Abstract
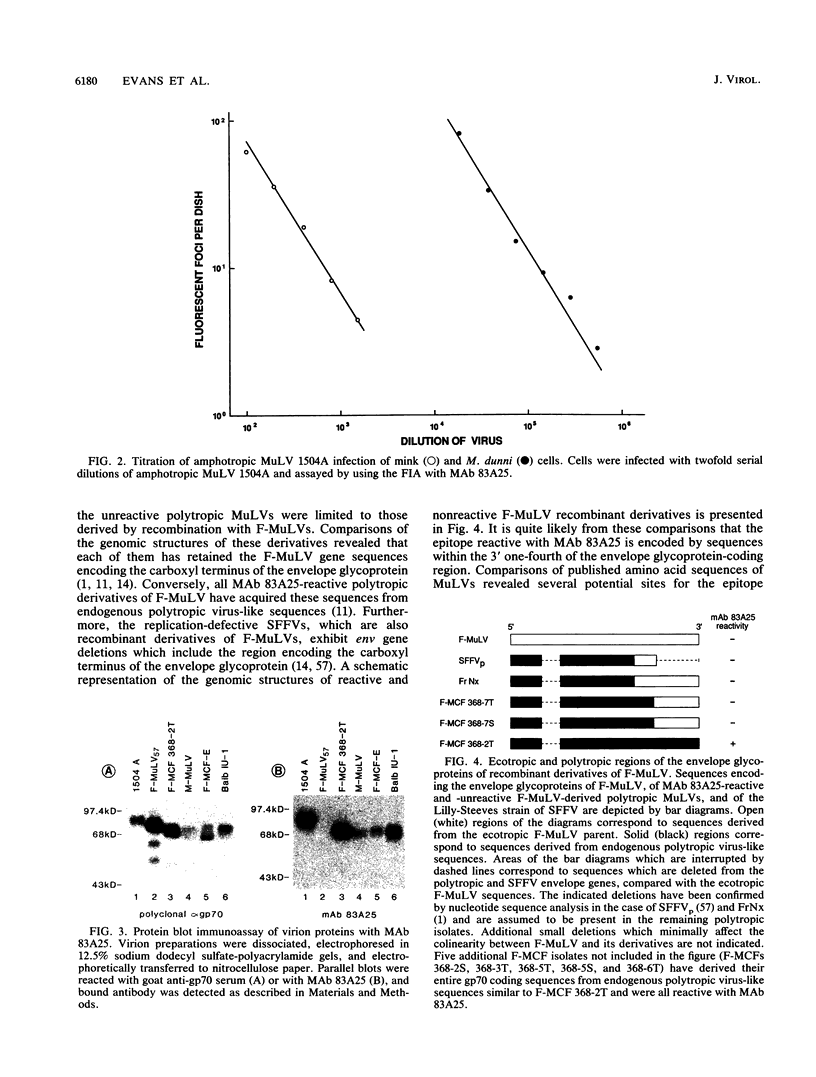
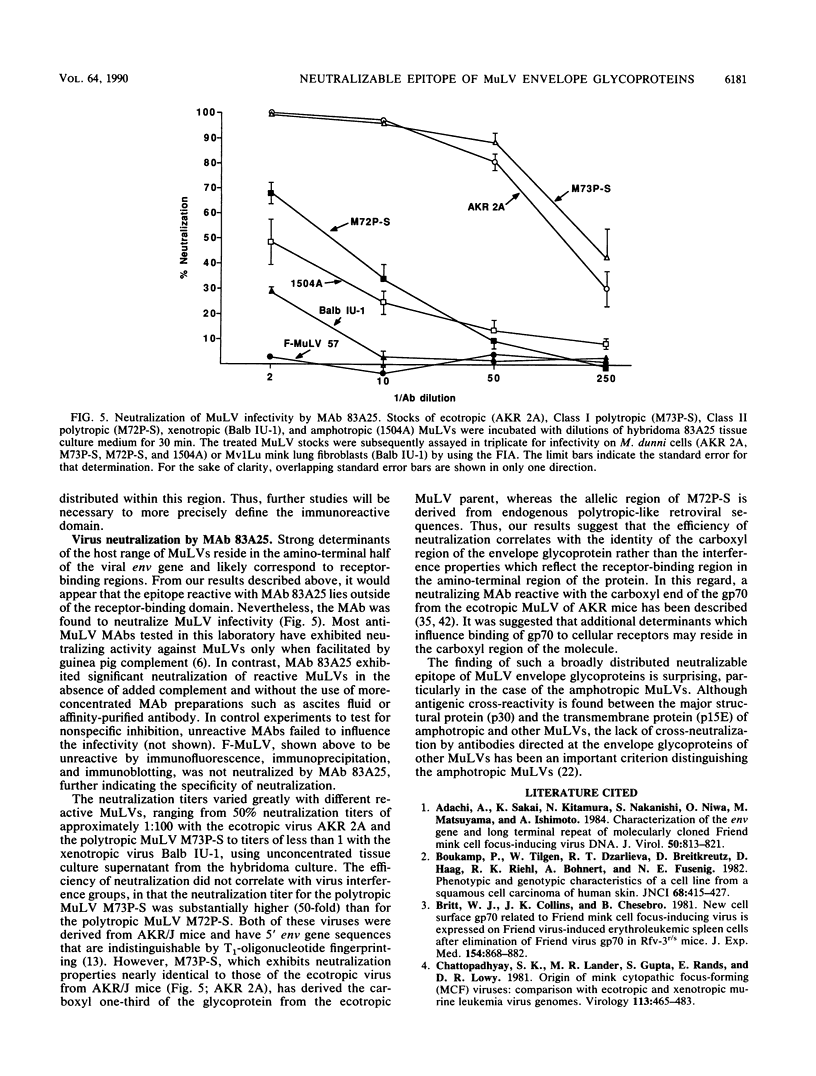
An epitope common to all classes of murine leukemia viruses (MuLVs) was detected by reactivity of MuLVs with a rat monoclonal antibody (MAb) termed 83A25. The antibody is of the immunoglobulin G2a isotype and was derived after fusion of NS-1 myeloma cells with spleen cells from a Fischer rat immunized with a Friend polytropic MuLV. The antibody reacted with nearly all members of the ecotropic, polytropic, xenotropic, and amphotropic classes of MuLVs. Unreactive viruses were limited to the Friend ecotropic MuLV, Rauscher MuLV, and certain recombinant derivatives of Friend ecotropic MuLV. The presence of an epitope common to nearly all MuLVs facilitated a direct quantitative focal immunofluorescence assay for MuLVs, including the amphotropic MuLVs for which no direct assay has been previously available. Previously described MAbs which react with all classes of MuLVs have been limited to those which react with virion core or transmembrane proteins. In contrast, protein immunoblot and immunoprecipitation analyses established that the epitope reactive with MAb 83A25 resides in the envelope glycoproteins of the viruses. Structural comparisons of reactive and nonreactive Friend polytropic viruses localized the epitope near the carboxyl terminus of the glycoprotein. The epitope served as a target for neutralization of all classes of MuLV with MAb 83A25. The efficiency of neutralization varied with different MuLV isolates but did not correlate with MuLV interference groups.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi A., Sakai K., Kitamura N., Nakanishi S., Niwa O., Matsuyama M., Ishimoto A. Characterization of the env gene and long terminal repeat of molecularly cloned Friend mink cell focus-inducing virus DNA. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):813–821. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.813-821.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boukamp P., Tilgen W., Dzarlieva R. T., Breitkreutz D., Haag D., Riehl R. K., Bohnert A., Fusenig N. E. Phenotypic and genotypic characteristics of a cell line from a squamous cell carcinoma of human skin. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1982 Mar;68(3):415–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britt W. J., Collins J. K., Chesebro B. New cell surface gp70 related to Friend mink cell focus-inducing virus is expressed on Friend virus-induced erythroleukemic spleen cells after elimination of ecotropic Friend virus gp70 in Rfv-3r/s mice. J Exp Med. 1981 Sep 1;154(3):868–882. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.3.868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Lander M. R., Gupta S., Rands E., Lowy D. R. Origin of mink cytopathic focus-forming (MCF) viruses:comparison with ecotropic and xenotropic murine leukemia virus genomes. Virology. 1981 Sep;113(2):465–483. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Britt W., Evans L., Wehrly K., Nishio J., Cloyd M. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies reactive with murine leukemia viruses: use in analysis of strains of friend MCF and Friend ecotropic murine leukemia virus. Virology. 1983 May;127(1):134–148. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90378-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Wehrly K., Cloyd M., Britt W., Portis J., Collins J., Nishio J. Characterization of mouse monoclonal antibodies specific for Friend murine leukemia virus-induced erythroleukemia cells: friend-specific and FMR-specific antigens. Virology. 1981 Jul 15;112(1):131–144. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90619-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Wehrly K., Nishio J., Evans L. Leukemia induction by a new strain of Friend mink cell focus-inducing virus: synergistic effect of Friend ecotropic murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):63–70. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.63-70.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloyd M. W., Chesebro B., Portis J. L., Weir M. MCF-specific murine monoclonal antibodies made against AKR-247 MCF virus recognize a unique determinant associated with the gp70-p-15(E) complex. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):1112–1117. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.1112-1117.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloyd M. W., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Cell-surface antigens associated with recombinant mink cell focus-inducing murine leukemia viruses. J Exp Med. 1979 Mar 1;149(3):702–712. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.3.702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloyd M. W., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Lymphomagenicity of recombinant mink cell focus-inducing murine leukemia viruses. J Exp Med. 1980 Mar 1;151(3):542–552. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.3.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L. H., Cloyd M. W. Friend and Moloney murine leukemia viruses specifically recombine with different endogenous retroviral sequences to generate mink cell focus-forming viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):459–463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L. H., Cloyd M. W. Generation of mink cell focus-forming viruses by Friend murine leukemia virus: recombination with specific endogenous proviral sequences. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):772–781. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.772-781.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L. H., Malik F. G. Class II polytropic murine leukemia viruses (MuLVs) of AKR/J mice: possible role in the generation of class I oncogenic polytropic MuLVs. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):1882–1892. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.1882-1892.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L., Nunn M., Duesberg P. H., Troxler D., Scolnick E. RNAs of defective and nondefective components of Friend anemia and polycythemia virus strains identified and compared. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 2):823–835. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEND C. Cell-free transmission in adult Swiss mice of a disease having the character of a leukemia. J Exp Med. 1957 Apr 1;105(4):307–318. doi: 10.1084/jem.105.4.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischinger P. J., Nomura S., Bolognesi D. P. A novel murine oncornavirus with dual eco- and xenotropic properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):5150–5155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.5150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geering G., Old L. J., Boyse E. A. Antigens of leukemias induced by naturally occurring murine leukemia virus: their relation to the antigens of gross virus and other murine leukemia viruses. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):753–772. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregoriades A., Old L. J. Isolation and some characteristics of a group-specific antigen of the murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1969 Feb;37(2):189–202. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90198-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Capps W. I., Huebner R. J. Complement fixation and tissue culture assays for mouse leukemia viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 May;53(5):931–938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.5.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Capps W. I., Huebner R. J. Isolation of naturally occurring viruses of the murine leukemia virus group in tissue culture. J Virol. 1969 Feb;3(2):126–132. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.2.126-132.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Clonal cells lines from a feral mouse embryo which lack host-range restrictions for murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1975 May;65(1):128–134. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Naturally occurring murine leukemia viruses in wild mice: characterization of a new "amphotropic" class. J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):19–25. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.19-25.