Abstract
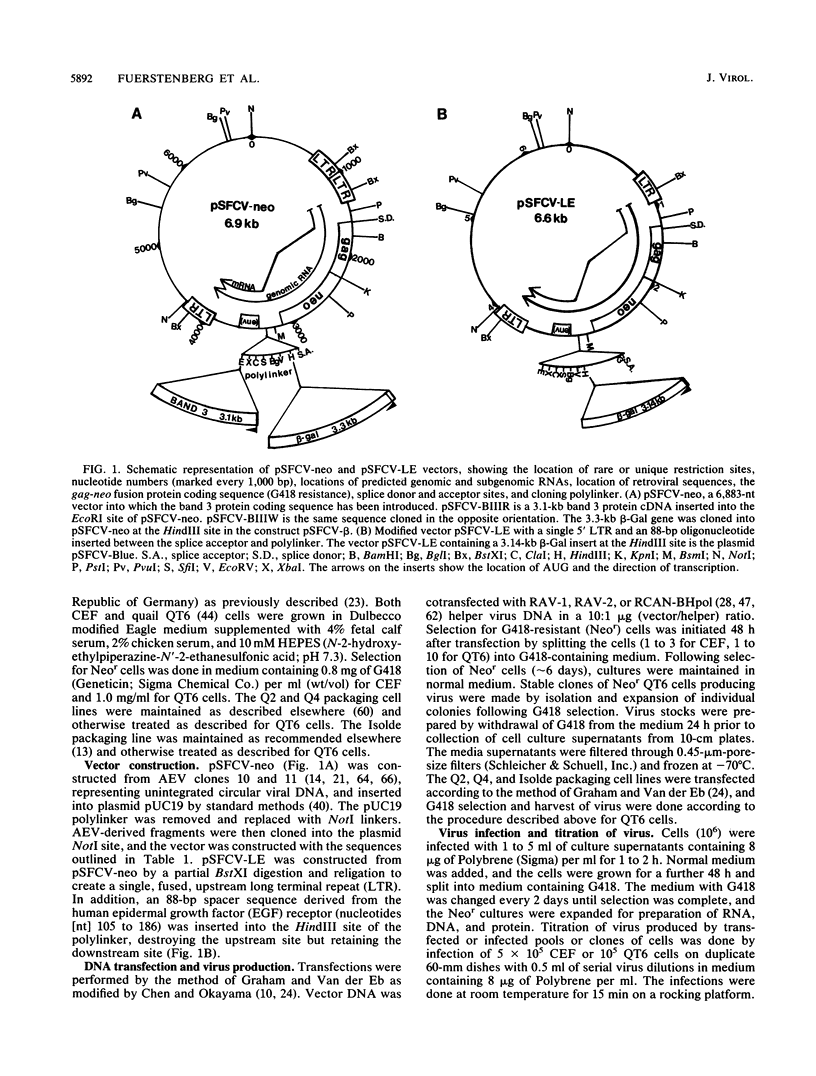
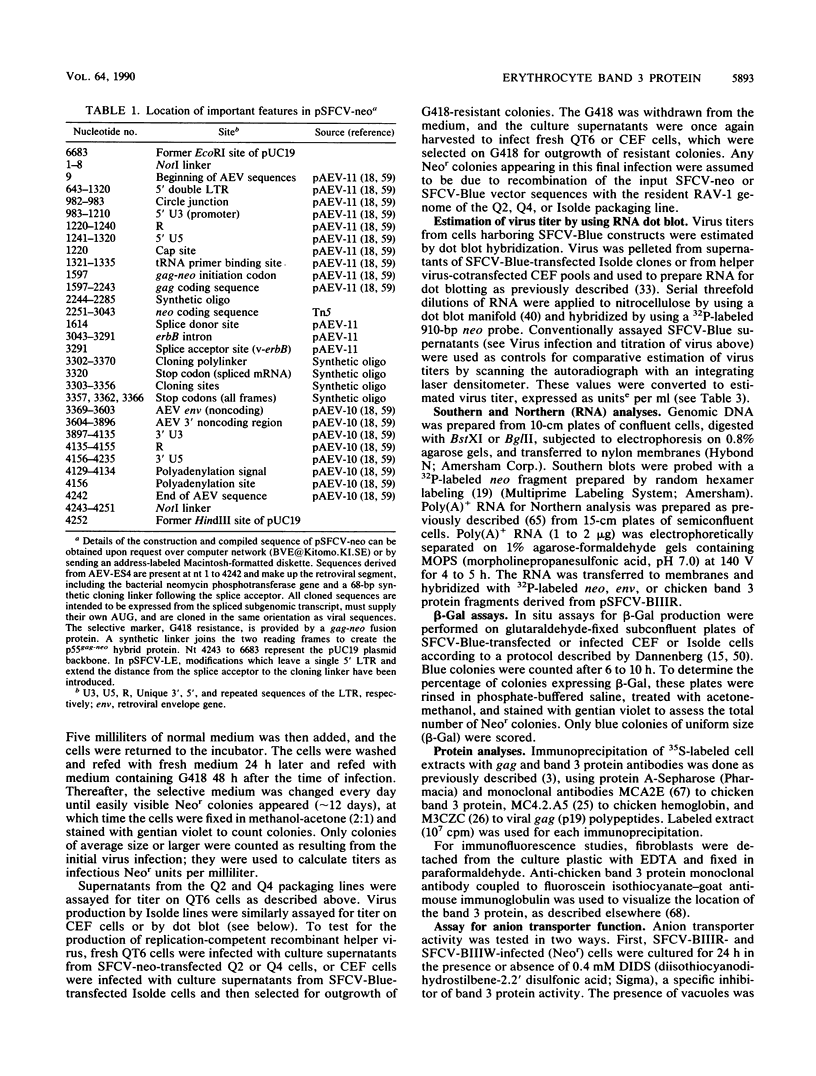
A retrovirus vector was constructed from the genome of avian erythroblastosis virus ES4. The v-erbA sequences of avian erythroblastosis virus were replaced by those coding for neomycin phosphotransferase, creating a gag-neo fusion protein which provides G418 resistance as a selectable marker. The v-erbB sequences following the splice acceptor were replaced by a cloning linker allowing insertion of foreign genes. The vector has been tested in conjunction with several helper viruses for the transmission of G418 resistance, titer, stability, transcription, and the transduction and expression of foreign genes in both chicken embryo fibroblasts and the QT6 quail cell line. The results show that the vector is capable of producing high titers of Neor virus from stably integrated proviruses. These proviruses express a balanced ratio of genome length to spliced transcripts which are efficiently translated into protein. Using the Escherichia coli beta-galactosidase gene cloned into the vector as a test construct, expression of enzyme activity could be detected in 90 to 95% of transfected target cells and in 80 to 85% of subsequently infected cells. In addition, a cDNA encoding the avian erythrocyte band 3 anion exchange protein has been expressed from the vector in both chicken embryo fibroblasts and QT6 cells and appears to function as an active, plasma membrane-based anion transporter. The ectopic expression of band 3 protein provides a visual marker for vector function in these cells.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arrigo S., Yun M., Beemon K. cis-acting regulatory elements within gag genes of avian retroviruses. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):388–397. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartel D., Lepke S., Layh-Schmitt G., Legrum B., Passow H. Anion transport in oocytes of Xenopus laevis induced by expression of mouse erythroid band 3 protein--encoding cRNA and of a cRNA derivative obtained by site-directed mutagenesis at the stilbene disulfonate binding site. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3601–3609. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08533.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beug H., Graf T., Hayman M. J. Production and characterization of antisera specific for the erb-portion of p75, the presumptive transforming protein of avian erythroblastosis virus. Virology. 1981 May;111(1):201–210. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90665-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beug H., von Kirchbach A., Döderlein G., Conscience J. F., Graf T. Chicken hematopoietic cells transformed by seven strains of defective avian leukemia viruses display three distinct phenotypes of differentiation. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):375–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90057-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieth E., Gabus C., Darlix J. L. A study of the dimer formation of Rous sarcoma virus RNA and of its effect on viral protein synthesis in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 11;18(1):119–127. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosselman R. A., Hsu R. Y., Boggs T., Hu S., Bruszewski J., Ou S., Souza L., Kozar L., Martin F., Nicolson M. Replication-defective vectors of reticuloendotheliosis virus transduce exogenous genes into somatic stem cells of the unincubated chicken embryo. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2680–2689. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2680-2689.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulter C. A., Wagner E. F. A universal retroviral vector for efficient constitutive expression of exogenous genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):7194–7194. