584. doi: 10.1177/000992287201101011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith F. R., Goodman D. S. Vitamin A transport in human vitamin A toxicity. N Engl J Med. 1976 Apr 8;294(15):805–808. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197604082941503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer A., Tarwotjo I., Djunaedi E., West K. P., Jr, Loeden A. A., Tilden R., Mele L. Impact of vitamin A supplementation on childhood mortality. A randomised controlled community trial. Lancet. 1986 May 24;1(8491):1169–1173. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91157-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer A., Tarwotjo I., Hussaini G., Susanto D., Soegiharto T. Incidence, prevalence, and scale of blinding malnutrition. Lancet. 1981 Jun 27;1(8235):1407–1408. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92581-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoltzfus R. J., Hakimi M., Miller K. W., Rasmussen K. M., Dawiesah S., Habicht J. P., Dibley M. J. High dose vitamin A supplementation of breast-feeding Indonesian mothers: effects on the vitamin A status of mother and infant. J Nutr. 1993 Apr;123(4):666–675. doi: 10.1093/jn/123.4.666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West K. P., Jr, Chirambo M., Katz J., Sommer A. Breast-feeding, weaning patterns, and the risk of xerophthalmia in Southern Malawi. Am J Clin Nutr. 1986 Nov;44(5):690–697. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/44.5.690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West K. P., Jr, Khatry S. K., LeClerq S. C., Adhikari R., See L., Katz J., Shrestha S. R., Pradhan E. K., Pokhrel R. P., Sommer A. Tolerance of young infants to a single, large dose of vitamin A: a randomized community trial in Nepal. Bull World Health Organ. 1992;70(6):733–739. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West K. P., Jr, Pokhrel R. P., Katz J., LeClerq S. C., Khatry S. K., Shrestha S. R., Pradhan E. K., Tielsch J. M., Pandey M. R., Sommer A. Efficacy of vitamin A in reducing preschool child mortality in Nepal. Lancet. 1991 Jul 13;338(8759):67–71. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


