Abstract
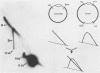
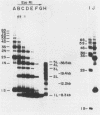
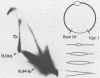
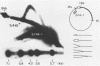
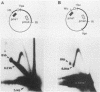
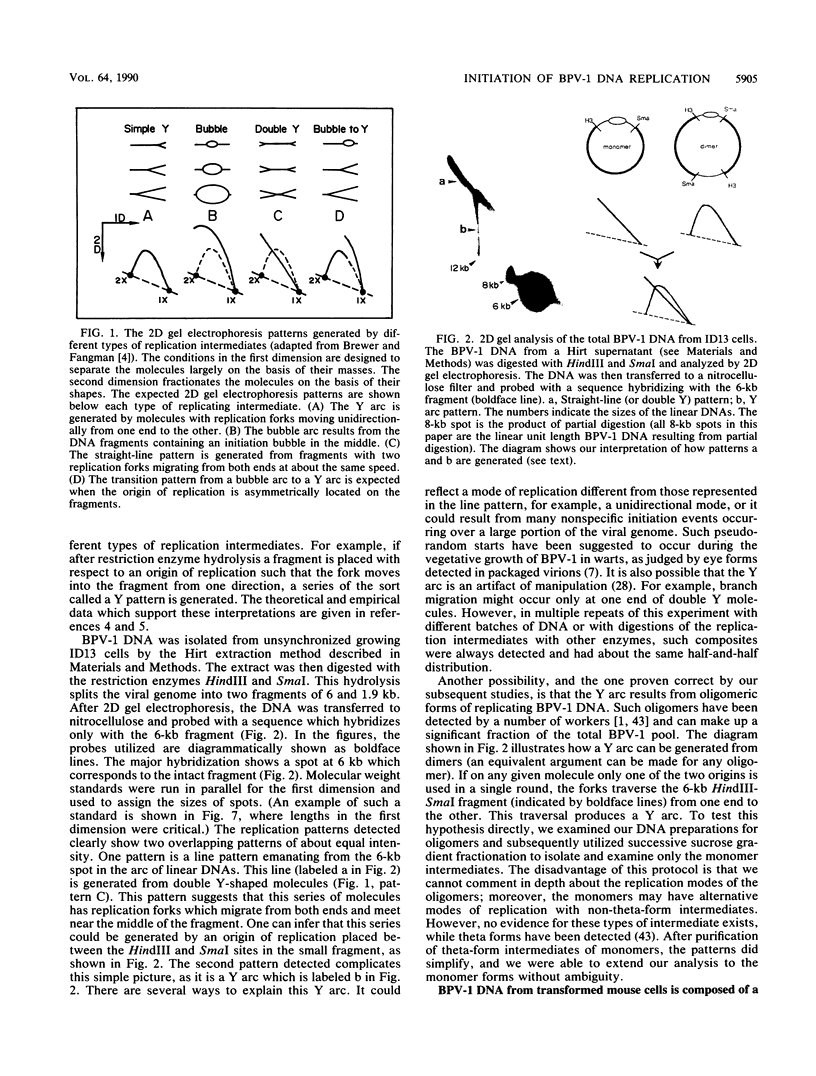
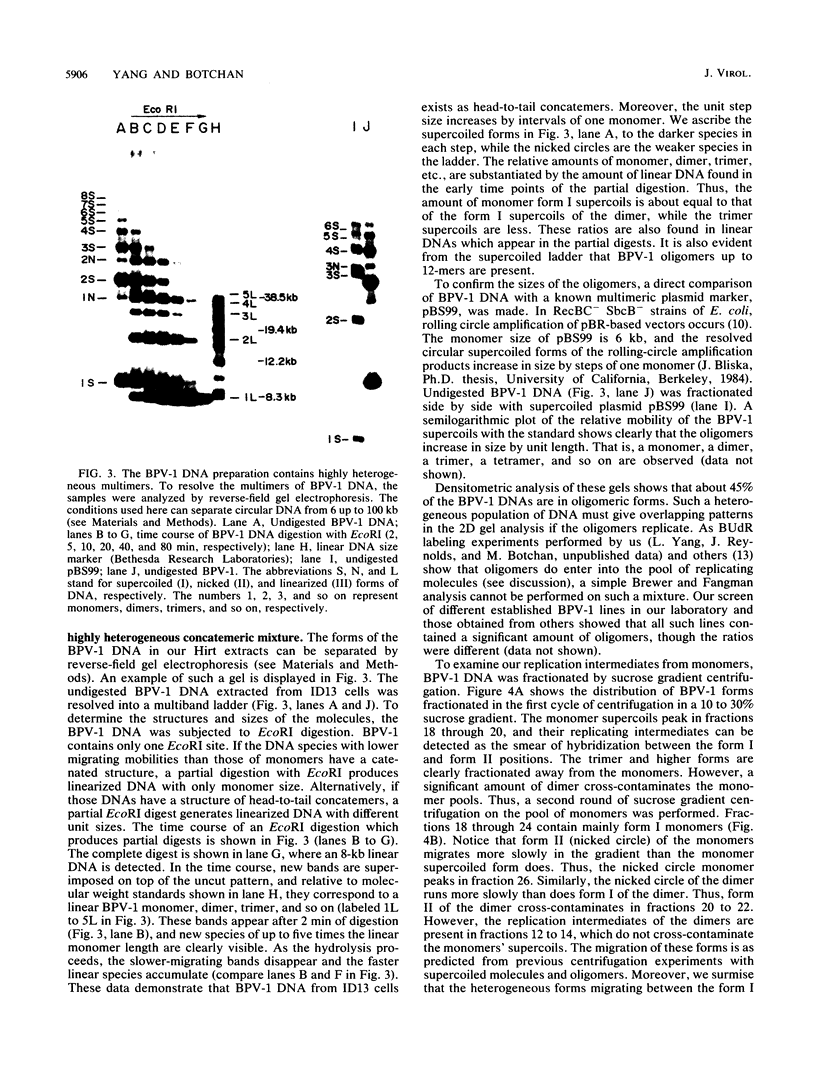
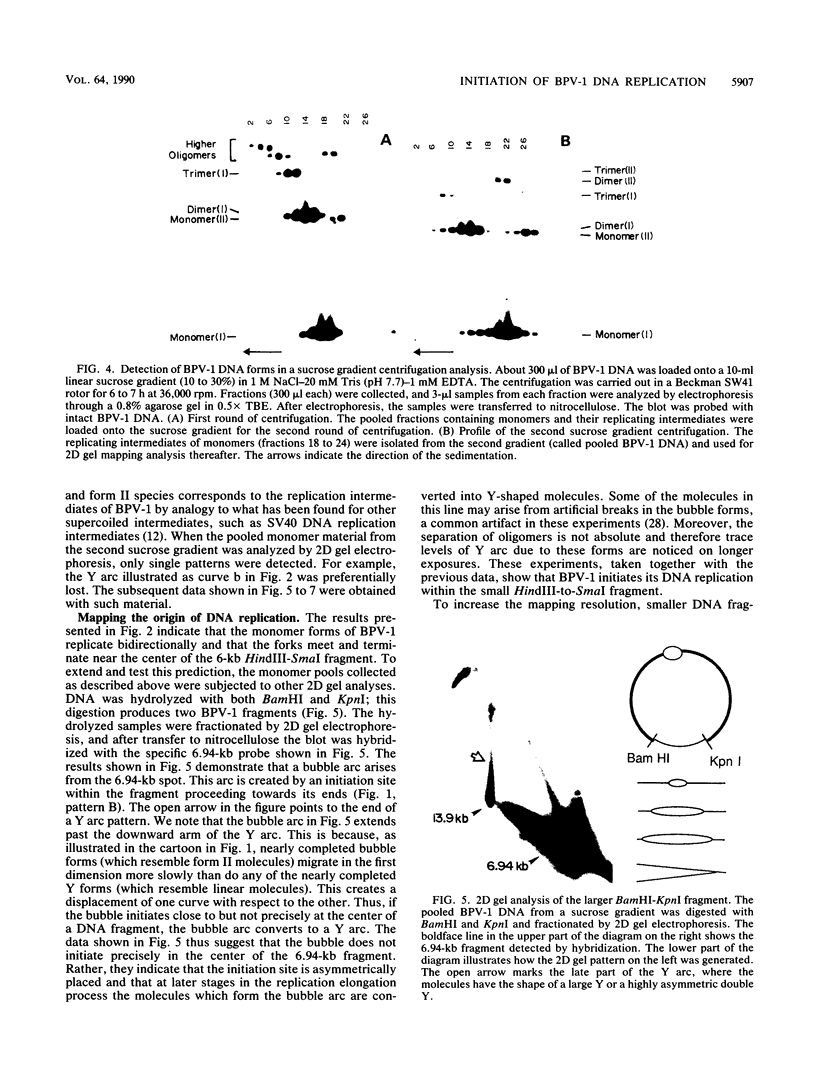
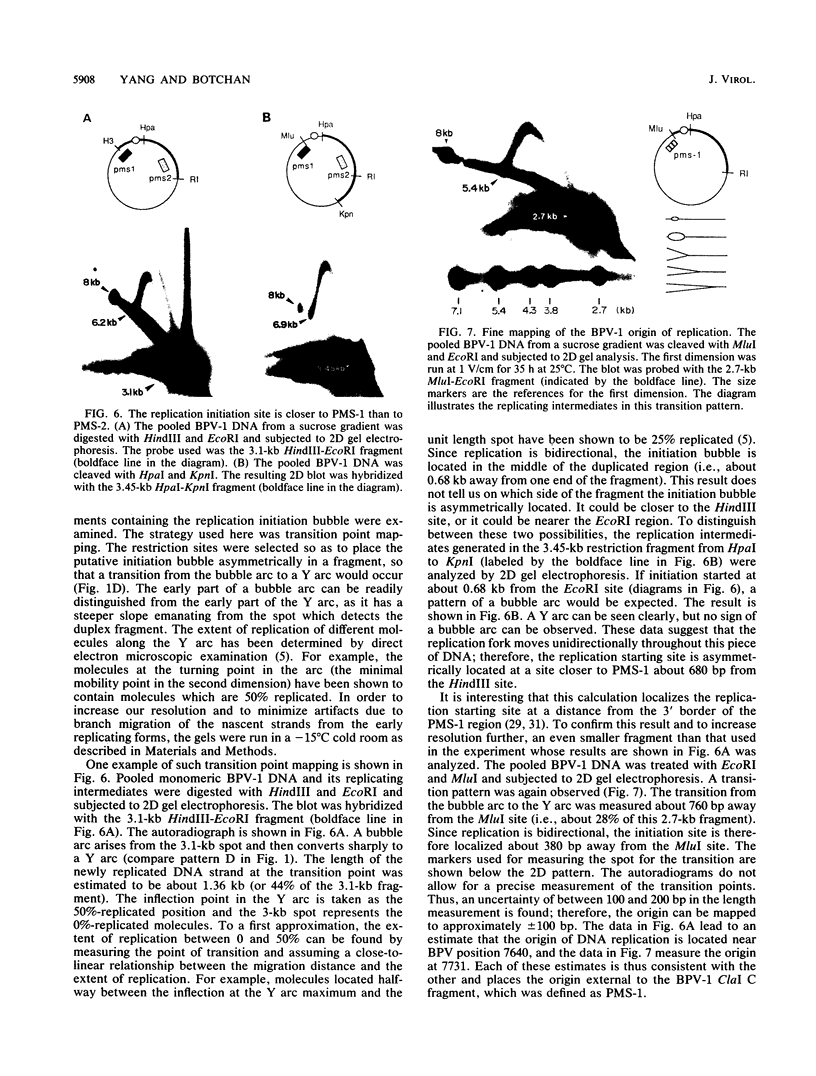
When bovine papillomavirus transforms cells in vitro, it maintains its genome as a multicopy nuclear plasmid. Plasmid DNA extracted from such transformed cells was analyzed by the two-dimensional gel electrophoresis technique of Brewer and Fangman (B. Brewer and W. Fangman, Cell 51:463-471, 1987). The replication intermediates detected in these assays were found to be the sums of the oligomeric and monomeric forms of the replicating plasmids. The multimeric DNAs were shown by field inversion gel electrophoresis and partial restriction digestion to be head-to-tail concatemers of the monomeric forms. Furthermore, the multimers progressed in size by steps of one monomer, indicating that they did not arise by replication segregation mistakes of the unit length, which would predict a ladder spaced by integrals of two monomers. To map the plasmid DNA replication origin, the replication intermediates of the monomers were isolated by successive sucrose gradient centrifugation and then examined by the two-dimensional gel electrophoresis method. The patterns detected show that bovine papillomavirus type 1 replicates in these cells bidirectionally and that one replication origin site in the viral genome is utilized. By employing several restriction enzymes and specific viral DNA probes to dissect the replication intermediates, we were able to map the origin of initiation site with some precision. The initiation site, which maps to bovine papillomavirus type 1 DNA position 7730 +/- 100 bp, places the origin within that region of the viral upstream regulatory region which contains the major cluster of transcription factor E2-binding sites, E2RE1. Thus, the actual viral plasmid origin of replication maps near, but outside, genetic elements previously shown to be important for plasmid maintenance.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allshire R. C., Bostock C. J. Structure of bovine papillomavirus type 1 DNA in a transformed mouse cell line. J Mol Biol. 1986 Mar 5;188(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90475-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Androphy E. J., Lowy D. R., Schiller J. T. Bovine papillomavirus E2 trans-activating gene product binds to specific sites in papillomavirus DNA. Nature. 