Abstract
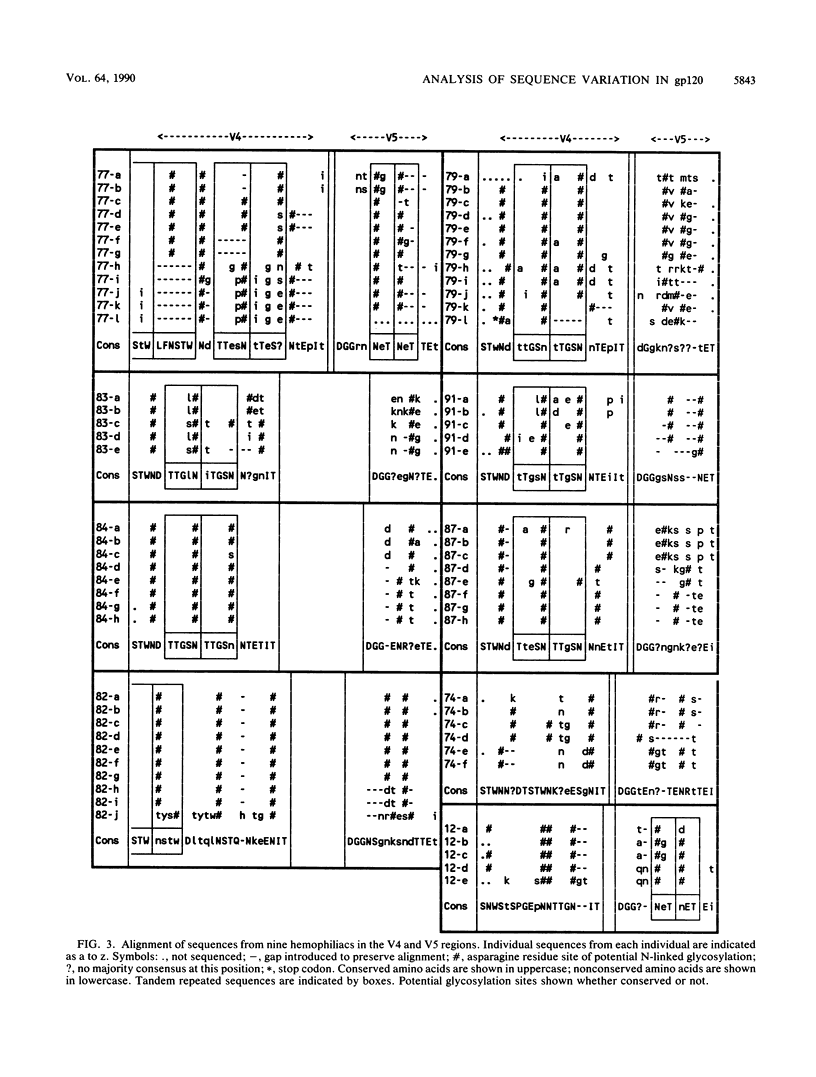
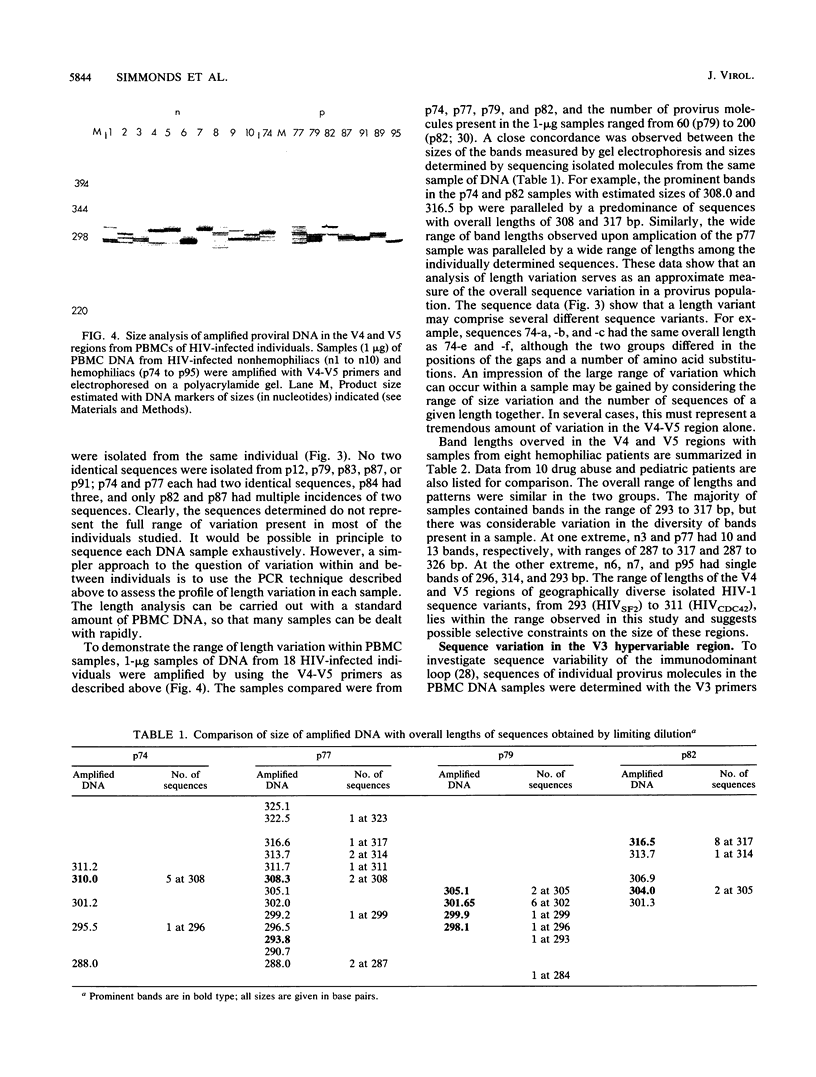
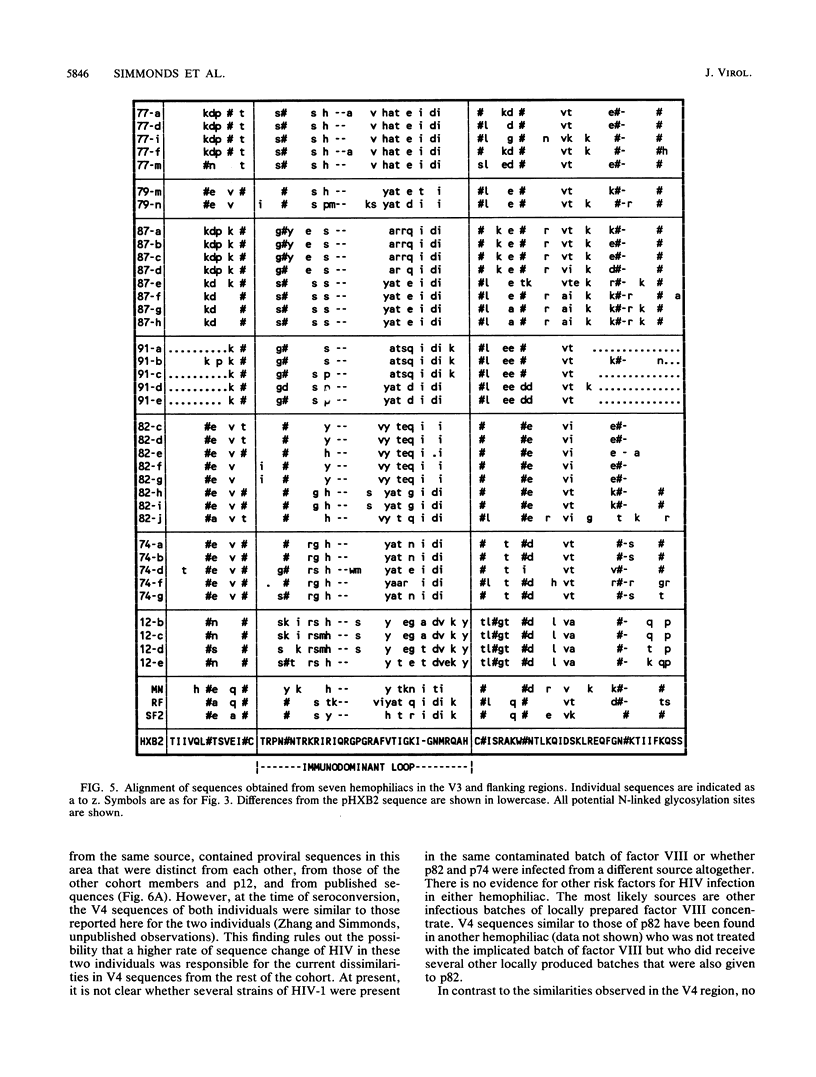
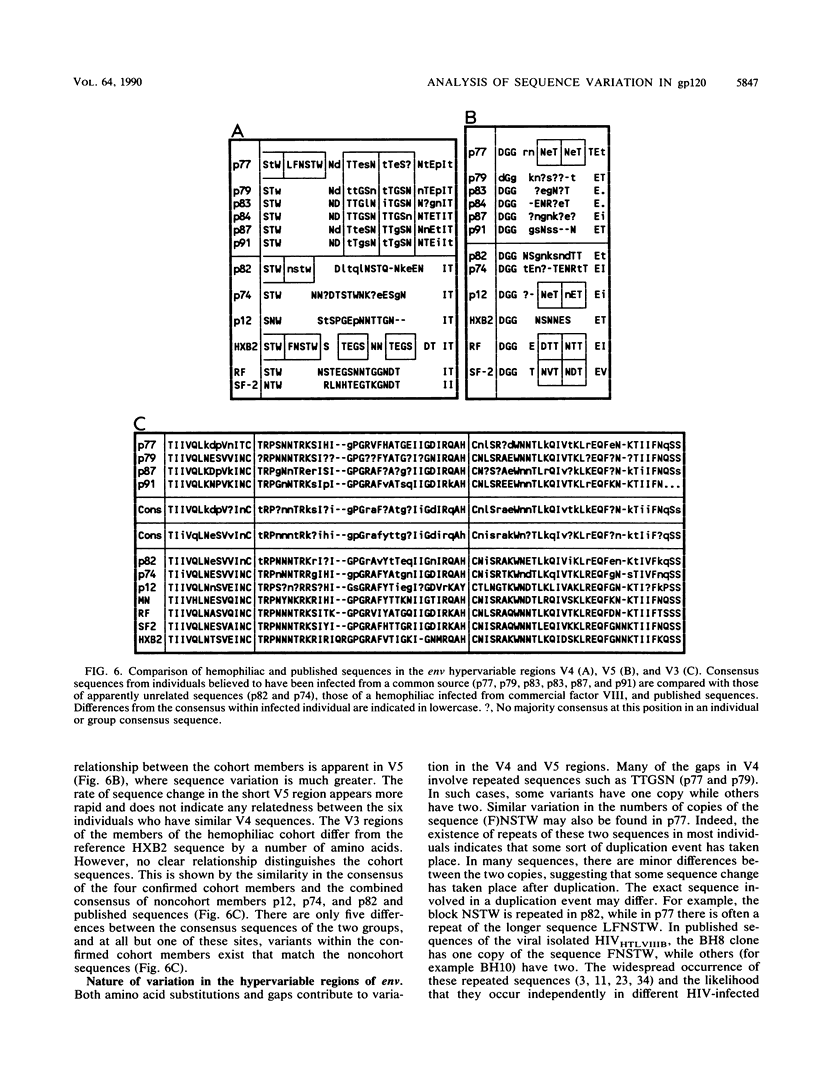
Nucleotide sequences in three hypervariable regions of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) env gene were obtained by sequencing provirus present in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of HIV-infected individuals. Single molecules of target sequences were isolated by limiting dilution and amplified in two stages by the polymerase chain reaction, using nested primers. The product was directly sequenced to avoid errors introduced by Taq polymerase during the amplification process. There was extensive variation between sequences from the same individual as well as between sequences from different individuals. Interpatient variability was markedly less in individuals infected from a common source. A high proportion of amino acid substitutions in the hypervariable regions altered the number and positions of potential N-linked glycosylation sites. Sequences in two hypervariable regions frequently contained short (3- to 15-bp) duplications or deletions, and by amplifying peripheral blood mononuclear cell DNA containing 10(2) or 10(3) proviral molecules and analyzing the product by high-resolution electrophoresis, the total number and abundance of distinct length variants within an individual could be estimated, providing a more comprehensive analysis of the variants present than would be obtained by sequencing alone. Sequences from many individuals showed frequent amino acid substitutions at certain key positions for neutralizing-antibody and cytotoxic T-cell recognition in the immunodominant loop. The rates of synonymous and nonsynonymous nucleotide substitution in the region of this and flanking regions indicate that strong positive selection for amino acid change is operating in the generation of antigenic diversity.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert J., Abrahamsson B., Nagy K., Aurelius E., Gaines H., Nyström G., Fenyö E. M. Rapid development of isolate-specific neutralizing antibodies after primary HIV-1 infection and consequent emergence of virus variants which resist neutralization by autologous sera. AIDS. 1990 Feb;4(2):107–112. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199002000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander S., Elder J. H. Carbohydrate dramatically influences immune reactivity of antisera to viral glycoprotein antigens. Science. 1984 Dec 14;226(4680):1328–1330. doi: 10.1126/science.6505693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alizon M., Wain-Hobson S., Montagnier L., Sonigo P. Genetic variability of the AIDS virus: nucleotide sequence analysis of two isolates from African patients. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):63–74. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90860-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. L., Monaghan P. Evolution of the structural proteins of human immunodeficiency virus: selective constraints on nucleotide substitution. