Abstract
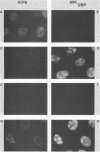
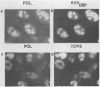
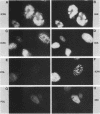
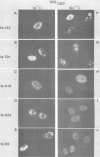
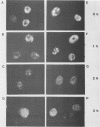
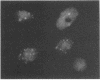
Using indirect immunofluorescence, well-characterized monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies, and temperature-sensitive (ts) mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1, we demonstrated that the 65-kilodalton DNA-binding protein (65KDBP), the major DNA-binding protein (infected cell polypeptide 8 [ICP8]), and the viral DNA polymerase (Pol) colocalize to replication compartments in the nuclei of infected cells under conditions which permit viral DNA synthesis. When viral DNA synthesis was blocked by incubation of the wild-type virus with phosphonoacetic acid, the 65KDBP, Pol, and ICP8 failed to localize to replication compartments. Instead, ICP8 accumulated nearly exclusively to prereplication sites, while the 65KDBP was only diffusely localized within the nuclei. Although some of the Pol accumulated in prereplication sites occupied by ICP8 in the presence of phosphonoacetic acid, a significant amount of Pol also was distributed throughout the nuclei. Examination by double-labeling immunofluorescence of DNA- ts mutant virus-infected cells revealed that the 65KDBP also did not colocalize with ICP8 to prereplication sites at temperatures nonpermissive for virus replication. These results are in disagreement with the hypothesis that ICP8 is the major organizational protein responsible for attracting other replication protein to prereplication sites in preparation for viral DNA synthesis (A. de Bruyn Kops and D. M. Knipe, Cell 55:857-868, 1988), and they suggest that other viral proteins, perhaps in addition to ICP8, or replication fork progression per se are required to organize the 65KDBP.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carmichael E. P., Kosovsky M. J., Weller S. K. Isolation and characterization of herpes simplex virus type 1 host range mutants defective in viral DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):91–99. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.91-99.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu C. T., Parris D. S., Dixon R. A., Farber F. E., Schaffer P. A. Hydroxylamine mutagenesis of HSV DNA and DNA fragments: introduction of mutations into selected regions of the viral genome. Virology. 1979 Oct 15;98(1):168–181. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90535-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen D. M., Aschman D. P., Gelep P. T., Retondo M. J., Weller S. K., Schaffer P. A. Fine mapping and molecular cloning of mutations in the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase locus. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):236–247. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.236-247.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crute J. J., Tsurumi T., Zhu L. A., Weller S. K., Olivo P. D., Challberg M. D., Mocarski E. S., Lehman I. R. Herpes simplex virus 1 helicase-primase: a complex of three herpes-encoded gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2186–2189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsky D. I., Crumpacker C. S. Expression of herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA polymerase gene by in vitro translation and effects of gene deletions on activity. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3224–3232. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3224-3232.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo M. L., Dorsky D. I., Crumpacker C. S., Parris D. S. The essential 65-kilodalton DNA-binding protein of herpes simplex virus stimulates the virus-encoded DNA polymerase. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5023–5029. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5023-5029.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo M. L., Jackwood D. H., Murphy M., Marsden H. S., Parris D. S. Purification of the herpes simplex virus type 1 65-kilodalton DNA-binding protein: properties of the protein and evidence of its association with the virus-encoded DNA polymerase. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2874–2883. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2874-2883.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. J., Weller S. K. An ICP6::lacZ insertional mutagen is used to demonstrate that the UL52 gene of herpes simplex virus type 1 is required for virus growth and DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2970–2977. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2970-2977.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodrich L. D., Rixon F. J., Parris D. S. Kinetics of expression of the gene encoding the 65-kilodalton DNA-binding protein of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):137–147. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.137-147.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jofre J. T., Schaffer P. A., Parris D. S. Genetics of resistance to phosphonoacetic acid in strain KOS of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):833–836. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.833-836.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipe D. M., Senechek D., Rice S. A., Smith J. L. Stages in the nuclear association of the herpes simplex virus transcriptional activator protein ICP4. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):276–284. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.276-284.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasken R. S., Kornberg A. The beta subunit dissociates readily from the Escherichia coli DNA polymerase III holoenzyme. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1720–1724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinbach S. S., Casto J. F. Identification and characterization of deoxyribonucleoprotein complexes containing the major DNA-binding protein of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1983 Dec;131(2):274–286. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90496-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinbach S. S., Casto J. F., Pickett T. K. Deoxyribonucleoprotein complexes and DNA synthesis of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1984 Sep;137(2):287–296. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90220-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little S. P., Jofre J. T., Courtney R. J., Schaffer P. A. A virion-associated glycoprotein essential for infectivity of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1981 Nov;115(1):149–160. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao J. C., Robishaw E. E. Mode of inhibition of herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase by phosphonoacetate. Biochemistry. 