Abstract
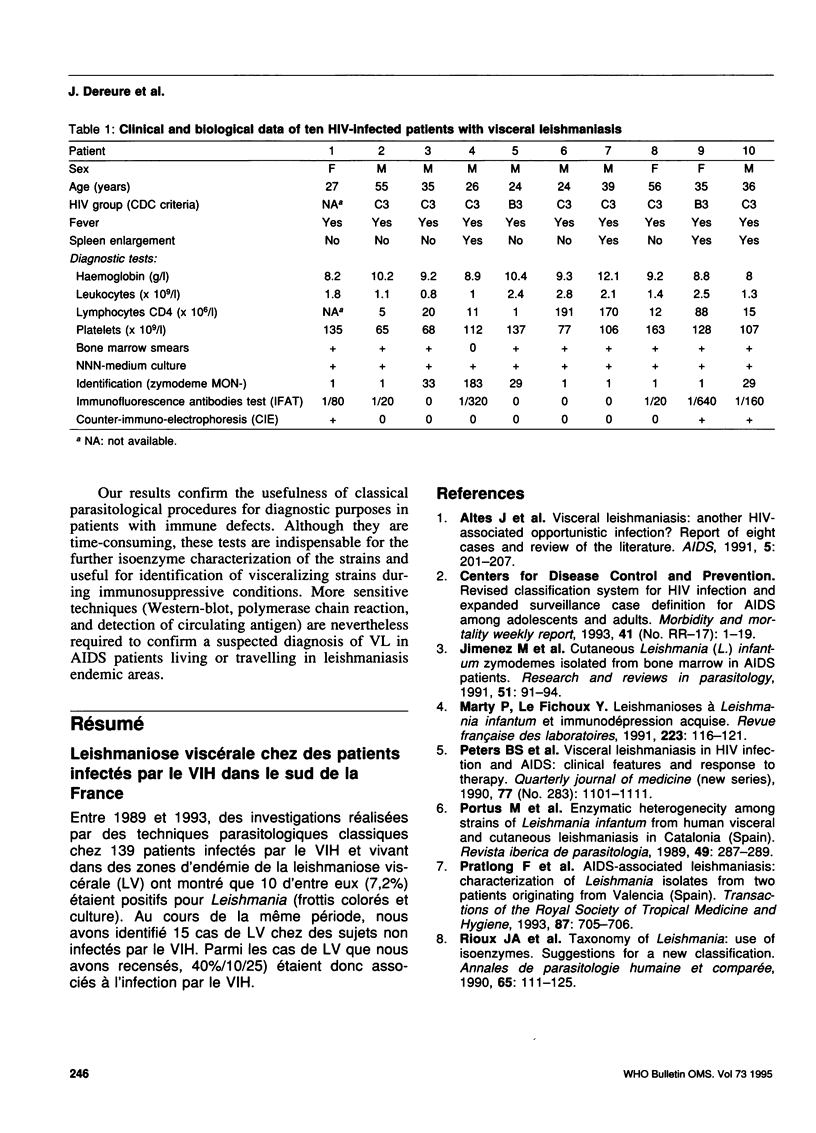
Between 1989 and 1993, investigations by classical parasitological procedures of 139 HIV-infected adults living in visceral leishmaniasis (VL) endemic areas showed that 10 of them (7.2%) were positive for Leishmania (by stained smears and culture). In the same period we identified 15 VL cases in patients not infected with HIV. Thus, 40% (10/25) of our VL cases were associated with HIV infection.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altés J., Salas A., Riera M., Udina M., Galmés A., Balanzat J., Ballesteros A., Buades J., Salvá F., Villalonga C. Visceral leishmaniasis: another HIV-associated opportunistic infection? Report of eight cases and review of the literature. AIDS. 1991 Feb;5(2):201–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rioux J. A., Lanotte G., Serres E., Pratlong F., Bastien P., Perieres J. Taxonomy of Leishmania. Use of isoenzymes. Suggestions for a new classification. Ann Parasitol Hum Comp. 1990;65(3):111–125. doi: 10.1051/parasite/1990653111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