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1988 Dec;4(6):399–407. doi: 10.1089/aid.1988.4.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter S., Evans L. H., Sevoian M., Chesebro B. Role of the host immune response in selection of equine infectious anemia virus variants. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3783–3789. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3783-3789.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. E., Pedersen F. S., Narayan O., Haseltine W. A. Genomic changes associated with antigenic variation of visna virus durig persistent infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4454–4458. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordonnier A., Montagnier L., Emerman M. Single amino-acid changes in HIV envelope affect viral tropism and receptor binding. Nature. 1989 Aug 17;340(6234):571–574. doi: 10.1038/340571a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feizi T., Childs R. A. Carbohydrates as antigenic determinants of glycoproteins. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 1;245(1):1–11. doi: 10.1042/bj2450001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnann J. W., Jr, Schwimmbeck P. L., Nelson J. A., Truax A. B., Oldstone M. B. Diagnosis of AIDS by using a 12-amino acid peptide representing an immunodominant epitope of the human immunodeficiency virus. J Infect Dis. 1987 Aug;156(2):261–267. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.2.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goudsmit J., Boucher C. A., Meloen R. H., Epstein L. G., Smit L., van der Hoek L., Bakker M. Human antibody response to a strain-specific HIV-1 gp120 epitope associated with cell fusion inhibition. AIDS. 1988 Jun;2(3):157–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goudsmit J., Debouck C., Meloen R. H., Smit L., Bakker M., Asher D. M., Wolff A. V., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 neutralization epitope with conserved architecture elicits early type-specific antibodies in experimentally infected chimpanzees. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4478–4482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn B. H., Shaw G. M., Taylor M. E., Redfield R. R., Markham P. D., Salahuddin S. Z., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C., Parks E. S., Parks W. P. Genetic variation in HTLV-III/LAV over time in patients with AIDS or at risk for AIDS. Science. 1986 Jun 20;232(4757):1548–1553. doi: 10.1126/science.3012778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. E., Hastie N. D. Accelerated evolution in the reactive centre regions of serine protease inhibitors. Nature. 