Abstract
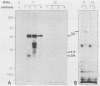
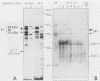
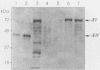
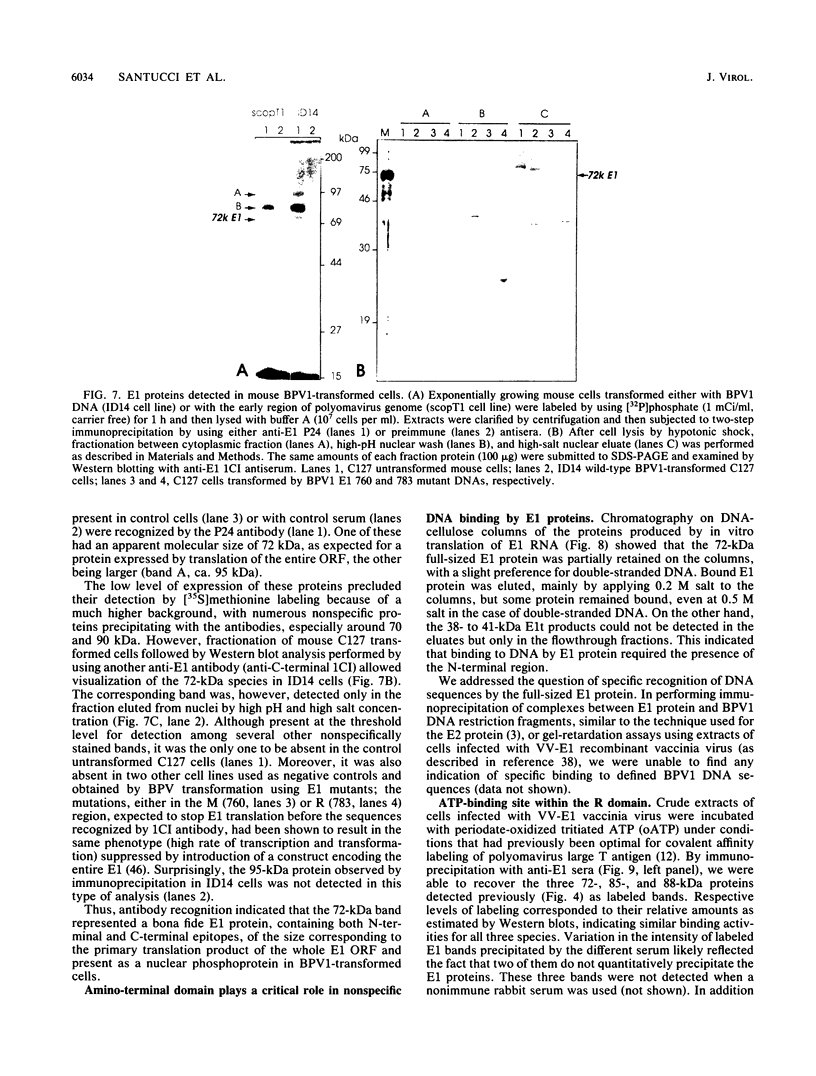
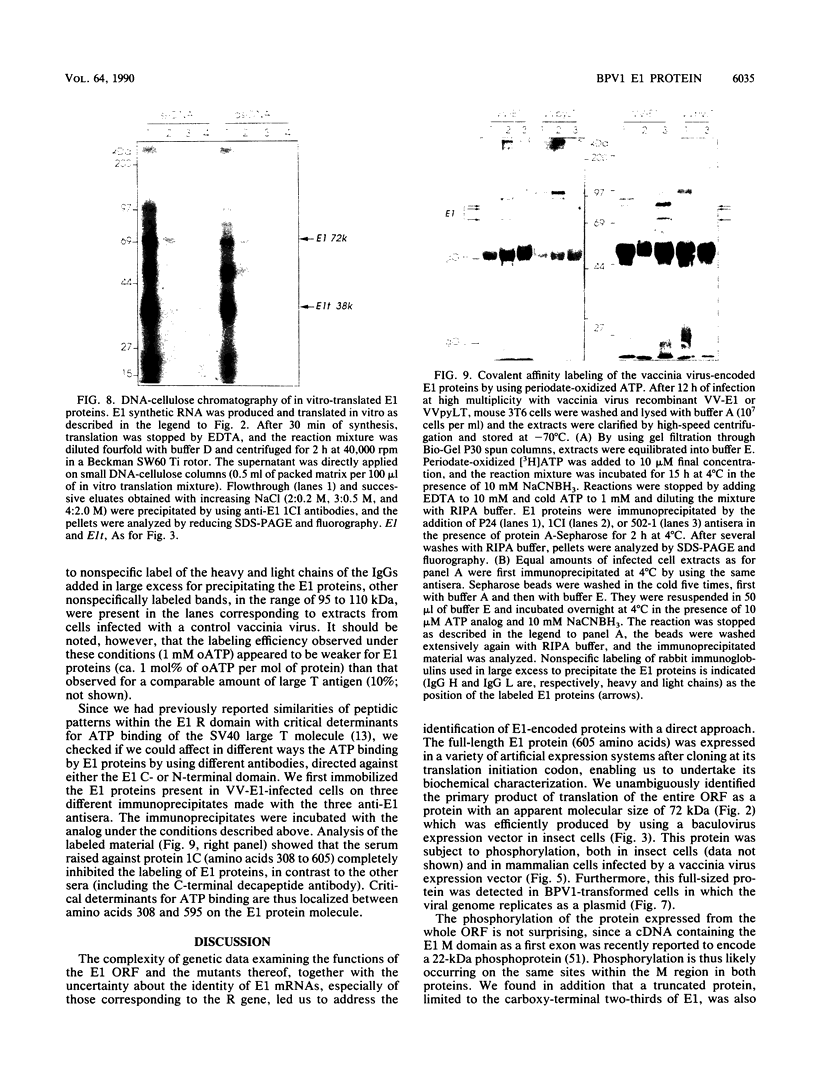
The E1 open reading frame (ORF) of bovine papillomavirus type 1 is required for the persistence of viral genomes as multicopy plasmid molecules in transformed rodent fibroblasts. E1 has been reported to contain two separate complementation groups (M and R, corresponding to N- and C-terminal domains, respectively) which regulate viral replication. However, E1 behaves as a single gene with respect to cell transformation and viral transcription. We examined the proteins translated from the entire ORF by using three antisera raised against E1 peptide or bacterial fusion proteins. The capacity of the whole ORF to encode a 72-kDa protein was demonstrated by translation of synthetic RNA in a reticulocyte lysate system, by microinjection of RNA into Xenopus oocytes, and by expression in recombinant baculoviruses and vaccinia viruses. In eucaryotic cells, this protein was found to be phosphorylated and targeted to the cell nucleus. In vitro translation also produced shorter peptides, containing only the E1 C-terminal domain, because of internal translation starts on the third and fourth methionine codons within E1 ORF. On the other hand, mammalian cells infected by vaccinia E1 recombinant virus contained additional larger E1 phosphoproteins (transient 85-kDa and stable 88-kDa species), likely representing processed forms of the 72-kDa species. The E1 72-kDa nuclear phosphoprotein was detected in bovine papillomavirus type 1-transformed cells. We report the biochemical characteristics of full-sized and truncated E1 proteins: (i) the C-terminal half of E1 ORF contains a phosphorylation site(s); (ii) the full-sized E1, but not the C-terminal protein, binds DNA, without indication for recognition of defined sequences, and critical determinants for this activity are likely confined to an N-terminal domain of the protein; (iii) covalent affinity labeling experiments performed on vaccinia virus-encoded E1 proteins with an ATP analog confirmed our previous observation of sequence similarities between the E1 C-terminal domain and the ATPase domain of simian virus 40 large T antigen.