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.7194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlberg K., Ryden T. A., Beemon K. Localization and footprinting of an enhancer within the avian sarcoma virus gag gene. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1617–1624. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1617-1624.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cepko C. L., Roberts B. E., Mulligan R. C. Construction and applications of a highly transmissible murine retrovirus shuttle vector. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1053–1062. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90440-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone R. D., Mulligan R. C. High-efficiency gene transfer into mammalian cells: generation of helper-free recombinant retrovirus with broad mammalian host range. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6349–6353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosset F. L., Legras C., Chebloune Y., Savatier P., Thoraval P., Thomas J. L., Samarut J., Nigon V. M., Verdier G. A new avian leukosis virus-based packaging cell line that uses two separate transcomplementing helper genomes. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1070–1078. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1070-1078.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damm K., Beug H., Graf T., Vennström B. A single point mutation in erbA restores the erythroid transforming potential of a mutant avian erythroblastosis virus (AEV) defective in both erbA and erbB oncogenes. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):375–382. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04765.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty J. P., Wisniewski R., Yang S. L., Rhode B. W., Temin H. M. New retrovirus helper cells with almost no nucleotide sequence homology to retrovirus vectors. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):3209–3212. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.3209-3212.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eglitis M. A., Anderson W. F. Retroviral vectors for introduction of genes into mammalian cells. Biotechniques. 1988 Jul-Aug;6(7):608–614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerman M., Temin H. M. Genes with promoters in retrovirus vectors can be independently suppressed by an epigenetic mechanism. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):449–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freudenstein C., Beug H., Palmieri S., Graf T. Expression of embryonic haemoglobin in tsAEV-transformed embryonic erythroid cells during temperature-induced differentiation. Differentiation. 1982;22(3):231–234. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1982.tb01257.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frykberg L., Palmieri S., Beug H., Graf T., Hayman M. J., Vennström B. Transforming capacities of avian erythroblastosis virus mutants deleted in the erbA or erbB oncogenes. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):227–238. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90513-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf T., Beug H. Avian leukemia viruses: interaction with their target cells in vivo and in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 17;516(3):269–299. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(78)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf T. Two types of target cells for transformation with avian myelocytomatosis virus. Virology. 1973 Aug;54(2):398–413. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90152-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayman M. J., Beug H., Savin K. W. Changes in the expression of membrane antigens during the differentiation of chicken erythroblasts. J Cell Biochem. 1982;18(3):351–362. doi: 10.1002/jcb.1982.240180308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayman M. J., Royer-Pokora B., Graf T. Defectiveness of avian erythroblastosis virus: synthesis of a 75K gag-related protein. Virology. 