Abstract
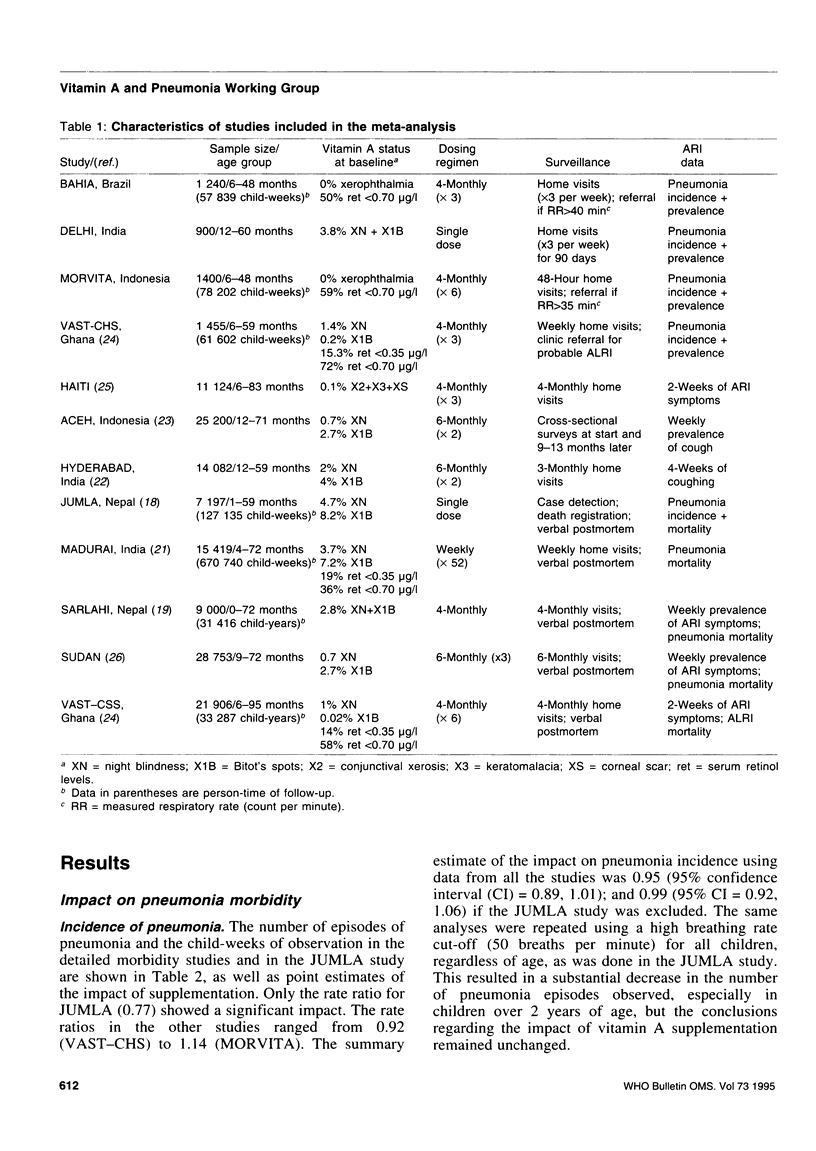
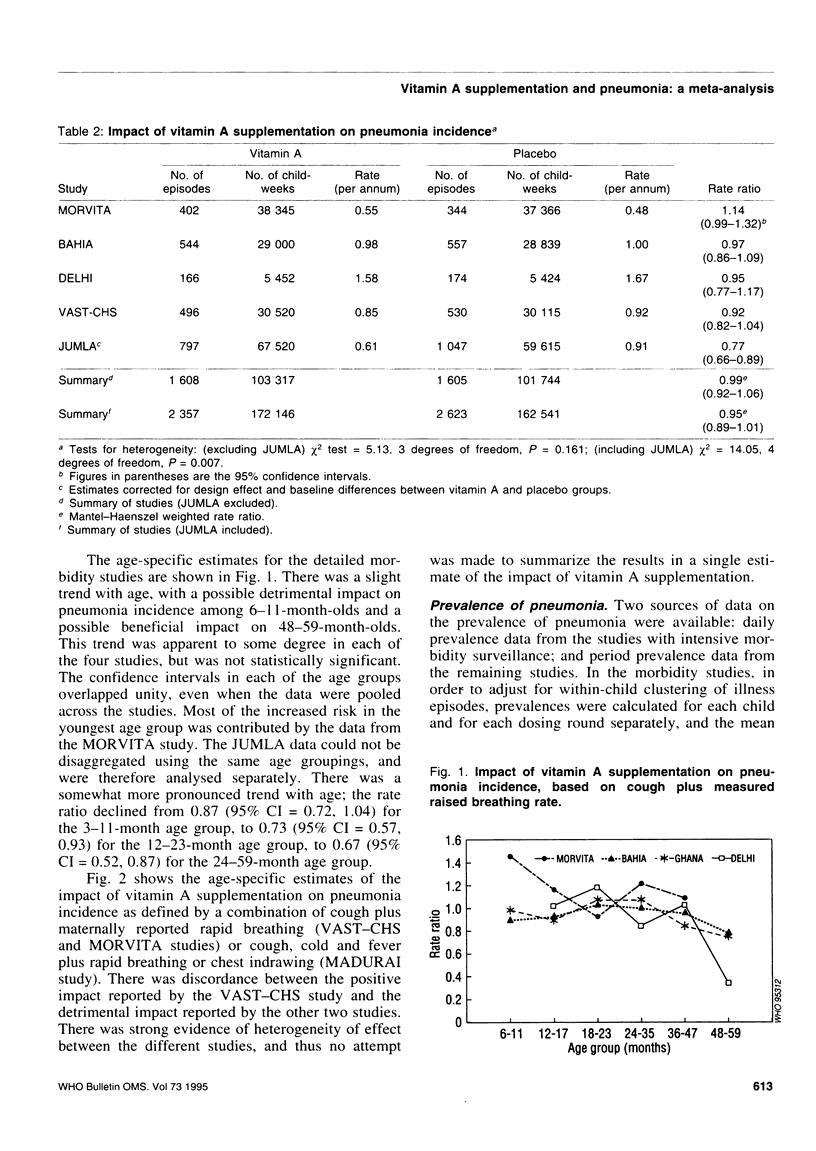
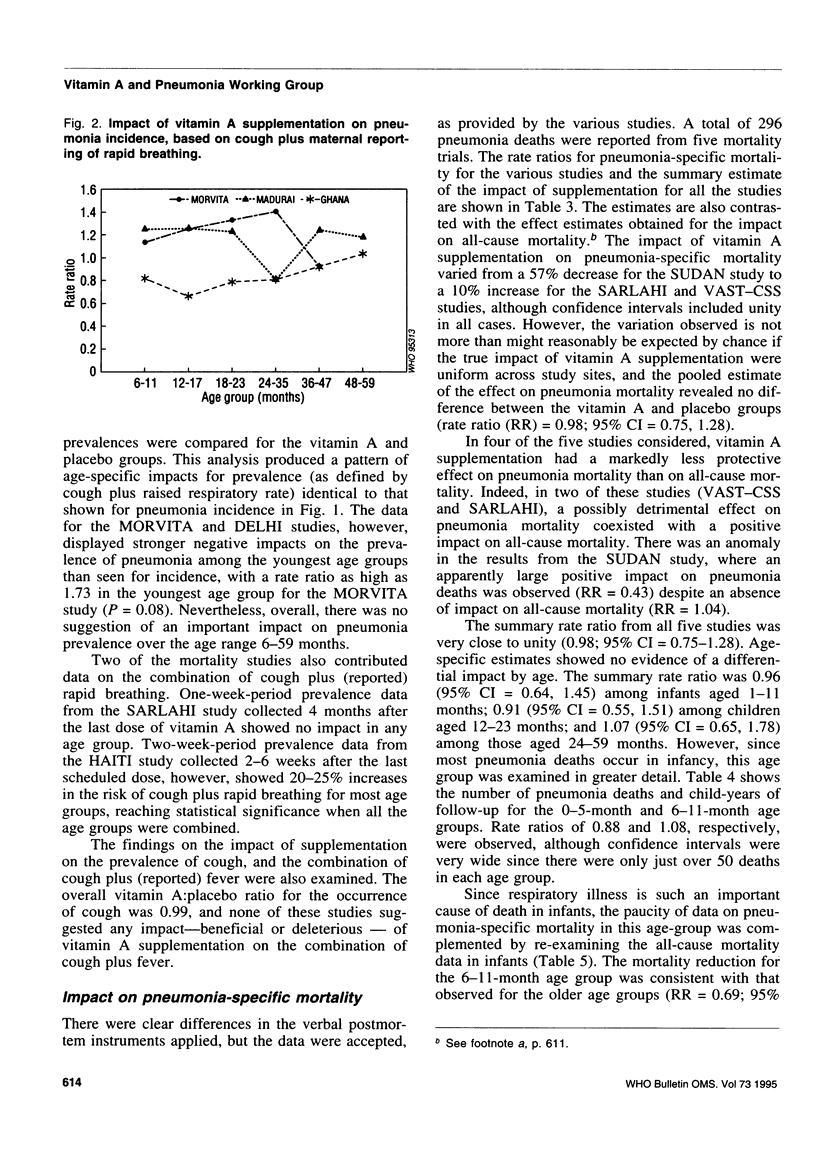
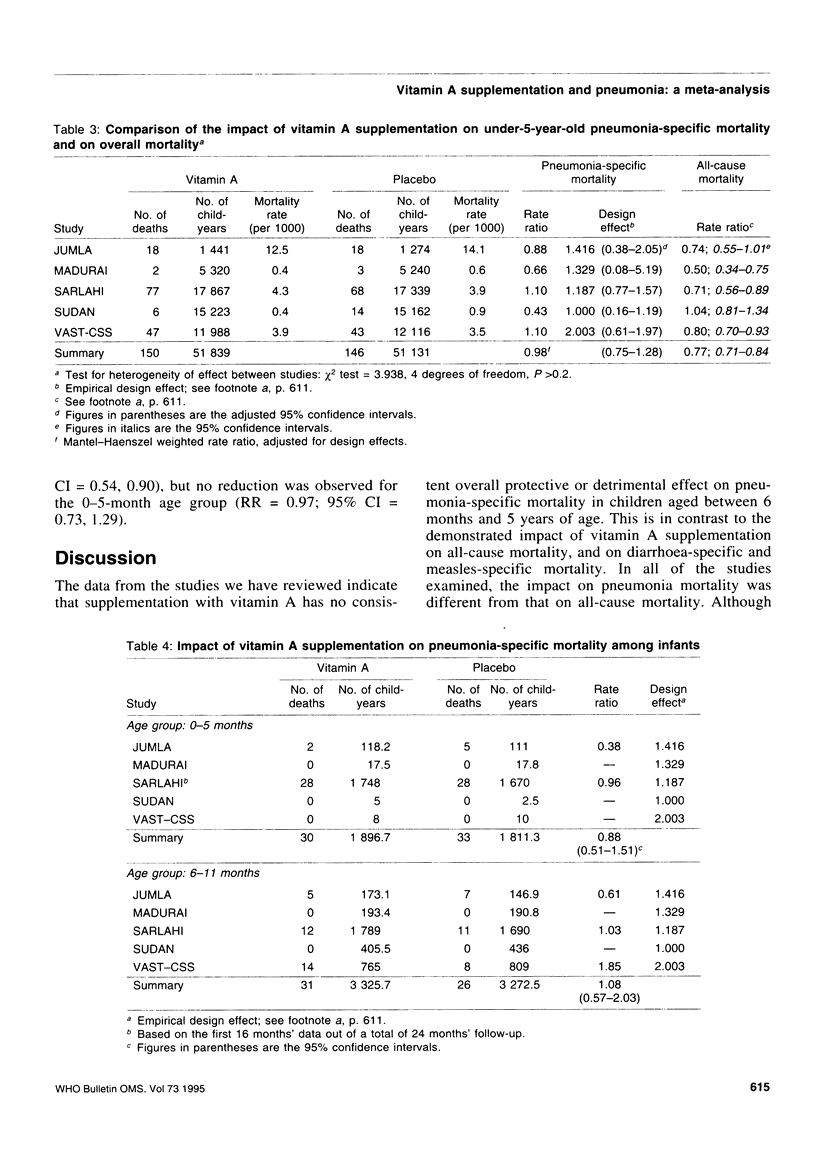
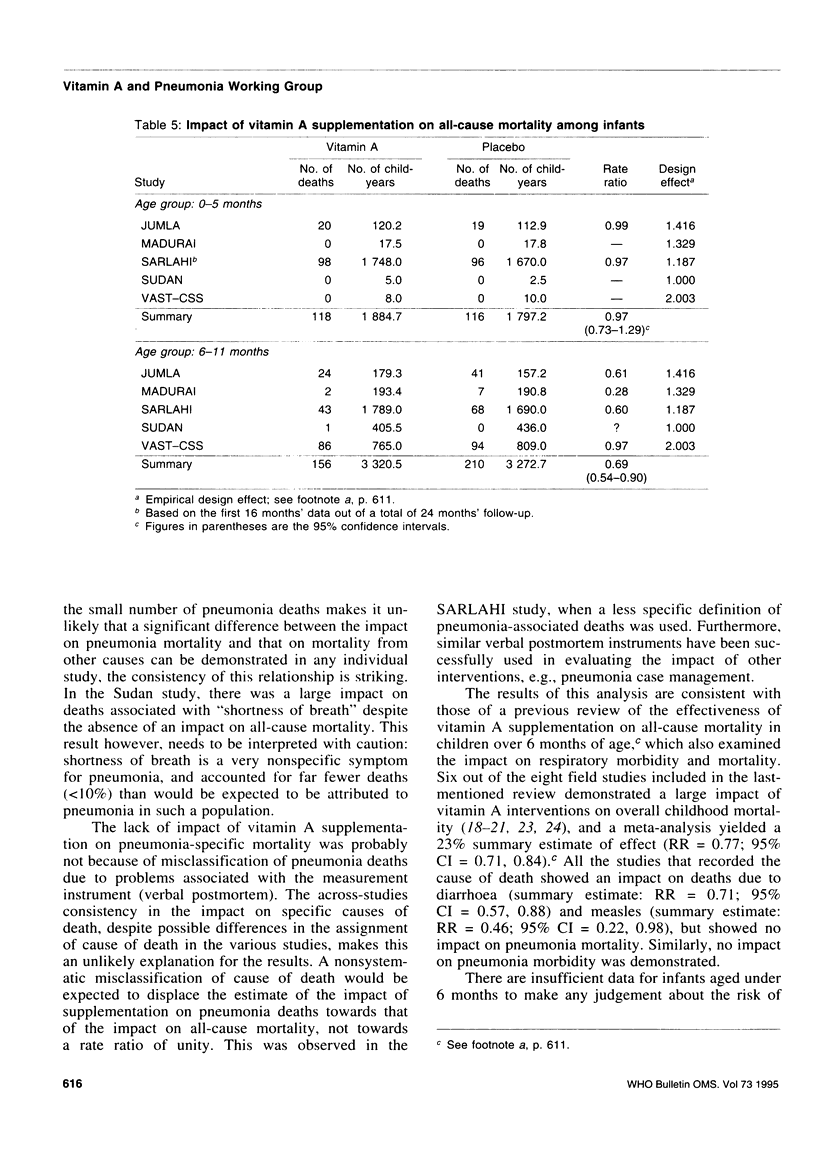
Reported are the results of a meta-analysis (12 large-scale field trials in seven countries) of the impact of vitamin A supplementation on pneumonia morbidity and mortality, undertaken as part of a wider review process of a range of possible potential interventions for the prevention of childhood pneumonia. The summary estimate of the relative risk for the impact of vitamin A supplementation on pneumonia incidence was 0.95 (95% confidence interval (CI) = 0.89, 1.01), and for pneumonia mortality, 0.98 (95% CI = 0.75, 1.28). This is in marked contrast to the substantial impact of vitamin A supplementation on all-cause mortality (combined rate ratio (RR) = 0.77, 95% CI = 0.71, 0.84), and on diarrhoea-specific and measles-specific mortality. There was no evidence for a differential impact on pneumonia mortality by age. Since the majority of pneumonia deaths occur in the first year of life, we complemented the paucity of data on pneumonia-specific mortality among this age group with a detailed examination of all-cause mortality among infants. The mortality reduction in the 6-11 month age group was consistent with that observed for older age groups (RR = 0.69; 95% CI = 0.54, 0.90), but there was no reduction for 0-5 month-olds (RR = 0.97; 95% CI = 0.73, 1.29).