Full text
PDF



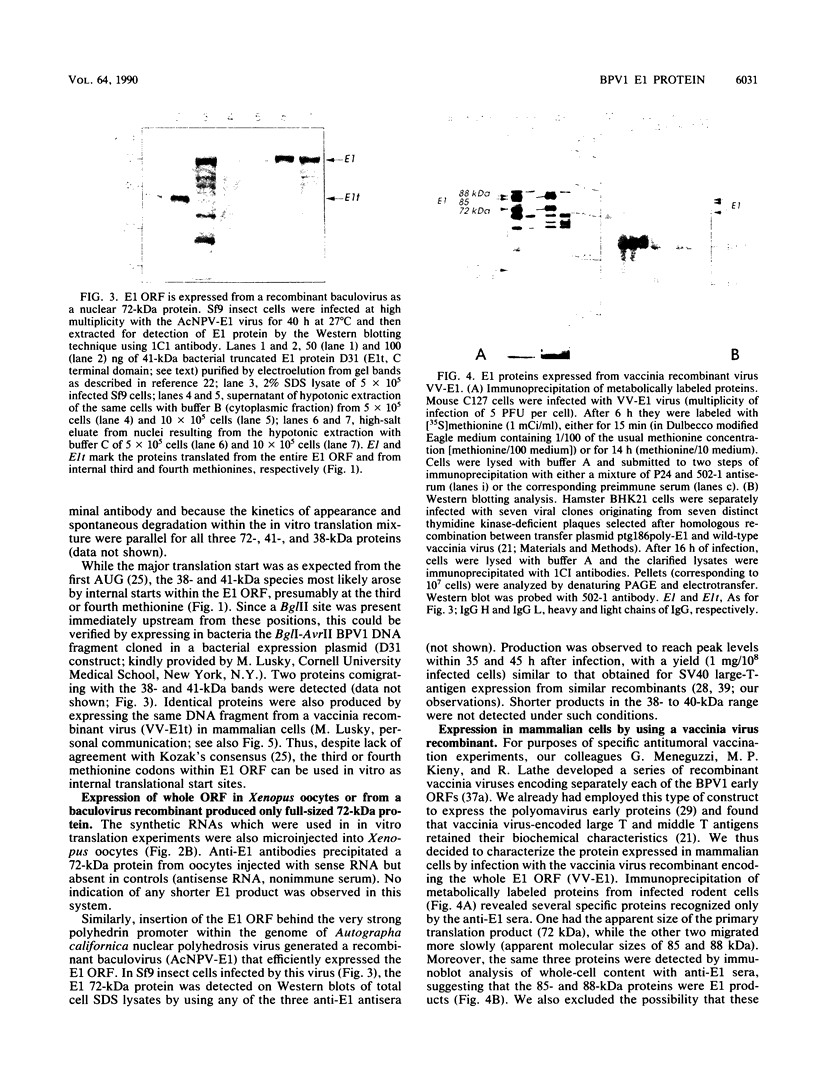

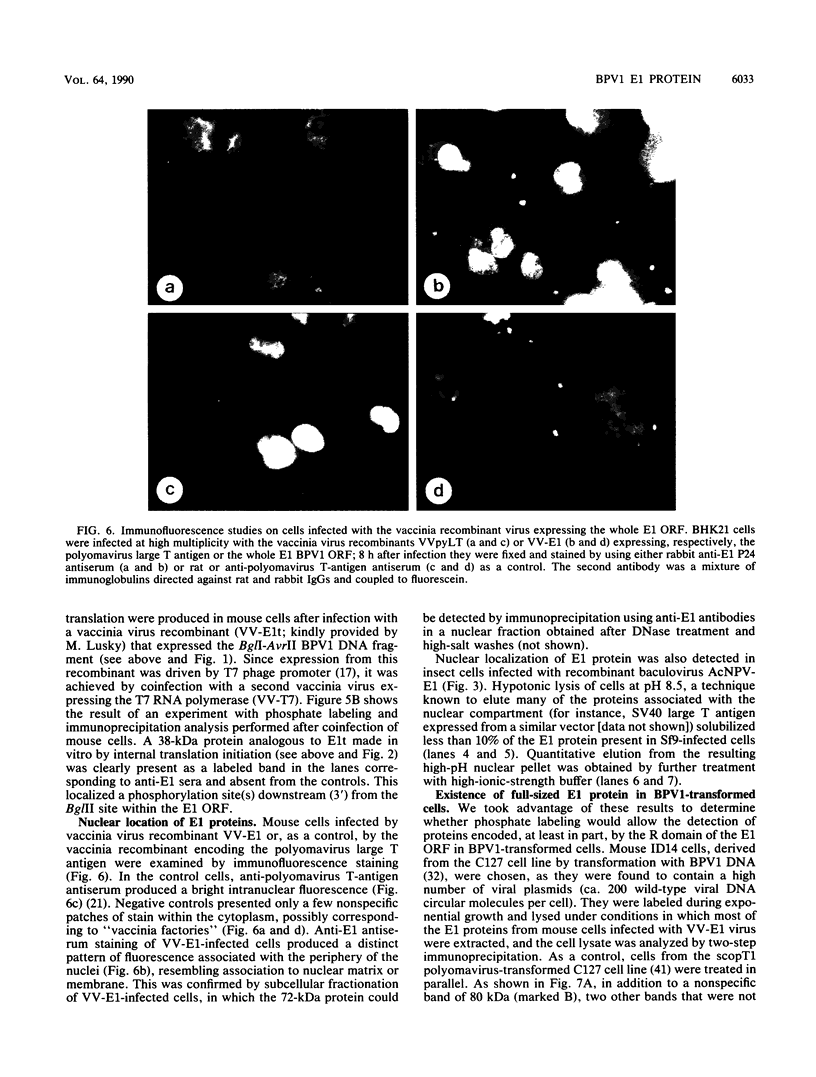




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahola H., Stenlund A., Moreno-López J., Pettersson U. Promoters and processing sites within the transforming region of bovine papillomavirus type 1. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2240–2244. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2240-2244.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Androphy E. J., Lowy D. R., Schiller J. T. Bovine papillomavirus E2 trans-activating gene product binds to specific sites in papillomavirus DNA. Nature. 1987 Jan 1;325(6099):70–73. doi: 10.1038/325070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Androphy E. J., Schiller J. T., Lowy D. R. Identification of the protein encoded by the E6 transforming gene of bovine papillomavirus. Science. 1985 Oct 25;230(4724):442–445. doi: 10.1126/science.2996134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg L., Lusky M., Stenlund A., Botchan M. R. Repression of bovine papilloma virus replication is mediated by a virally encoded trans-acting factor. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):753–762. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90351-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowiec J. A., Dean F. B., Bullock P. A., Hurwitz J. Binding and unwinding--how T antigen engages the SV40 origin of DNA replication. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):181–184. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90730-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley M. K., Smith T. F., Lathrop R. H., Livingston D. M., Webster T. A. Consensus topography in the ATP binding site of the simian virus 40 and polyomavirus large tumor antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4026–4030. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnett S., Moreno-Lopez J., Pettersson U. Messenger RNAs from the E1 region of bovine papillomavirus type 1 detected in virus-infected bovine cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):8607–8620. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.8607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Howley P. M., Levinson A. D., Seeburg P. H. The primary structure and genetic organization of the bovine papillomavirus type 1 genome. Nature. 1982 Oct 7;299(5883):529–534. doi: 10.1038/299529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choe J., Vaillancourt P., Stenlund A., Botchan M. Bovine papillomavirus type 1 encodes two forms of a transcriptional repressor: structural and functional analysis of new viral cDNAs. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1743–1755. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1743-1755.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clertant P., Cuzin F. Covalent affinity labeling by periodate-oxidized [alpha-32P]ATP of the large-T proteins of polyoma and SV40 viruses. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6300–6305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clertant P., Gaudray P., May E., Cuzin F. The nucleotide binding site detected by affinity labeling in the large T proteins of polyoma and SV40 viruses is distinct from their ATPase catalytic site. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15196–15203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clertant P., Seif I. A common function for polyoma virus large-T and papillomavirus E1 proteins? Nature. 1984 Sep 20;311(5983):276–279. doi: 10.1038/311276a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMaio D. Nonsense mutation in open reading frame E2 of bovine papillomavirus DNA. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):475–480. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.475-480.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMaio D., Settleman J. Bovine papillomavirus mutant temperature sensitive for transformation, replication and transactivation. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1197–1204. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02931.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Earl P. L., Moss B. Use of a hybrid vaccinia virus-T7 RNA polymerase system for expression of target genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2538–2544. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudray P., Clertant P., Cuzin F. ATP phosphohydrolase (ATPase) activity of a polyoma virus T antigen. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Aug;109(2):553–560. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04827.