1987 Mar 5;326(6108):96–99. doi: 10.1038/326096a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A. L., Nei M. Nucleotide substitution at major histocompatibility complex class II loci: evidence for overdominant selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):958–962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozarsky K., Penman M., Basiripour L., Haseltine W., Sodroski J., Krieger M. Glycosylation and processing of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope protein. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1989;2(2):163–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskowski M., Jr, Kato I., Ardelt W., Cook J., Denton A., Empie M. W., Kohr W. J., Park S. J., Parks K., Schatzley B. L. Ovomucoid third domains from 100 avian species: isolation, sequences, and hypervariability of enzyme-inhibitor contact residues. Biochemistry. 1987 Jan 13;26(1):202–221. doi: 10.1021/bi00375a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasky L. A., Nakamura G., Smith D. H., Fennie C., Shimasaki C., Patzer E., Berman P., Gregory T., Capon D. J. Delineation of a region of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 glycoprotein critical for interaction with the CD4 receptor. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90524-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W. H., Wu C. I., Luo C. C. A new method for estimating synonymous and nonsynonymous rates of nucleotide substitution considering the relative likelihood of nucleotide and codon changes. Mol Biol Evol. 1985 Mar;2(2):150–174. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Looney D. J., Fisher A. G., Putney S. D., Rusche J. R., Redfield R. R., Burke D. S., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Type-restricted neutralization of molecular clones of human immunodeficiency virus. Science. 1988 Jul 15;241(4863):357–359. doi: 10.1126/science.3388046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludlam C. A., Tucker J., Steel C. M., Tedder R. S., Cheingsong-Popov R., Weiss R. A., McClelland D. B., Philp I., Prescott R. J. Human T-lymphotropic virus type III (HTLV-III) infection in seronegative haemophiliacs after transfusion of factor VIII. Lancet. 1985 Aug 3;2(8449):233–236. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90288-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melbye M., Froebel K. S., Madhok R., Biggar R. J., Sarin P. S., Stenbjerg S., Lowe G. D., Forbes C. D., Goedert J. J., Gallo R. C. HTLV-III seropositivity in European haemophiliacs exposed to Factor VIII concentrate imported from the USA. Lancet. 1984 Dec 22;2(8417-8418):1444–1446. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91632-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meloen R. H., Liskamp R. M., Goudsmit J. Specificity and function of the individual amino acids of an important determinant of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 that induces neutralizing activity. J Gen Virol. 1989 Jun;70(Pt 6):1505–1512. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-6-1505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modrow S., Hahn B. H., Shaw G. M., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F., Wolf H. Computer-assisted analysis of envelope protein sequences of seven human immunodeficiency virus isolates: prediction of antigenic epitopes in conserved and variable regions. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):570–578. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.570-578.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayan O., Griffin D. E., Chase J. Antigenic shift of visna virus in persistently infected sheep. Science. 1977 Jul 22;197(4301):376–378. doi: 10.1126/science.195339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Strick N., Lee E. S. B cell epitope mapping of human immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoproteins with long (19- to 36-residue) synthetic peptides. J Gen Virol. 1990 Jan;71(Pt 1):85–95. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-1-85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palker T. J., Matthews T. J., Clark M. E., Cianciolo G. J., Randall R. R., Langlois A. J., White G. C., Safai B., Snyderman R., Bolognesi D. P. A conserved region at the COOH terminus of human immunodeficiency virus gp120 envelope protein contains an immunodominant epitope. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2479–2483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitz M. S., Jr, Wilson C., Naugle C., Gallo R. C., Robert-Guroff M. Generation of a neutralization-resistant variant of HIV-1 is due to selection for a point mutation in the envelope gene. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):57–63. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90179-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusche J. R., Javaherian K., McDanal C., Petro J., Lynn D. L., Grimaila R., Langlois A., Gallo R. C., Arthur L. O., Fischinger P. J. Antibodies that inhibit fusion of human immunodeficiency virus-infected cells bind a 24-amino acid sequence of the viral envelope, gp120. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3198–3202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saag M. S., Hahn B. H., Gibbons J., Li Y., Parks E. S., Parks W. P., Shaw G. M. Extensive variation of human immunodeficiency virus type-1 in vivo. Nature. 1988 Aug 4;334(6181):440–444. doi: 10.1038/334440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds P., Balfe P., Peutherer J. F., Ludlam C. A., Bishop J. O., Brown A. J. Human immunodeficiency virus-infected individuals contain provirus in small numbers of peripheral mononuclear cells and at low copy numbers. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):864–872. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.864-872.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds P., Lainson F. A., Cuthbert R., Steel C. M., Peutherer J. F., Ludlam C. A. HIV antigen and antibody detection: variable responses to infection in the Edinburgh haemophiliac cohort. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1988 Feb 27;296(6622):593–598. doi: 10.1136/bmj.296.6622.