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barclay A. J., Foster A., Sommer A. Vitamin A supplements and mortality related to measles: a randomised clinical trial. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1987 Jan 31;294(6567):294–296. doi: 10.1136/bmj.294.6567.294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhaskaram C., Reddy V. Cell-mediated immunity in iron- and vitamin-deficient children. Br Med J. 1975 Aug 30;3(5982):522–522. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5982.522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloem M. W., Wedel M., Egger R. J., Speek A. J., Schrijver J., Saowakontha S., Schreurs W. H. Mild vitamin A deficiency and risk of respiratory tract diseases and diarrhea in preschool and school children in northeastern Thailand. Am J Epidemiol. 1990 Feb;131(2):332–339. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandra R. K. Increased bacterial binding to respiratory epithelial cells in vitamin A deficiency. BMJ. 1988 Oct 1;297(6652):834–835. doi: 10.1136/bmj.297.6652.834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daulaire N. M., Starbuck E. S., Houston R. M., Church M. S., Stukel T. A., Pandey M. R. Childhood mortality after a high dose of vitamin A in a high risk population. BMJ. 1992 Jan 25;304(6821):207–210. doi: 10.1136/bmj.304.6821.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A., Sklan D. Antigen-specific immune response impairment in the chick as influenced by dietary vitamin A. J Nutr. 1989 May;119(5):790–795. doi: 10.1093/jn/119.5.790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera M. G., Nestel P., el Amin A., Fawzi W. W., Mohamed K. A., Weld L. Vitamin A supplementation and child survival. Lancet. 1992 Aug 1;340(8814):267–271. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)92357-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussey G. D., Klein M. A randomized, controlled trial of vitamin A in children with severe measles. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jul 19;323(3):160–164. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199007193230304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milton R. C., Reddy V., Naidu A. N. Mild vitamin A deficiency and childhood morbidity--an Indian experience. Am J Clin Nutr. 1987 Nov;46(5):827–829. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/46.5.827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohanram M., Reddy V., Mishra S. Lysozyme activity in plasma and leucocytes in malnourished children. Br J Nutr. 1974 Sep;32(2):313–316. doi: 10.1079/bjn19740084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muhilal, Permeisih D., Idjradinata Y. R., Muherdiyantiningsih, Karyadi D. Vitamin A-fortified monosodium glutamate and health, growth, and survival of children: a controlled field trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 1988 Nov;48(5):1271–1276. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/48.5.1271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinnock C. B., Douglas R. M., Badcock N. R. Vitamin A status in children who are prone to respiratory tract infections. Aust Paediatr J. 1986 May;22(2):95–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1754.1986.tb00197.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahmathullah L., Underwood B. A., Thulasiraj R. D., Milton R. C., Ramaswamy K., Rahmathullah R., Babu G. Reduced mortality among children in southern India receiving a small weekly dose of vitamin A. N Engl J Med. 1990 Oct 4;323(14):929–935. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199010043231401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semba R. D., Muhilal, Scott A. L., Natadisastra G., Wirasasmita S., Mele L., Ridwan E., West K. P., Jr, Sommer A. Depressed immune response to tetanus in children with vitamin A deficiency. J Nutr. 1992 Jan;122(1):101–107. doi: 10.1093/jn/122.1.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer A., Katz J., Tarwotjo I. Increased risk of respiratory disease and diarrhea in children with preexisting mild vitamin A deficiency. Am J Clin Nutr. 1984 Nov;40(5):1090–1095. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/40.5.1090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer A., Tarwotjo I., Djunaedi E., West K. P., Jr, Loeden A. A., Tilden R., Mele L. Impact of vitamin A supplementation on childhood mortality. A randomised controlled community trial. Lancet. 1986 May 24;1(8491):1169–1173. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91157-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stansfield S. K., Pierre-Louis M., Lerebours G., Augustin A. Vitamin A supplementation and increased prevalence of childhood diarrhoea and acute respiratory infections. Lancet. 1993 Sep 4;342(8871):578–582. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91410-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West K. P., Jr, Pokhrel R. P., Katz J., LeClerq S. C., Khatry S. K., Shrestha S. R., Pradhan E. K., Tielsch J. M., Pandey M. R., Sommer A. Efficacy of vitamin A in reducing preschool child mortality in Nepal. Lancet. 1991 Jul 13;338(8759):67–71. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolbach S. B., Howe P. R. TISSUE CHANGES FOLLOWING DEPRIVATION OF FAT-SOLUBLE A VITAMIN. J Exp Med. 1925 Nov 30;42(6):753–777. doi: 10.1084/jem.42.6.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong Y. C., Buck R. C. An electron microscopic study of metaplasia of the rat tracheal epithelium in vitamin A deficiency. Lab Invest. 1971 Jan;24(1):55–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


