Abstract
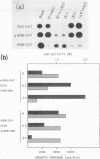
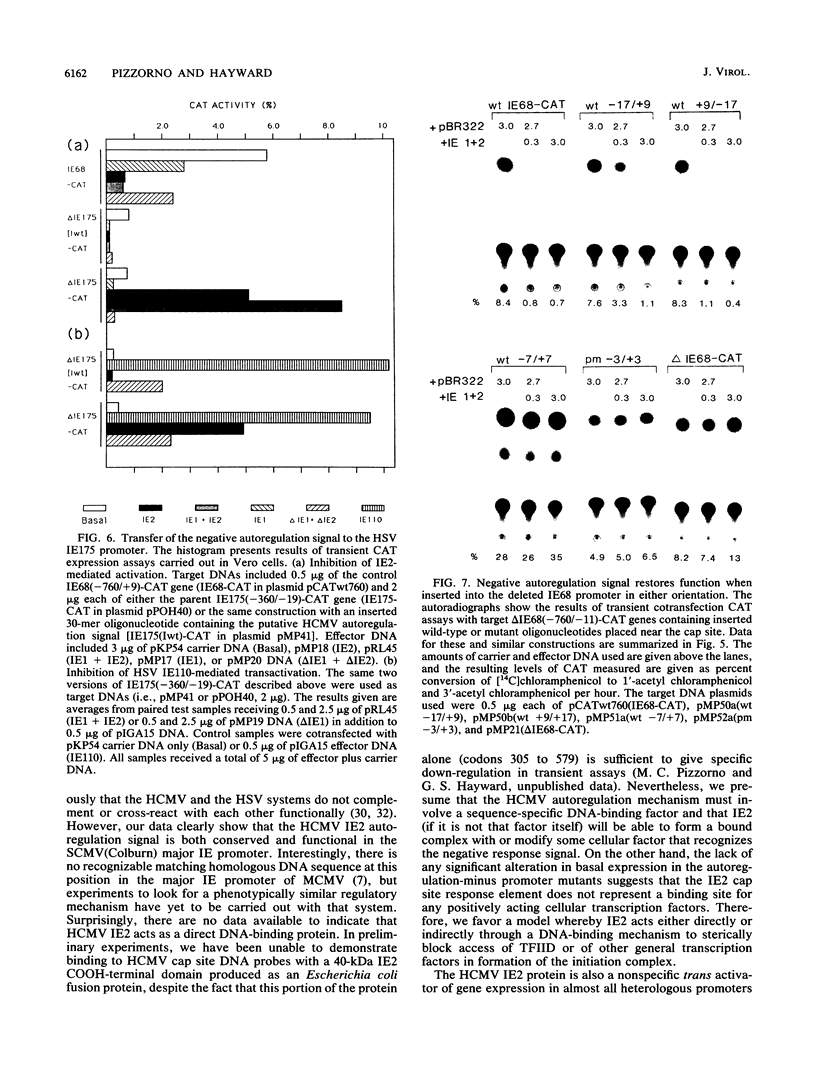
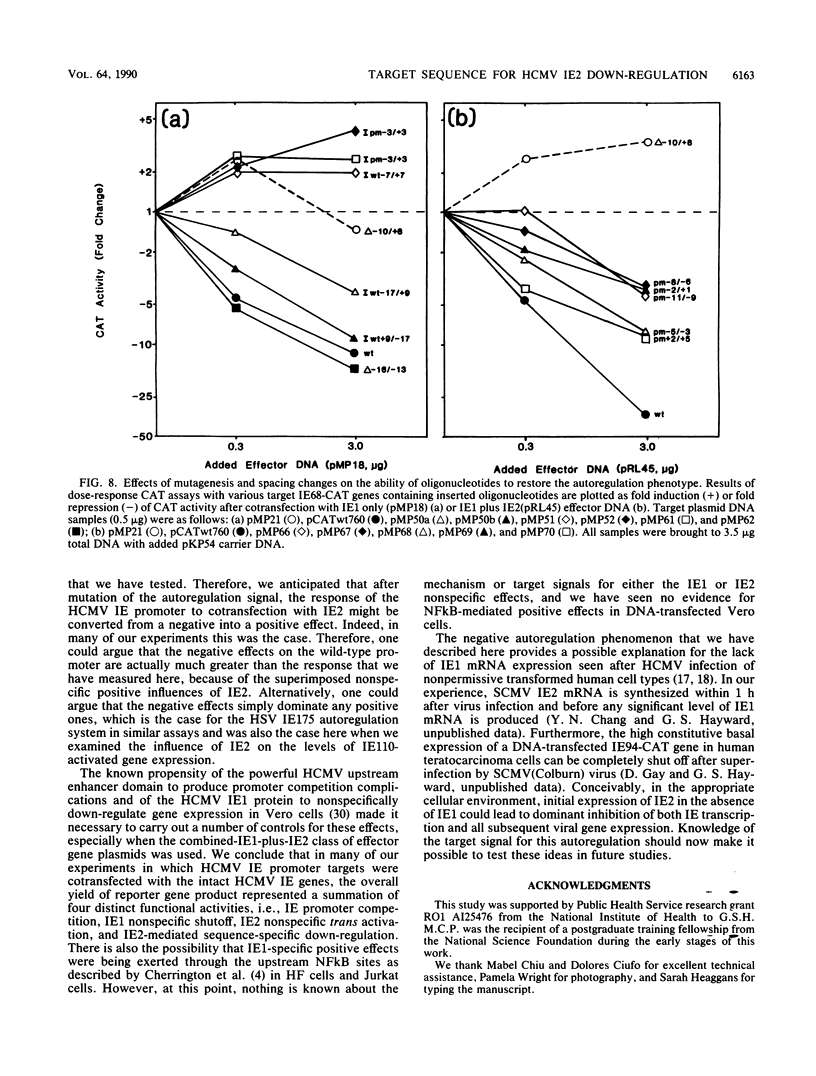
The 82-kDa IE2 protein of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) acts as both a powerful nonspecific trans activator of heterologous promoters and a negative autoregulator of HCMV immediate-early gene expression in transient assays. We show here that the highly specific down-regulation effect occurs in permissive diploid human fibroblast cells as well as in nonpermissive Vero cells and that the target sequences are conserved within the major immediate-early promoters of both HCMV and simian cytomegalovirus. The response sequences were localized between -67 and +30 in the simian cytomegalovirus IE94 promoter and upstream of position +9 in the HCMV IE68 promoter. Deletion of sequences downstream of -14 in a target IE68-CAT gene abolished the negative phenotype and resulted in a reporter gene that was stimulated instead of inhibited by cotransfection with IE2 effector DNA. Insertion of an oligonucleotide containing sequences from between -17 and +9 into the IE68-CAT deletion construction restored autoregulation in either orientation. Furthermore, this same oligonucleotide transferred the full down-regulation phenotype when inserted at +10 into the nonresponsive IE175 promoter from herpes simplex virus. Therefore, a specific response signal that acts at the DNA level must lie within these boundaries. Additional analysis with inserted oligonucleotides containing deletions or point mutations revealed that essential components of the signal lie between positions -12 and +5. Therefore, negative autoregulation by HCMV IE2 in DNA cotransfection systems resembles that for simian virus 40 large T antigen and herpes simplex virus IE175 by acting through a signal located near the cap site, but the target sequence itself bears no resemblance to those utilized in these other viral systems.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boshart M., Weber F., Jahn G., Dorsch-Häsler K., Fleckenstein B., Schaffner W. A very strong enhancer is located upstream of an immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):521–530. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. N., Crawford S., Stall J., Rawlins D. R., Jeang K. T., Hayward G. S. The palindromic series I repeats in the simian cytomegalovirus major immediate-early promoter behave as both strong basal enhancers and cyclic AMP response elements. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):264–277. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.264-277.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherrington J. M., Mocarski E. S. Human cytomegalovirus ie1 transactivates the alpha promoter-enhancer via an 18-base-pair repeat element. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1435–1440. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1435-1440.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. G., Kenney S. C., Kamine J., Pagano J. S., Huang E. S. Immediate-early gene region of human cytomegalovirus trans-activates the promoter of human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8642–8646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depto A. S., Stenberg R. M. Regulated expression of the human cytomegalovirus pp65 gene: octamer sequence in the promoter is required for activation by viral gene products. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1232–1238. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1232-1238.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsch-Häsler K., Keil G. M., Weber F., Jasin M., Schaffner W., Koszinowski U. H. A long and complex enhancer activates transcription of the gene coding for the highly abundant immediate early mRNA in murine cytomegalovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8325–8329. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghazal P., Lubon H., Fleckenstein B., Hennighausen L. Binding of transcription factors and creation of a large nucleoprotein complex on the human cytomegalovirus enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3658–3662. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermiston T. W., Malone C. L., Witte P. R., Stinski M. F. Identification and characterization of the human cytomegalovirus immediate-early region 2 gene that stimulates gene expression from an inducible promoter. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3214–3221. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3214-3221.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Monick M. M., Liu B., Stinski M. F. The promoter-regulatory region of the major immediate-early gene of human cytomegalovirus responds to T-lymphocyte stimulation and contains functional cyclic AMP-response elements. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):3026–3033. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.3026-3033.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeang K. T., Chin G., Hayward G. S. Characterization of cytomegalovirus immediate-early genes. I. Nonpermissive rodent cells overproduce the IE94K protein form CMV (Colburn). Virology. 1982 Sep;121(2):393–403. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeang K. T., Cho M. S., Hayward G. S. Abundant constitutive expression of the immediate-early 94K protein from cytomegalovirus (Colburn) in a DNA-transfected mouse cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):2214–2223. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.2214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeang K. T., Gibson W. A cycloheximide-enhanced protein in cytomegalovirus-infected cells. Virology. 1980 Dec;107(2):362–374. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90304-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeang K. T., Rawlins D. R., Rosenfeld P. J., Shero J. H., Kelly T. J., Hayward G. S. Multiple tandemly repeated binding sites for cellular nuclear factor 1 that surround the major immediate-early promoters of simian and human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1559–1570. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1559-1570.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaFemina R. L., Hayward G. S. Replicative forms of human cytomegalovirus DNA with joined termini are found in permissively infected human cells but not in non-permissive Balb/c-3T3 mouse cells. J Gen Virol. 1983 Feb;64(Pt 2):373–389. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-2-373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaFemina R., Hayward G. S. Constitutive and retinoic acid-inducible expression of cytomegalovirus immediate-early genes in human teratocarcinoma cells. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):434–440. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.434-440.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafemina R. L., Hayward G. S. Differences in cell-type-specific blocks to immediate early gene expression and DNA replication of human, simian and murine cytomegalovirus. J Gen Virol. 1988 Feb;69(Pt 2):355–374. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-2-355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafemina R. L., Pizzorno M. C., Mosca J. D., Hayward G. S. Expression of the acidic nuclear immediate-early protein (IE1) of human cytomegalovirus in stable cell lines and its preferential association with metaphase chromosomes. Virology. 1989 Oct;172(2):584–600. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90201-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Khoury G., Gorman C., Howard B., Gruss P. Host-specific activation of transcription by tandem repeats from simian virus 40 and Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6453–6457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markovitz D. M., Kenney S., Kamine J., Smith M. S., Davis M., Huang E. S., Rosen C., Pagano J. S. Disparate effects of two herpesvirus [corrected] immediate-early gene trans-activators on the HIV-1 LTR. Virology. 1989 Dec;173(2):750–754. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90591-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Wang C., Tjian R. Positive and negative regulation of transcription in vitro: enhancer-binding protein AP-2 is inhibited by SV40 T antigen. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):847–861. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90512-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosca J. D., Bednarik D. P., Raj N. B., Rosen C. A., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A., Hayward G. S., Pitha P. M. Activation of human immunodeficiency virus by herpesvirus infection: identification of a region within the long terminal repeat that responds to a trans-acting factor encoded by herpes simplex virus 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7408–7412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosca J. D., Jeang K. T., Pitha P. M., Hayward G. S. Novel induction by herpes simplex virus of hybrid interferon gene transcripts driven by the strong cytomegalovirus IE94 promoter. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):819–828. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.819-828.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Comparison of upstream sequence requirements for positive and negative regulation of a herpes simplex virus immediate-early gene by three virus-encoded trans-acting factors. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):190–199. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.190-199.