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skehel J. J., Stevens D. J., Daniels R. S., Douglas A. R., Knossow M., Wilson I. A., Wiley D. C. A carbohydrate side chain on hemagglutinins of Hong Kong influenza viruses inhibits recognition by a monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1779–1783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodora D. L., Cohen G. H., Eisenberg R. J. Influence of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides on antigenicity, processing, and cell surface expression of herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein D. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5184–5193. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5184-5193.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starcich B. R., Hahn B. H., Shaw G. M., McNeely P. D., Modrow S., Wolf H., Parks E. S., Parks W. P., Josephs S. F., Gallo R. C. Identification and characterization of conserved and variable regions in the envelope gene of HTLV-III/LAV, the retrovirus of AIDS. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):637–648. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90778-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugawara K., Kitame F., Nishimura H., Nakamura K. Operational and topological analyses of antigenic sites on influenza C virus glycoprotein and their dependence on glycosylation. J Gen Virol. 1988 Mar;69(Pt 3):537–547. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-3-537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi H., Merli S., Putney S. D., Houghten R., Moss B., Germain R. N., Berzofsky J. A. A single amino acid interchange yields reciprocal CTL specificities for HIV-1 gp160. Science. 1989 Oct 6;246(4926):118–121. doi: 10.1126/science.2789433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang T. C., Bentley D. R. An improved sequencing method using Sequenase that is independent of template concentration. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):6238–6238. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.6238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willey R. L., Rutledge R. A., Dias S., Folks T., Theodore T., Buckler C. E., Martin M. A. Identification of conserved and divergent domains within the envelope gene of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome retrovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5038–5042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P., Simmonds P., Yap P. L., Balfe P., Bishop J., Brettle R., Hague R., Hargreaves D., Inglis J., Brown A. L. The polymerase chain reaction in the diagnosis of vertically transmitted HIV infection. AIDS. 1990 May;4(5):393–398. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199005000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winship P. R. An improved method for directly sequencing PCR amplified material using dimethyl sulphoxide. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 11;17(3):1266–1266. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.3.1266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]