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Wolford N. K., Old L. J., Rowe W. P. A new class of murine leukemia virus associated with development of spontaneous lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):789–792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson I. C., Lieber M. M., Todaro G. J. Mink cell line Mv 1 Lu (CCL 64). Focus formation and the generation of "nonproducer" transformed cell lines with murine and feline sarcoma viruses. Virology. 1974 Jul;60(1):282–287. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90386-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Derivation of specific antibody-producing tissue culture and tumor lines by cell fusion. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Jul;6(7):511–519. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander M. R., Chattopadhyay S. K. A Mus dunni cell line that lacks sequences closely related to endogenous murine leukemia viruses and can be infected by ectropic, amphotropic, xenotropic, and mink cell focus-forming viruses. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):695–698. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.695-698.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A., Kazan P., Varnier O., Kleiman H. Murine xenotropic type C viruses I. Distribution and further characterization of the virus in NZB mice. J Virol. 1975 Oct;16(4):844–853. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.4.844-853.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lostrom M. E., Stone M. R., Tam M., Burnette W. N., Pinter A., Nowinski R. C. Monoclonal antibodies against murine leukemia viruses: identification of six antigenic determinants on the p 15(E) and gp70 envelope proteins. Virology. 1979 Oct 30;98(2):336–350. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90557-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathieu-Mahul D., Heard J. M., Fichelson S., Gisselbrecht S., Sola B., Larsen C. J. Viral expression in two myelomonocytic cell lines obtained from long-term bone marrow culture infected with the Friend polycythemia-inducing virus (FV-P). Virology. 1982 May;119(1):59–67. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90065-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAtee F. J., Portis J. L. Monoclonal antibodies specific for wild mouse neurotropic retrovirus: detection of comparable levels of virus replication in mouse strains susceptible and resistant to paralytic disease. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):1018–1022. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.1018-1022.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison R. P., Lyng K., Caldwell H. D. Chlamydial disease pathogenesis. Ocular hypersensitivity elicited by a genus-specific 57-kD protein. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):663–675. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowinski R. C., Lostrom M. E., Tam M. R., Stone M. R., Burnette W. N. The isolation of hybrid cell lines producing monoclonal antibodies against the p15(E) protein of ecotropic murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1979 Feb;93(1):111–126. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90280-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowinski R. C., Pickering R., O'Donnell P. V., Pinter A., Hammerling U. Selective neutralization of ecotropic murine leukemia virus by monoclonal antibodies: localization of a site on the gp70 protein associated with ecotropism. Virology. 1981 May;111(1):84–92. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90655-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell P. V., Stockert E. Induction of GIX antigen and gross cell surface antigen after infection by ecotropic and xenotropic murine leukemia viruses in vitro. J Virol. 1976 Dec;20(3):545–554. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.3.545-554.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obata Y., Ikeda H., Stockert E., Boyse E. A. Relation of GIX antigen of thymocytes to envelope glycoprotein of murine leukemia virus. J Exp Med. 1975 Jan 1;141(1):188–197. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.1.