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert D. M., Cohen S. N. Bovine papilloma virus plasmids replicate randomly in mouse fibroblasts throughout S phase of the cell cycle. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):59–68. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90662-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groff D. E., Lancaster W. D. Genetic analysis of the 3' early region transformation and replication functions of bovine papillomavirus type 1. Virology. 1986 Apr 15;150(1):221–230. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90281-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guizani I., Kieny M. P., Lathe R., Clertant P. Characterization of polyoma virus early proteins expressed from vaccinia virus recombinants. Gene. 1988 Dec 15;73(1):163–173. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90322-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y. Polyoma virus-specific 55K protein isolated from plasma membrane of productively infected cells is virus-coded and important for cell transformation. Virology. 1979 Oct 15;98(1):261–266. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90545-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson S. P., Tjian R. O-glycosylation of eukaryotic transcription factors: implications for mechanisms of transcriptional regulation. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. F., Howley P. M. Bovine papillomavirus type 1 E1 replication-defective mutants are altered in their transcriptional regulation. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4009–4015. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4009-4015.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanford R. E. Expression of simian virus 40 T antigen in insect cells using a baculovirus expression vector. Virology. 1988 Nov;167(1):72–81. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90055-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathe R., Kieny M. P., Gerlinger P., Clertant P., Guizani I., Cuzin F., Chambon P. Tumour prevention and rejection with recombinant vaccinia. 1987 Apr 30-May 6Nature. 326(6116):878–880. doi: 10.1038/326878a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law M. F., Lowy D. R., Dvoretzky I., Howley P. M. Mouse cells transformed by bovine papillomavirus contain only extrachromosomal viral DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2727–2731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe P. N., Beechey R. B. Interactions between the mitochondrial adenosinetriphosphatase and periodate-oxidized adenosine 5'-triphosphate, an affinity label for adenosine 5'-triphosphate binding sites. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 17;21(17):4073–4082. doi: 10.1021/bi00260a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowy D. R., Dvoretzky I., Shober R., Law M. F., Engel L., Howley P. M. In vitro tumorigenic transformation by a defined sub-genomic fragment of bovine papilloma virus DNA. Nature. 1980 Sep 4;287(5777):72–74. doi: 10.1038/287072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow V. A., Summers M. D. High level expression of nonfused foreign genes with Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus expression vectors. Virology. 1989 May;170(1):31–39. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90348-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. R. A bovine papillomavirus type 1-encoded modulator function is dispensable for transient viral replication but is required for establishment of the stable plasmid state. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):729–742. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.729-742.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. R. Characterization of the bovine papilloma virus plasmid maintenance sequences. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):391–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90232-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. R. Genetic analysis of bovine papillomavirus type 1 trans-acting replication factors. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):955–965. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.955-965.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. R. Transient replication of bovine papilloma virus type 1 plasmids: cis and trans requirements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3609–3613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meneguzzi G., Kieny M. P., Lecocq J. P., Chambon P., Cuzin F., Lathe R. Vaccinia recombinants expressing early bovine papilloma virus (BPV1) proteins: retardation of BPV1 tumour development. Vaccine. 1990 Jun;8(3):199–204. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(90)90045-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meneguzzi G., Lathe R., Kieny M. P., Vogt N. The E2 trans-activating protein of bovine papillomavirus type 1 (BPV1) is serine-phosphorylated in vivo. Oncogene. 1989 Nov;4(11):1285–1290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy C. I., Weiner B., Bikel I., Piwnica-Worms H., Bradley M. K., Livingston D. M. Purification and functional properties of simian virus 40 large and small T antigens overproduced in insect cells. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2951–2959. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2951-2959.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabson M. S., Yee C., Yang Y. C., Howley P. M. Bovine papillomavirus type 1 3' early region transformation and plasmid maintenance functions. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):626–634. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.626-634.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rautmann G., Glaichenhaus N., Nahgashfar Z., Breathnach R., Rassoulzadegan M. Complementation of a tsa mutant and replication of a recombinant DNA carrying the viral ori region in mouse cells transformed by polyoma virus. Virology. 1982 Oct 30;122(2):306–317. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90230-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. M., Weintraub H. Cis-acting negative control of DNA replication in eukaryotic cells. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):397–404. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80032-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. M., Weintraub H. Negative control of DNA replication in composite SV40-bovine papilloma virus plasmids. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90350-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers S., Wells R., Rechsteiner M. Amino acid sequences common to rapidly degraded proteins: the PEST hypothesis. Science. 1986 Oct 17;234(4774):364–368. doi: 10.1126/science.2876518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarver N., Rabson M. S., Yang Y. C., Byrne J. C., Howley P. M. Localization and analysis of bovine papillomavirus type 1 transforming functions. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):377–388. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.377-388.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller J. T., Kleiner E., Androphy E. J., Lowy D. R., Pfister H. Identification of bovine papillomavirus E1 mutants with increased transforming and transcriptional activity. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1775–1782. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1775-1782.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt M. K., Mann K. Glycosylation of simian virus 40 T antigen and localization of glycosylated T antigen in the nuclear matrix. Virology. 1987 Feb;156(2):268–281. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90407-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalholz B. A., Yang Y. C., Howley P. M. Transactivation of a bovine papilloma virus transcriptional regulatory element by the E2 gene product. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):183–191. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamatos N. M., Chakrabarti S., Moss B., Hare J. D. Expression of polyomavirus virion proteins by a vaccinia virus vector: association of VP1 and VP2 with the nuclear framework. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):516–525. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.516-525.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorner L., Bucay N., Choe J., Botchan M. The product of the bovine papillomavirus type 1 modulator gene (M) is a phosphoprotein. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2474–2482. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2474-2482.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldeck W., Rösl F., Zentgraf H. Origin of replication in episomal bovine papilloma virus type 1 DNA isolated from transformed cells. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2173–2178. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02109.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R. S., Kohn K. W., Bonner W. M. Metabolism of ubiquitinated histones. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5916–5920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y. C., Okayama H., Howley P. M. Bovine papillomavirus contains multiple transforming genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1030–1034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]