Abstract
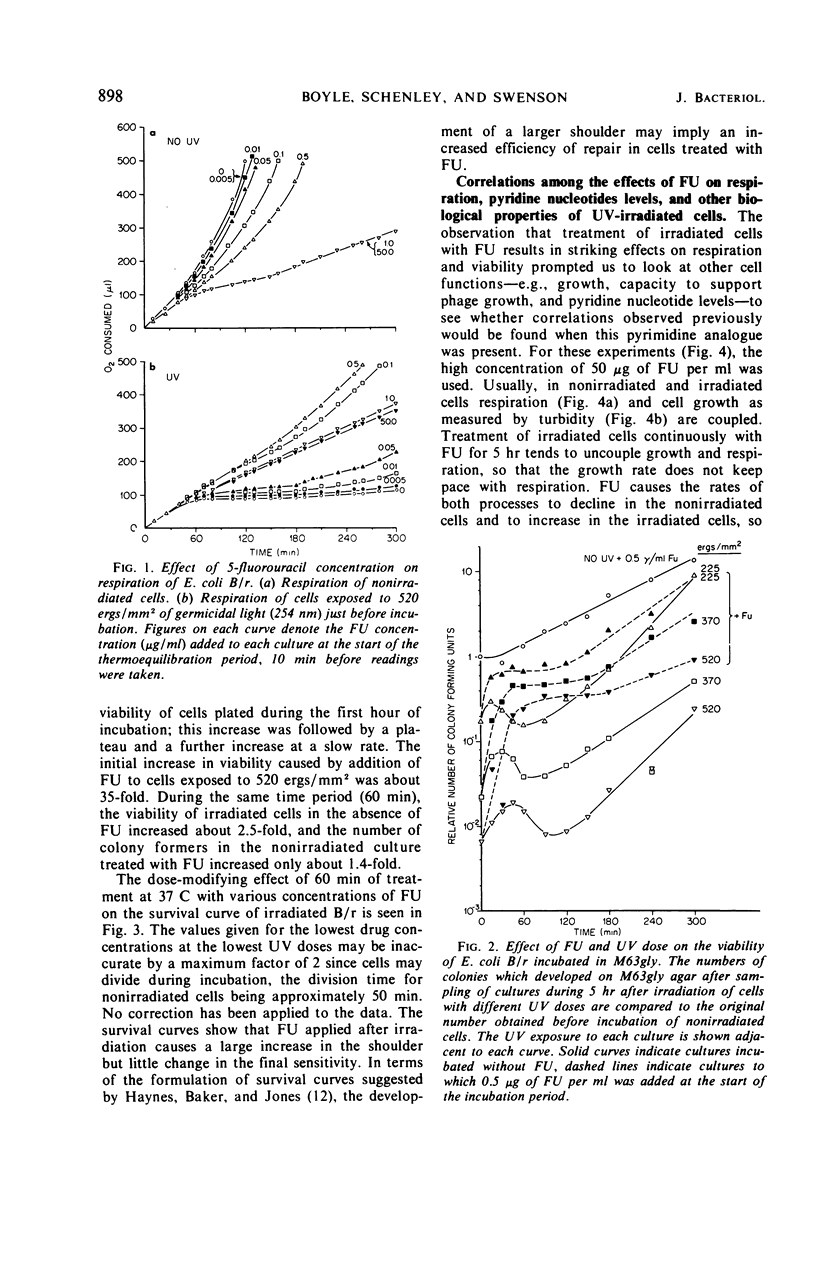
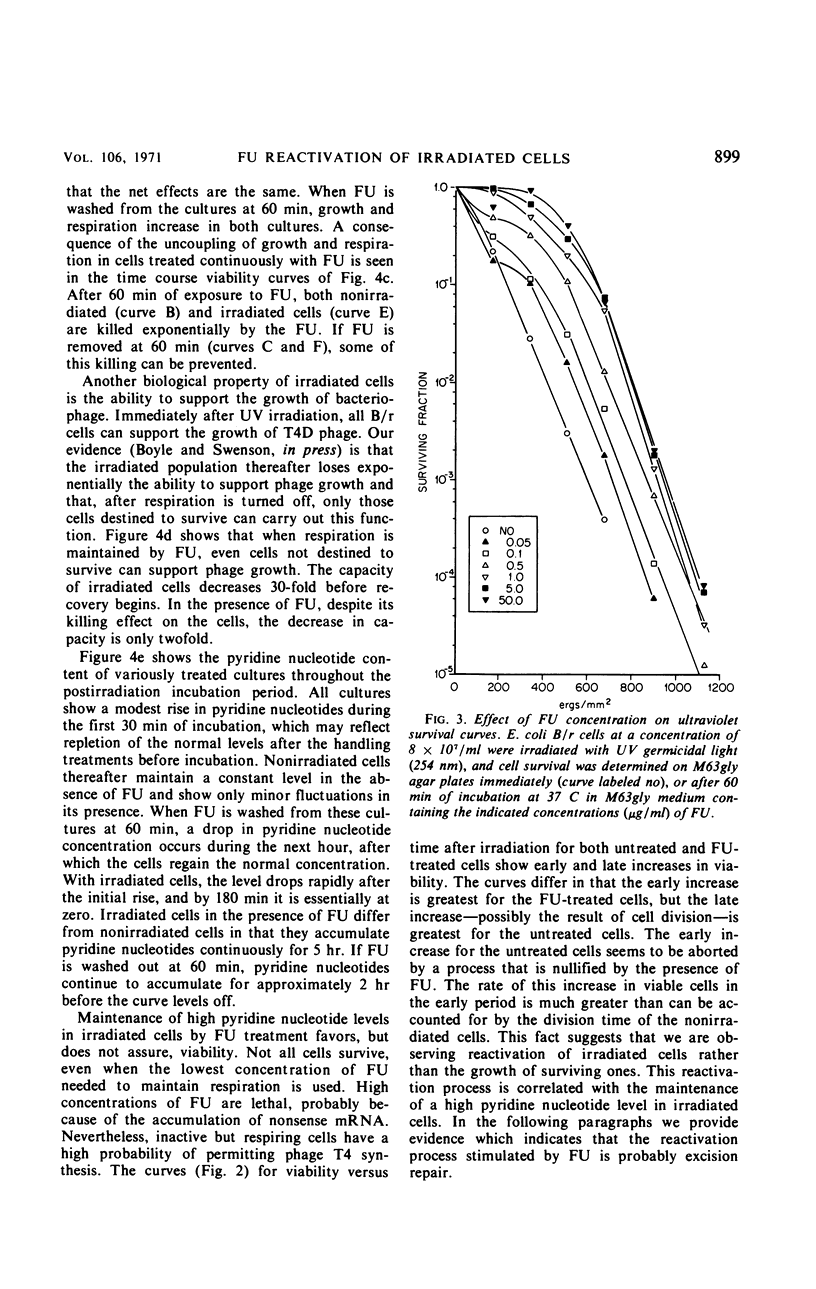
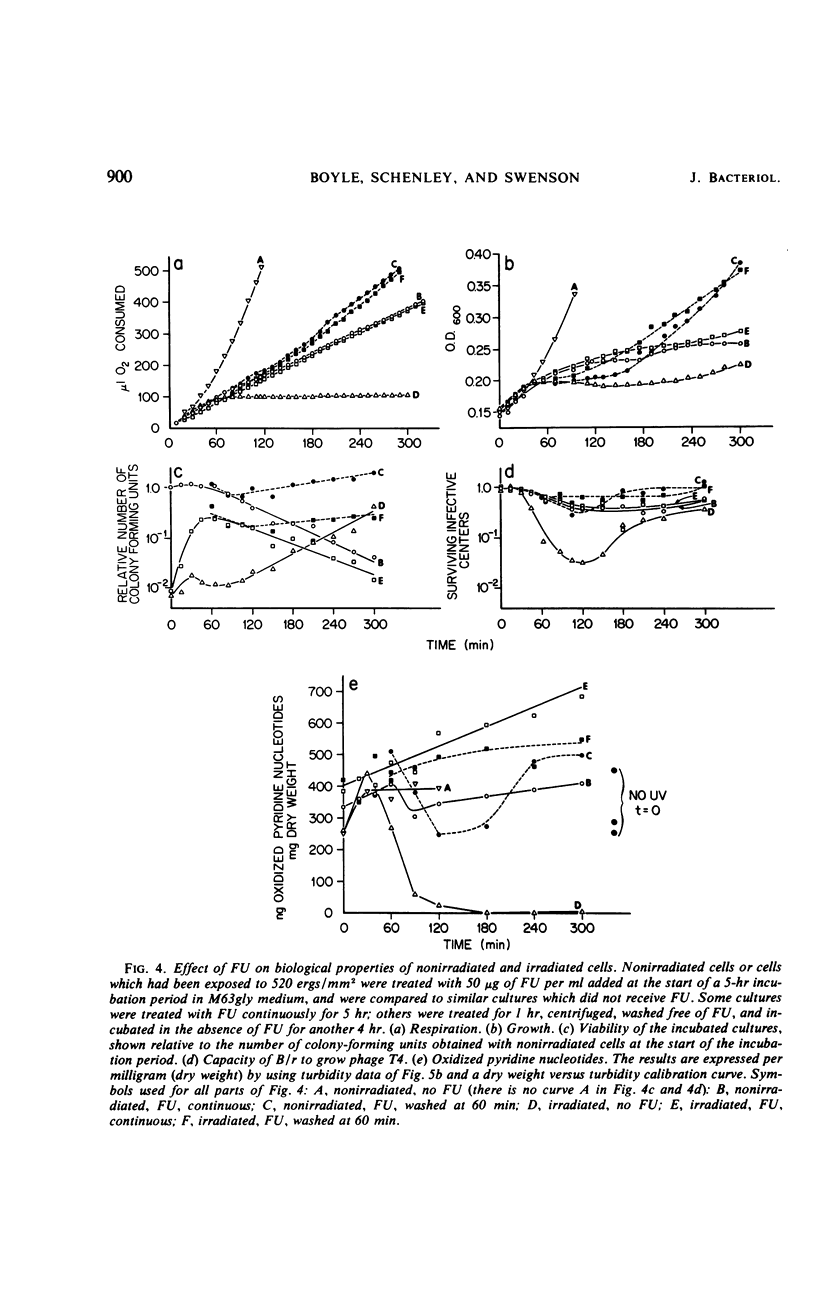
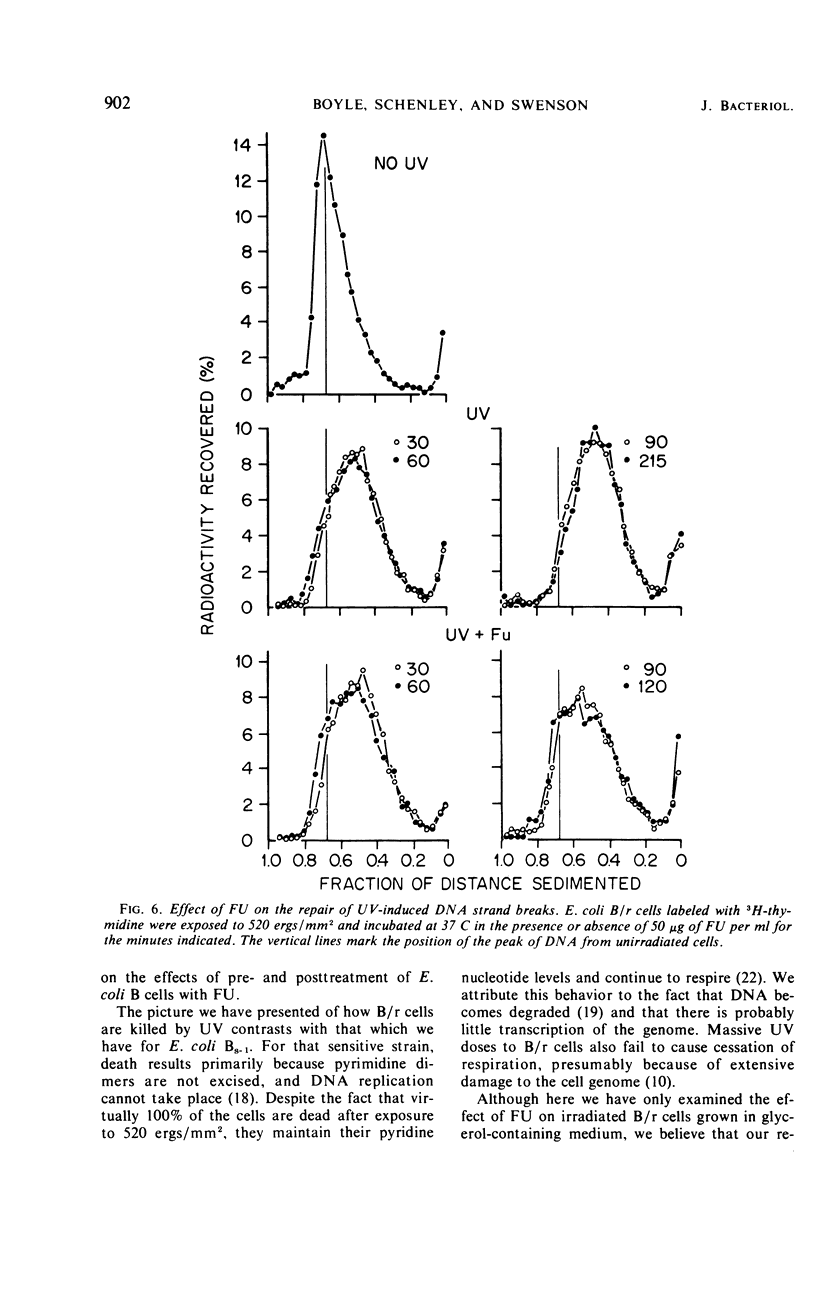
Ultraviolet irradiation (520 ergs/mm2 at 254 nm) causes the respiration of Escherichia coli B/r cells to cease after about 90 min postirradiation incubation in a minimal medium containing glycerol as the sole source of carbon. The cessation of respiration is associated with loss of pyridine nucleotides. Agents which interfere with postirradiation transcription and translation prevent cessation of respiration. We have studied the effects of one of these agents, 5-fluorouracil (FU), on respiration, pyridine nucleotide levels, viability, capacity to support phage growth, and the repair of irradiated deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Addition of FU to cells immediately after irradiation results in the continuance of respiration at a linear rate and the maintenance of high levels of pyridine nucleotides. Cellular viability increases dramatically during the first 60 min of postirradiation incubation in the presence of FU. The ability of irradiated cells to support the growth of phage T4 is also greatly increased. FU treatment has no effect on the kinetics of pyrimidine dimer excision or the degradation of DNA. However, treated cells repair single-strand breaks resulting from early steps in excision repair slightly more efficiently than do untreated cells. The results support the hypothesis that one of the causes of death in these irradiated cells is the disappearance of pyridine nucleotides, coenzymes of certain respiratory dehydrogenases, and, in the case of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, for polynucleotide ligase, the enzyme responsible for the final step in the repair of DNA.