1979 Jan 15;92(1):31–45. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90212-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano A., Wong T. C. Mutations in 3'-untranslated region of avian sarcoma virus mutant LA46 genome confer the cis-acting temperature-sensitive replication defect. Virology. 1989 Oct;172(2):651–654. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90209-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. H., Greenhouse J. J., Petropoulos C. J., Sutrave P. Adaptor plasmids simplify the insertion of foreign DNA into helper-independent retroviral vectors. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3004–3012. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3004-3012.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S., Kosik E. Mutagenesis of the region between env and src of the SR-A strain of Rous sarcoma virus for the purpose of constructing helper-independent vectors. Virology. 1984 Jul 15;136(1):89–99. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90250-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay D. G. Characterization of the chicken erythrocyte anion exchange protein. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9431–9436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantoff P. W., Gillio A. P., McLachlin J. R., Bordignon C., Eglitis M. A., Kernan N. A., Moen R. C., Kohn D. B., Yu S. F., Karson E. Expression of human adenosine deaminase in nonhuman primates after retrovirus-mediated gene transfer. J Exp Med. 1987 Jul 1;166(1):219–234. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.1.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz R. A., Terry R. W., Skalka A. M. A conserved cis-acting sequence in the 5' leader of avian sarcoma virus RNA is required for packaging. J Virol. 1986 Jul;59(1):163–167. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.1.163-167.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khazaie K., Dull T. J., Graf T., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A., Beug H., Vennström B. Truncation of the human EGF receptor leads to differential transforming potentials in primary avian fibroblasts and erythroblasts. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3061–3071. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03171.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
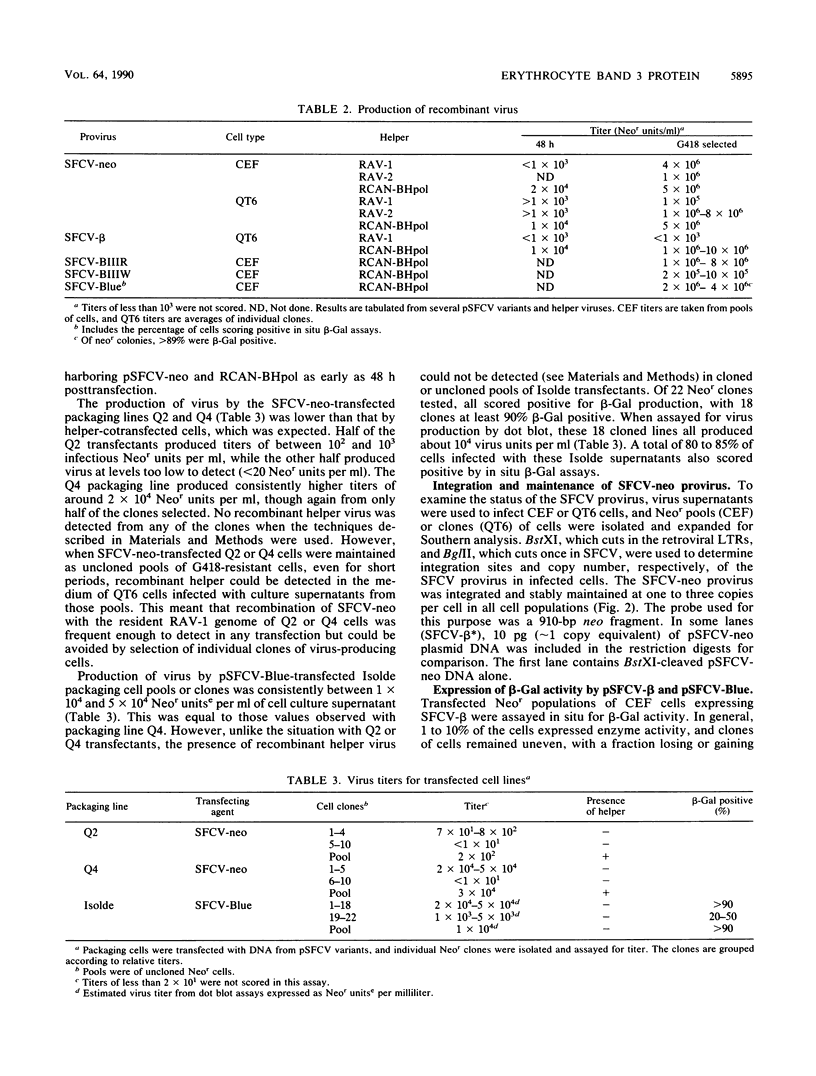
- Kim H. R., Kennedy B. S., Engel J. D. Two chicken erythrocyte band 3 mRNAs are generated by alternative transcriptional initiation and differential RNA splicing. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5198–5206. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. R., Yew N. S., Ansorge W., Voss H., Schwager C., Vennström B., Zenke M., Engel J. D. Two different mRNAs are transcribed from a single genomic locus encoding the chicken erythrocyte anion transport proteins (band 3). Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4416–4424. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopito R. R., Lee B. S., Simmons D. M., Lindsey A. E., Morgans C. W., Schneider K. Regulation of intracellular pH by a neuronal homolog of the erythrocyte anion exchanger. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):927–937. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90615-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Effects of intercistronic length on the efficiency of reinitiation by eucaryotic ribosomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3438–3445. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Tsichlis P., Khoury G. Multiple enhancer domains in the 3' terminus of the Prague strain of Rous sarcoma virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 24;12(16):6427–6442. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.16.6427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levantis P., Gillespie D. A., Hart K., Bissell M. J., Wyke J. A. Control of expression of an integrated Rous sarcoma provirus in rat cells: role of 5' genomic duplications reveals unexpected patterns of gene transcription and its regulation. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):907–916. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.907-916.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz D., Goff S., Bank A. A safe packaging line for gene transfer: separating viral genes on two different plasmids. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1120–1124. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1120-1124.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Law M. F., Verma I. M. Generation of helper-free amphotropic retroviruses that transduce a dominant-acting, methotrexate-resistant dihydrofolate reductase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):431–437. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. K., Temin H. M. Insertion of several different DNAs in reticuloendotheliosis virus strain T suppresses transformation by reducing the amount of subgenomic mRNA. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):75–80. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.75-80.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscovici C., Moscovici M. G., Jimenez H., Lai M. M., Hayman M. J., Vogt P. K. Continuous tissue culture cell lines derived from chemically induced tumors of Japanese quail. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan R. C., Berg P. Expression of a bacterial gene in mammalian cells. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1422–1427. doi: 10.1126/science.6251549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemeth S. P., Fox L. G., DeMarco M., Brugge J. S. Deletions within the amino-terminal half of the c-src gene product that alter the functional activity of the protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1109–1119. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton P. A., Coffin J. M. Bacterial beta-galactosidase as a marker of Rous sarcoma virus gene expression and replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):281–290. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen R. B., Moustakas A., Hackett P. B. A mutation in the short 5'-proximal open reading frame on Rous sarcoma virus RNA alters virus production. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4787–4796. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4787-4796.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price J., Turner D., Cepko C. Lineage analysis in the vertebrate nervous system by retrovirus-mediated gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):156–160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugatsch T., Stacey D. W. Analysis by microinjection of the biological effects of site-directed mutagenesis in cloned avian leukosis viral DNAs. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):503–510. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.503-510.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson E., Bradley A., Kuehn M., Evans M. Germ-line transmission of genes introduced into cultured pluripotential cells by retroviral vector. Nature. 1986 Oct 2;323(6087):445–448. doi: 10.1038/323445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson H. L., Reinsch S. S., Shank P. R. Sequences near the 5' long terminal repeat of avian leukosis viruses determine the ability to induce osteopetrosis. J Virol. 1986 Jul;59(1):45–49. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.1.45-49.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddell A., Linial M. L., Groudine M. Tissue-specific lability and expression of avian leukosis virus long terminal repeat enhancer-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5660–5668. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salter D. W., Smith E. J., Hughes S. H., Wright S. E., Crittenden L. B. Transgenic chickens: insertion of retroviral genes into the chicken germ line. Virology. 