1975 Dec 16;14(25):5475–5479. doi: 10.1021/bi00696a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao J. C., Robishaw E. E., Overby L. R. Inhibition of DNA polymerase from herpes simplex virus-infected wi-38 cells by phosphonoacetic Acid. J Virol. 1975 May;15(5):1281–1283. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.5.1281-1283.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchetti M. E., Smith C. A., Schaffer P. A. A temperature-sensitive mutation in a herpes simplex virus type 1 gene required for viral DNA synthesis maps to coordinates 0.609 through 0.614 in UL. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):715–721. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.715-721.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden H. S., Campbell M. E., Haarr L., Frame M. C., Parris D. S., Murphy M., Hope R. G., Muller M. T., Preston C. M. The 65,000-Mr DNA-binding and virion trans-inducing proteins of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2428–2437. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2428-2437.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dalrymple M. A., Davison A. J., Dolan A., Frame M. C., McNab D., Perry L. J., Scott J. E., Taylor P. The complete DNA sequence of the long unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jul;69(Pt 7):1531–1574. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-7-1531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McHenry C. S. DNA polymerase III holoenzyme of Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:519–550. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McHenry C., Kornberg A. DNA polymerase III holoenzyme of Escherichia coli. Purification and resolution into subunits. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6478–6484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivo P. D., Nelson N. J., Challberg M. D. Herpes simplex virus DNA replication: the UL9 gene encodes an origin-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5414–5418. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivo P. D., Nelson N. J., Challberg M. D. Herpes simplex virus type 1 gene products required for DNA replication: identification and overexpression. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):196–204. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.196-204.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parris D. S., Courtney R. J., Schaffer P. A. Temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1 defective in transcriptional and post-transcriptional functions required for viral DNA synthesis. Virology. 1978 Oct 15;90(2):177–186. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90301-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parris D. S., Cross A., Haarr L., Orr A., Frame M. C., Murphy M., McGeoch D. J., Marsden H. S. Identification of the gene encoding the 65-kilodalton DNA-binding protein of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):818–825. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.818-825.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pignatti P. F., Cassai E. Analysis of herpes simplex virus nucleoprotein complexes extracted from infected cells. J Virol. 1980 Dec;36(3):816–828. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.3.816-828.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pignatti P. F., Cassai E., Bertazzoni U. Herpes simplex virus DNA synthesis in a partially purified soluble extract from infected cells. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):1033–1036. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.1033-1036.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell K. L., Littler E., Purifoy D. J. Nonstructural proteins of herpes simplex virus. II. Major virus-specific DNa-binding protein. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):894–902. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.894-902.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purifoy D. J., Lewis R. B., Powell K. L. Identification of the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase gene. Nature. 1977 Oct 13;269(5629):621–623. doi: 10.1038/269621a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan M. P., Chen L. B., Knipe D. M. The intranuclear location of a herpes simplex virus DNA-binding protein is determined by the status of viral DNA replication. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):857–868. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall R. E., Dinwoodie N. Intranuclear localization of herpes simplex virus immediate-early and delayed-early proteins: evidence that ICP 4 is associated with progeny virus DNA. J Gen Virol. 1986 Oct;67(Pt 10):2163–2177. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-10-2163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH K. O. RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN THE ENVELOPE AND THE INFECTIVITY OF HERPES SIMPLEX VIRUS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Mar;115:814–816. doi: 10.3181/00379727-115-29045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffer P. A., Aron G. M., Biswal N., Benyesh-Melnick M. Temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1: isolation, complementation and partial characterization. Virology. 1973 Mar;52(1):57–71. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90398-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showalter S. D., Zweig M., Hampar B. Monoclonal antibodies to herpes simplex virus type 1 proteins, including the immediate-early protein ICP 4. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):684–692. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.684-692.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan P. J., Banks L. M., Purifoy D. J., Powell K. L. Interactions between herpes simplex virus DNA-binding proteins. J Gen Virol. 1984 Nov;65(Pt 11):2033–2041. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-11-2033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller S. K., Lee K. J., Sabourin D. J., Schaffer P. A. Genetic analysis of temperature-sensitive mutants which define the gene for the major herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA-binding protein. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):354–366. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.354-366.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. A., Nelson N. J., McGeoch D. J., Challberg M. D. Identification of herpes simplex virus type 1 genes required for origin-dependent DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):435–443. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.435-443.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruyn Kops A., Knipe D. M. Formation of DNA replication structures in herpes virus-infected cells requires a viral DNA binding protein. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):857–868. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90141-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]