Abstract
Reported are the results of a multicentre study involving 40 laboratories that was carried out in France to assess all the currently available methods used for the serodiagnosis of toxoplasmosis. For this purpose 10 batches of control sera were prepared with titres in the range 0-260 IU per ml. These sera were tested in nine laboratories using immunofluorescence methods; in three laboratories using dye tests; in forty laboratories using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; in four laboratories using direct agglutination and haemagglutination; in seven laboratories using the high-sensitivity IgG agglutination test; and in three laboratories using the latex agglutination test. In this way, 70 series of titrations were carried out using seven procedures and the results were compared with those obtained using the WHO reference serum in 15 cases, with the French national E6 serum in 16 other cases, and in 39 cases using 15 reference sera supplied by the reagent manufacturers. Rigorous comparison of the tests was not possible in all cases because one aim of the study was to ensure that the tests were carried out under the usual working conditions that prevailed in the participating laboratories. The results obtained indicate that the serological tests currently available for toxoplasmosis are acceptable for its serodiagnosis. Presentation of the titres in IU has advantages; however, caution is required since the definition of IU varies according to the test and reagents used. It is therefore essential that the conditions and limits for a positive reaction be carefully defined in each case, especially for commercially available kits.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carlier Y., Bout D., Dessaint J. P., Capron A., Van Knapen F., Ruitenberg E. J., Bergquist R., Huldt G. Evaluation of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and other serological tests for the diagnosis of toxoplasmosis. Bull World Health Organ. 1980;58(1):99–105. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derouin F., Garin Y. J., Buffard C., Berthelot F., Petithory J. C. Etude multicentrique de la sérologie toxoplasmique par différents réactifs ELISA commercialisés. Groupe de travail Toxoplasmose du Contrôle National de Qualité en Parasitologie. Bull World Health Organ. 1994;72(2):249–256. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARIN J. P., AMBROISE-THOMAS P. LA DIAGNOSTIC S'EROLOGIQUE DE LA TOXOPLASMOSE PAR LA M'ETHODE DES ANTICORPS FLUORESCENTS (TECHNIQUE INDIRECTE) Presse Med. 1963 Dec 7;71:2485–2488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mond J. J., Brunswick M. A role for IFN-gamma and NK cells in immune responses to T cell-regulated antigens types 1 and 2. Immunol Rev. 1987 Oct;99:105–118. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1987.tb01174.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
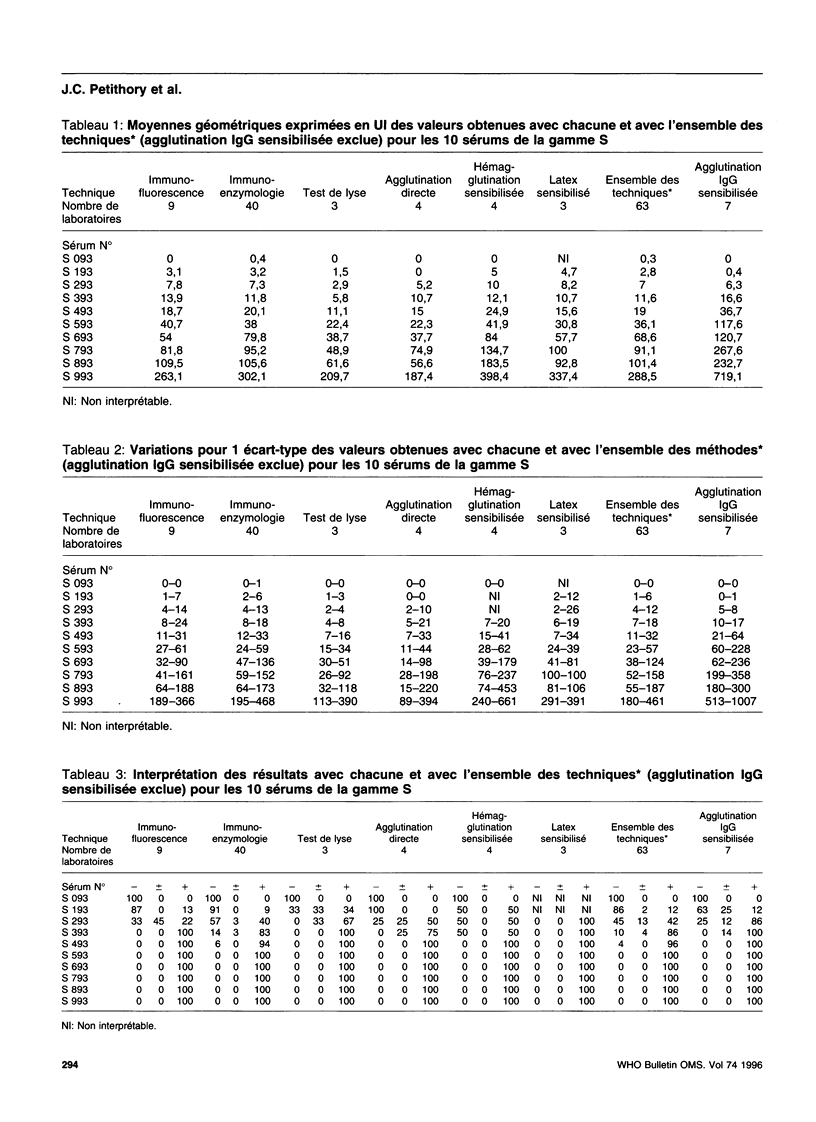
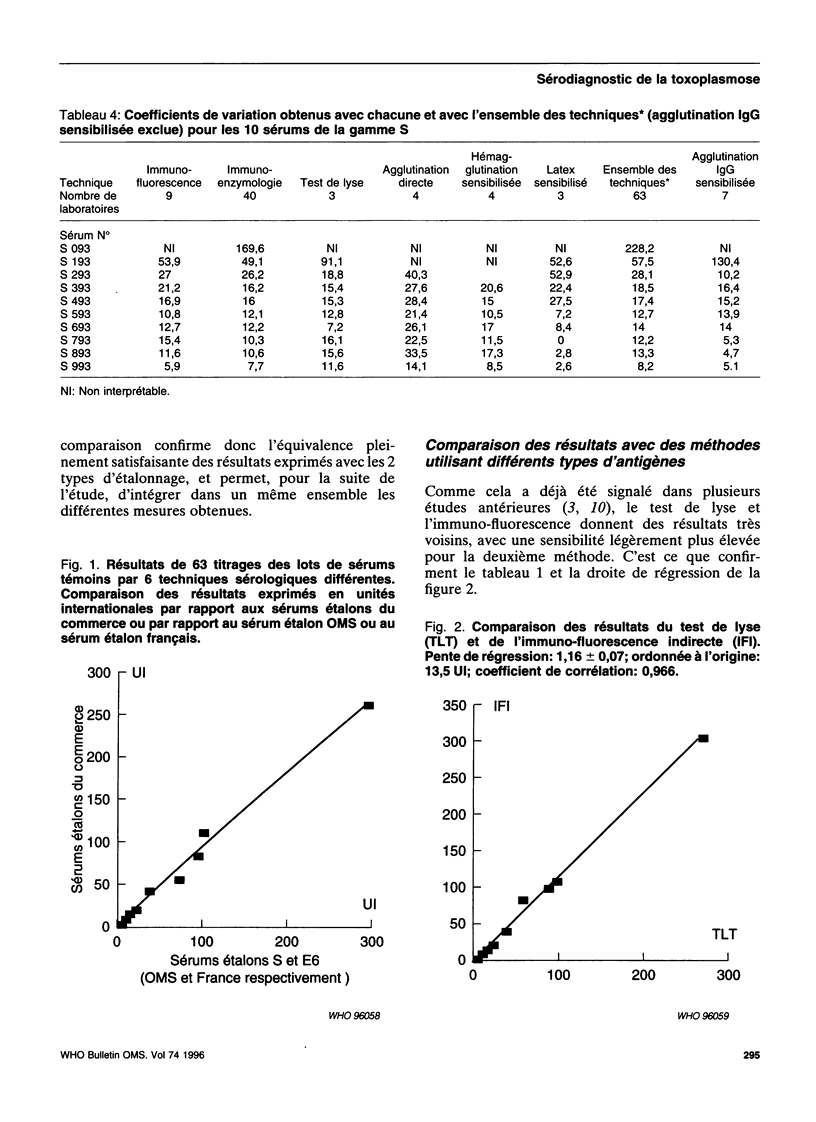
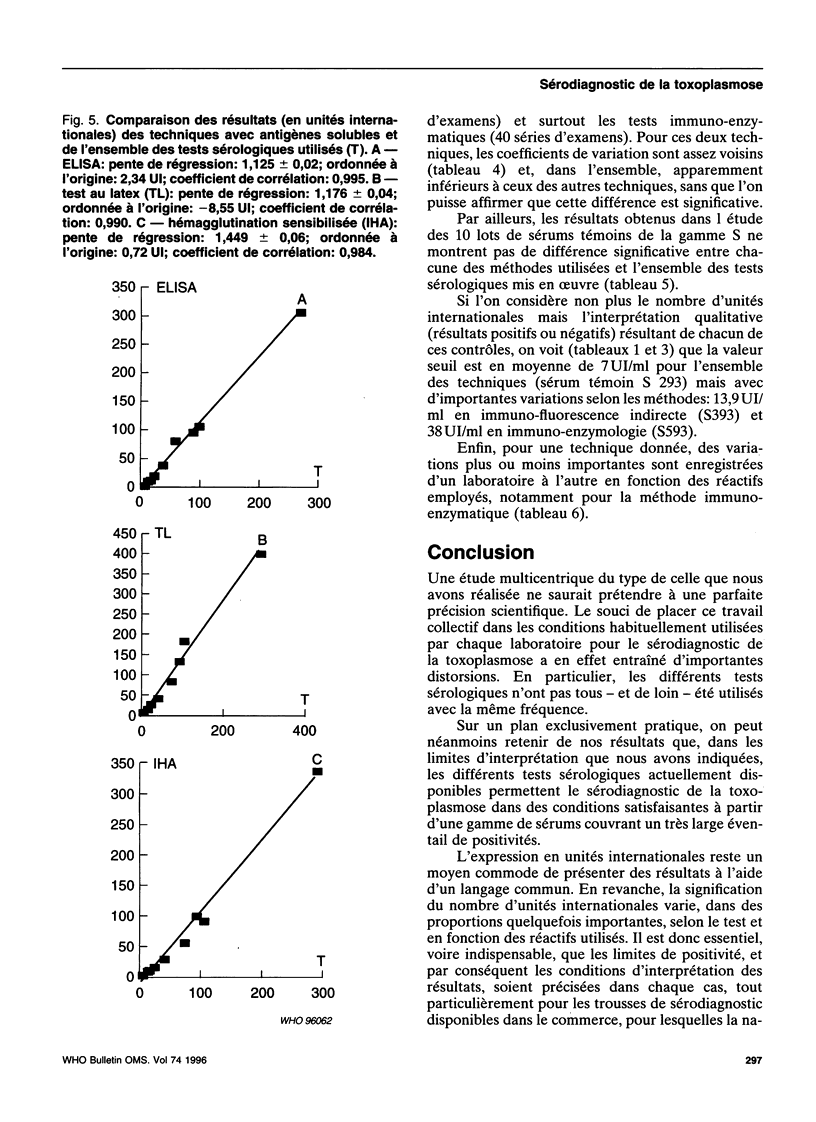