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEN-ISHAI R., GOLDIN C. H., KERPEL S. ON THE MECHANISM OF 5-FLUOROURACIL-INDUCED RESISTANCE TO ULTRAVIOLET IRRADIATION IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Feb 8;95:291–301. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90493-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEN-ISHAI R., GOLDIN H., OPPENHEIM B. The effect of ultraviolet irradiation on 5-fluorouracil-pretreated bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 May 14;55:748–754. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90853-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOLLUM F. J. Thermal conversion of nonpriming deoxyribonucleic acid to primer. J Biol Chem. 1959 Oct;234:2733–2734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ishai R., Zeevi N. Postirradiation cell division in 5-fluorouracil-pre-treated Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):749–753. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.749-753.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle J. M., Setlow R. B. Correlations between host-cell reactivation, ultraviolet reactivation and pyrimidine dimer excision in the DNA of bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jul 14;51(1):131–144. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90275-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle J. M., Swenson P. A. Loss of the capacity of UV-irradiated Escherichia coli B-r to grow T4D. Virology. 1971 Apr;44(1):37–45. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90150-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARPENTER K. J., KODICEK E. The fluorimetric estimation of N1-methylnicotinamide and its differentiation from coenzyme. Biochem J. 1950 Apr;46(4):421–426. doi: 10.1042/bj0460421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAMPE S. P., BENZER S. Reversal of mutant phenotypes by 5-fluorouracil: an approach to nucleotide sequences in messenger-RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Apr 15;48:532–546. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.4.532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILLIES N. E., ALPER T. Reduction in the lethal effects of radiations on Escherichia coli beta by treatment with chloramphenicol. Nature. 1959 Jan 24;183(4656):237–238. doi: 10.1038/183237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamkalo B. A., Swenson P. A. Effects of ultraviolet radiation on respiration and growth in radiation-resistant and radiation-sensitive strains of Escherichia coli B. J Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;99(3):815–823. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.3.815-823.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann G., Honikel K. O., Knüsel F., Nüesch J. The specific inhibition of the DNA-directed RNA synthesis by rifamycin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967;145(3):843–844. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90147-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maitra U., Barash F. DNA-dependent synthesis of RNA by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase: release and reinitiation of RNA chains from DNA templates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Oct;64(2):779–786. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.2.779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath R. A., Williams R. W. Reconstruction in vivo of irradiated Escherichia coli deoxyribonucleic acid; the rejoining of broken pieces. Nature. 1966 Oct 29;212(5061):534–535. doi: 10.1038/212534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivera B. M., Lehman I. R. Diphosphopyridine nucleotide: a cofactor for the polynucleotide-joining enzyme from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jun;57(6):1700–1704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.6.1700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen B., Rothman F., Weigert M. G. Miscoding caused by 5-fluorouracil. J Mol Biol. 1969 Sep 14;44(2):363–375. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90181-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouvière J., Wyngaarden J., Cantoni J., Gros F., Kepes A. Effect of T4 infection on messenger RNA synthesis in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Aug 23;166(1):94–114. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90494-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SETLOW R. B., CARRIER W. L. THE DISAPPEARANCE OF THYMINE DIMERS FROM DNA: AN ERROR-CORRECTING MECHANISM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Feb;51:226–231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.2.226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson P. A., Schenley R. L. Evidence for the control of respiration by DNA in ultraviolet-irradiated Escherichia coli B-r cells. Mutat Res. 1970 May;9(5):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(70)90028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson P. A., Schenley R. L. Role of Pyridine Nucleotides in the Control of Respiration in Ultraviolet-Irradiated Escherichia coli B/r Cells. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1230–1235. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1230-1235.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman S. B., Little J. W., Oshinsky C. K., Gellert M. Enzymatic joining of DNA strands: a novel reaction of diphosphopyridine nucleotide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jun;57(6):1841–1848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.6.1841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