1987 Jan 1;325(6099):70–73. doi: 10.1038/325070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg L., Lusky M., Stenlund A., Botchan M. R. Repression of bovine papilloma virus replication is mediated by a virally encoded trans-acting factor. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):753–762. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90351-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer B. J., Fangman W. L. The localization of replication origins on ARS plasmids in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):463–471. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90642-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockman W. W., Lee T. N., Nathans D. Characterization of cloned evolutionary variants of simian virus 40. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):119–127. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnett S., Zabielski J., Moreno-Lopez J., Pettersson U. Evidence for multiple vegetative DNA replication origins and alternative replication mechanisms of bovine papillomavirus type 1. J Mol Biol. 1989 Mar 5;206(1):239–244. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90537-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg M. D., Kelly T. J. Animal virus DNA replication. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:671–717. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clertant P., Seif I. A common function for polyoma virus large-T and papillomavirus E1 proteins? Nature. 1984 Sep 20;311(5983):276–279. doi: 10.1038/311276a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A., Clark A. J. Synthesis of linear plasmid multimers in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):327–335. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.327-335.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosa J. H. Three origins of replication are active in vivo in the R plasmid RSF1040. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11075–11077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMaio D., Settleman J. Bovine papillomavirus mutant temperature sensitive for transformation, replication and transactivation. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1197–1204. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02931.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert D. M., Cohen S. N. Bovine papilloma virus plasmids replicate randomly in mouse fibroblasts throughout S phase of the cell cycle. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):59–68. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90662-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S. P., Berg P. Structure and formation of circular dimers of simian virus 40 DNA. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):295–302. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.295-302.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand R. Eucaryotic DNA: organization of the genome for replication. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):317–325. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90001-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley-Nelson P., Androphy E. J., Lowy D. R., Schiller J. T. The specific DNA recognition sequence of the bovine papillomavirus E2 protein is an E2-dependent enhancer. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):525–531. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02841.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heck M. M., Spradling A. C. Multiple replication origins are used during Drosophila chorion gene amplification. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):903–914. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman J. A., Spotila L. D., Nawotka K. A., el-Assouli S. M., Davis L. R. The in vivo replication origin of the yeast 2 microns plasmid. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):473–481. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90643-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolter R., Helinski D. R. Plasmid R6K DNA replication. II. Direct nucleotide sequence repeats are required for an active gamma-origin. J Mol Biol. 1982 Oct 15;161(1):45–56. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90277-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. F., Baker C. C., Howley P. M. The genetics of bovine papillomavirus type 1. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:235–258. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.001315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster W. D., Olson C. Animal papillomaviruses. Microbiol Rev. 1982 Jun;46(2):191–207. doi: 10.1128/mr.46.2.191-207.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Harland R. M. Replication origins in the eucaryotic chromosome. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):283–284. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90316-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law M. F., Lowy D. R., Dvoretzky I., Howley P. M. Mouse cells transformed by bovine papillomavirus contain only extrachromosomal viral DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2727–2731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J., Kang H. S., Billheimer F. E. DNA replication in SV40 infected cells. I. Analysis of replicating SV40 DNA. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jun 14;50(2):549–568. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90211-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li R., Knight J., Bream G., Stenlund A., Botchan M. Specific recognition nucleotides and their DNA context determine the affinity of E2 protein for 17 binding sites in the BPV-1 genome. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):510–526. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linskens M. H., Huberman J. A. Ambiguities in results obtained with 2D gel replicon mapping techniques. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 11;18(3):647–652. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.3.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. R. A bovine papillomavirus type 1-encoded modulator function is dispensable for transient viral replication but is required for establishment of the stable plasmid state. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):729–742. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.729-742.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. R. Characterization of the bovine papilloma virus plasmid maintenance sequences. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):391–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90232-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. R. Transient replication of bovine papilloma virus type 1 plasmids: cis and trans requirements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3609–3613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mecsas J., Sugden B. Replication of plasmids derived from bovine papilloma virus type 1 and Epstein-Barr virus in cells in culture. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:87–108. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskaluk C., Bastia D. The E2 "gene" of bovine papillomavirus encodes an enhancer-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1215–1218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee S., Erickson H., Bastia D. Enhancer-origin interaction in plasmid R6K involves a DNA loop mediated by initiator protein. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):375–383. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80030-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives C. The replication functions of SV40 T antigen are regulated by phosphorylation. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):735–738. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90179-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schvartzman J. B., Adolph S., Martín-Parras L., Schildkraut C. L. Evidence that replication initiates at only some of the potential origins in each oligomeric form of bovine papillomavirus type 1 DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3078–3086. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalholz B. A., Lambert P. F., Yee C. L., Howley P. M. Bovine papillomavirus transcriptional regulation: localization of the E2-responsive elements of the long control region. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2128–2137. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2128-2137.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalholz B. A., Yang Y. C., Howley P. M. Transactivation of a bovine papilloma virus transcriptional regulatory element by the E2 gene product. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):183–191. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman B. Initiation of eukaryotic DNA replication in vitro. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:197–245. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.001213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun S., Thorner L., Lentz M., MacPherson P., Botchan M. Identification of a 68-kilodalton nuclear ATP-binding phosphoprotein encoded by bovine papillomavirus type 1. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):5093–5105. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.5093-5105.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorner L., Bucay N., Choe J., Botchan M. The product of the bovine papillomavirus type 1 modulator gene (M) is a phosphoprotein. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2474–2482. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2474-2482.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umek R. M., Linskens M. H., Kowalski D., Huberman J. A. New beginnings in studies of eukaryotic DNA replication origins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jan 23;1007(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(89)90123-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldeck W., Rösl F., Zentgraf H. Origin of replication in episomal bovine papilloma virus type 1 DNA isolated from transformed cells. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2173–2178. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02109.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang L., Jessee C. B., Lau K., Zhang H., Liu L. F. Template supercoiling during ATP-dependent DNA helix tracking: studies with simian virus 40 large tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6121–6125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]