- Niel G., Desmonts G., Gentilini M. Immunofluorescence quantitative et diagnostic sérologique de la toxoplasmose: introduction des unités internationales dans l'expression des positivés. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1973 Feb;21(2):157–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
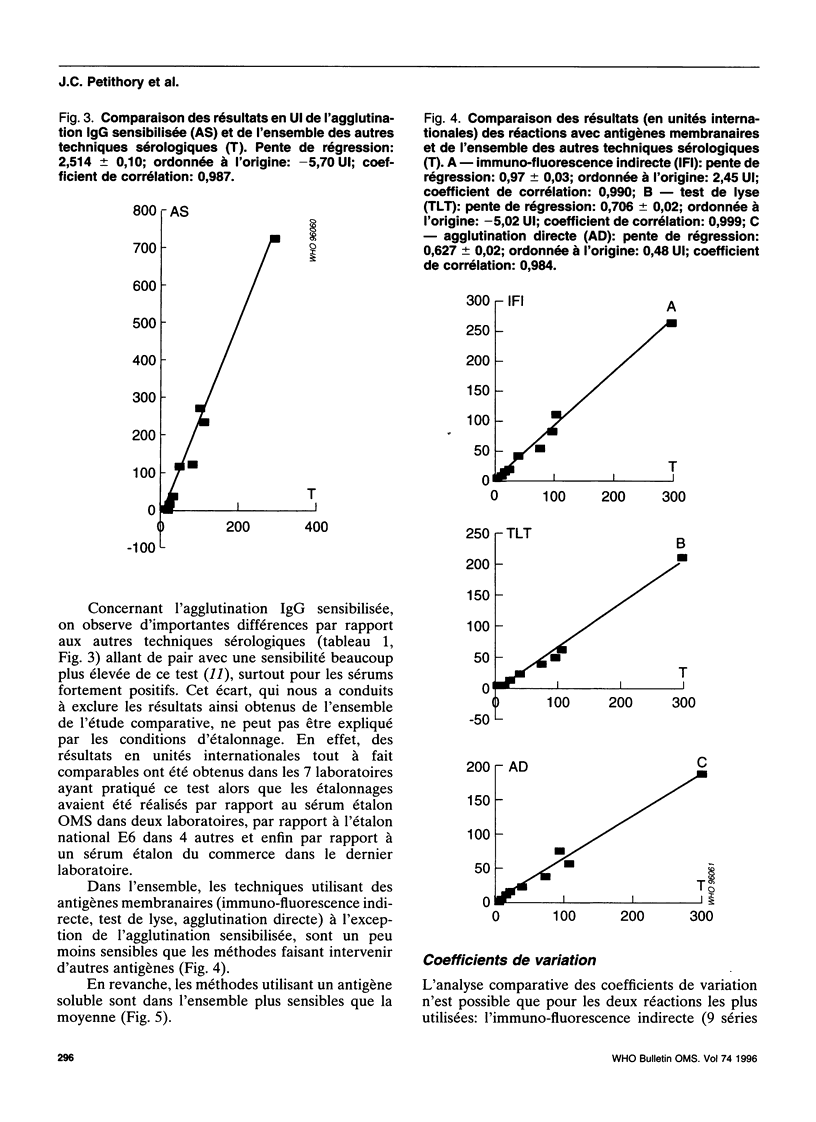
- Puygauthier-Toubas D., Jolly D., Bajolet O., Moreaux T., Marx-Chemla C., Bonhomme A., Blanchard F., Pinon J. M. Etude comparée des isotypes antitoxoplasmiques IgG titrés par agglutination directe haute sensibilité et immunofluorescence indirecte: incidence du choix des méthodes sur l'expression des résultats en unités internationales. Ann Biol Clin (Paris) 1990;48(10):737–741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M., Ware D. A., Walls K. W. Evaluation of commercial serodiagnostic kits for toxoplasmosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Dec;25(12):2262–2265. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.12.2262-2265.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