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Evidence for a direct role for both the 175,000- and 110,000-molecular-weight immediate-early proteins of herpes simplex virus in the transactivation of delayed-early promoters. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):751–760. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.751-760.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Expression of recombinant genes containing herpes simplex virus delayed-early and immediate-early regulatory regions and trans activation by herpesvirus infection. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):522–531. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.522-531.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Three trans-acting regulatory proteins of herpes simplex virus modulate immediate-early gene expression in a pathway involving positive and negative feedback regulation. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):723–733. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.723-733.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzorno M. C., O'Hare P., Sha L., LaFemina R. L., Hayward G. S. trans-activation and autoregulation of gene expression by the immediate-early region 2 gene products of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1167–1179. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1167-1179.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rio D. C., Tjian R. SV40 T antigen binding site mutations that affect autoregulation. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1227–1240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90305-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M. S., Boundy A., O'Hare P., Pizzorno M. C., Ciufo D. M., Hayward G. S. Direct correlation between a negative autoregulatory response element at the cap site of the herpes simplex virus type 1 IE175 (alpha 4) promoter and a specific binding site for the IE175 (ICP4) protein. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4307–4320. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4307-4320.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. J., Tevethia M. J. Identification of a human cytomegalovirus virus DNA segment that complements an adenovirus 5 immediate early mutant. Virology. 1986 Jun;151(2):329–338. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90053-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staprans S. I., Rabert D. K., Spector D. H. Identification of sequence requirements and trans-acting functions necessary for regulated expression of a human cytomegalovirus early gene. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3463–3473. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3463-3473.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Depto A. S., Fortney J., Nelson J. A. Regulated expression of early and late RNAs and proteins from the human cytomegalovirus immediate-early gene region. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2699–2708. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2699-2708.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Stinski M. F. Autoregulation of the human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early gene. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):676–682. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.676-682.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Witte P. R., Stinski M. F. Multiple spliced and unspliced transcripts from human cytomegalovirus immediate-early region 2 and evidence for a common initiation site within immediate-early region 1. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):665–675. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.665-675.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenlund A., Botchan M. R. The E2 trans-activator can act as a repressor by interfering with a cellular transcription factor. Genes Dev. 1990 Jan;4(1):123–136. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.1.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F., Roehr T. J. Activation of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus by cis-acting elements in the promoter-regulatory sequence and by virus-specific trans-acting components. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):431–441. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.431-441.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F., Thomsen D. R., Stenberg R. M., Goldstein L. C. Organization and expression of the immediate early genes of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):1–14. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.1-14.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen D. R., Stenberg R. M., Goins W. F., Stinski M. F. Promoter-regulatory region of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):659–663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]