1987 Mar;157(1):236–240. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90334-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savatier P., Bagnis C., Thoraval P., Poncet D., Belakebi M., Mallet F., Legras C., Cosset F. L., Thomas J. L., Chebloune Y. Generation of a helper cell line for packaging avian leukosis virus-based vectors. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):513–522. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.513-522.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schirm S., Moscovici G., Bishop J. M. A temperature-sensitive phenotype of avian myeloblastosis virus: determinants that influence the production of viral mRNAs. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):767–773. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.767-773.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorge J., Ricci W., Hughes S. H. cis-Acting RNA packaging locus in the 115-nucleotide direct repeat of Rous sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1983 Dec;48(3):667–675. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.3.667-675.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacey D. W., Kopchick J. J., Kahn M. The effects of transcriptional regulatory sequences introduced into a retroviral genome. DNA. 1986 Jun;5(3):195–202. doi: 10.1089/dna.1986.5.195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoker A. W., Bissell M. J. Development of avian sarcoma and leukosis virus-based vector-packaging cell lines. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):1008–1015. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.1008-1015.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoltzfus C. M., Chang L. J., Cripe T. P., Turek L. P. Efficient transformation by Prague A Rous sarcoma virus plasmid DNA requires the presence of cis-acting regions within the gag gene. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3401–3409. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3401-3409.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudol M., Lerner T. L., Hanafusa H. Polymerase-defective mutant of the Bryan high-titer strain of Rous sarcoma virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 11;14(5):2391–2405. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.5.2391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoraval P., Savatier P., Xiao J. H., Mallet F., Samarut J., Verdier G., Nigon V. Partial nucleotide sequence of the avian erythroblastosis virus (AEV ES4). Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9612–9612. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vennström B., Bishop J. M. Isolation and characterization of chicken DNA homologous to the two putative oncogenes of avian erythroblastosis virus. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90383-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vennström B., Fanshier L., Moscovici C., Bishop J. M. Molecular cloning of the avian erythroblastosis virus genome and recovery of oncogenic virus by transfection of chicken cells. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):575–585. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.575-585.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yew N. S., Choi H. R., Gallarda J. L., Engel J. D. Expression of cytoskeletal protein 4.1 during avian erythroid cellular maturation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1035–1039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenke M., Kahn P., Disela C., Vennström B., Leutz A., Keegan K., Hayman M. J., Choi H. R., Yew N., Engel J. D. v-erbA specifically suppresses transcription of the avian erythrocyte anion transporter (band 3) gene. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):107–119. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90535-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]