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obata Y., Stockert E., DeLeo A. B., O'Donnell P. V., Snyder H. W., Jr, Old L. J. A cell surface antigen of the mouse related to xenotropic MuLv defined by naturally occurring antibody and monoclonal antibody. Relation to Gix G(rada1), G(aksl2) systems of MuLV-related antigens. J Exp Med. 1981 Sep 1;154(3):659–675. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.3.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliff A. I., Hager G. L., Chang E. H., Scolnick E. M., Chan H. W., Lowy D. R. Transfection of molecularly cloned Friend murine leukemia virus DNA yields a highly leukemogenic helper-independent type C virus. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):475–486. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.475-486.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oroszlan S., Fisher C. L., Stanley T. B., Gilden R. V. Proteins of the murine C-type RNA tumour viruses: isolation of a group-specific antigen by isoelectric focusing. J Gen Virol. 1970 Jul;8(1):1–10. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-8-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostertag W., Pragnell I. B. Changes in genome composition of the Friend virus complex in erythroleukemia cells during the course of differentiation induced by dimethyl sulfoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3278–3282. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinter A., Honnen W. J., Tung J. S., O'Donnell P. V., Hämmerling U. Structural domains of endogenous murine leukemia virus gp70s containing specific antigenic determinants defined by monoclonal antibodies. Virology. 1982 Jan 30;116(2):499–516. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90143-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portis J. L., McAtee F. J., Cloyd M. W. Monoclonal antibodies to xenotropic and MCF murine leukemia viruses derived during the graft-versus-host reaction. Virology. 1982 Apr 15;118(1):181–190. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90331-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portis J. L., McAtee F. J. Monoclonal antibodies derived during graft-versus-host reaction. II. Antibodies detect unique determinants common to many MCF viruses. Virology. 1983 Apr 15;126(1):96–105. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90464-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pragnell I. B., McNab A., Harrison P. R., Osterag W. Are spleen focus-forming virus sequences related to xenotropic viruses and expressed specifically in normal erythroid cells? Nature. 1978 Mar 30;272(5652):456–458. doi: 10.1038/272456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAUSCHER F. J. A virus-induced disease of mice characterized by erythrocytopoiesis and lymphoid leukemia. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1962 Sep;29:515–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rein A., Schultz A. Different recombinant murine leukemia viruses use different cell surface receptors. Virology. 1984 Jul 15;136(1):144–152. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90255-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruta M., Kabat D. Plasma membrane glycoproteins encoded by cloned Rauscher and Friend spleen focus-forming viruses. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):844–853. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.844-853.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer W., Anderer F. A., Bauer H., Pister L. Studies on mouse leukemia viruses. I. Isolation and characterization of a group-specific antigen. Virology. 1969 Jul;38(3):387–394. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90151-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitbon M., Nishio J., Wehrly K., Lodmell D., Chesebro B. Use of a focal immunofluorescence assay on live cells for quantitation of retroviruses: distinction of host range classes in virus mixtures and biological cloning of dual-tropic murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1985 Feb;141(1):110–118. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90187-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitbon M., Sola B., Evans L., Nishio J., Hayes S. F., Nathanson K., Garon C. F., Chesebro B. Hemolytic anemia and erythroleukemia, two distinct pathogenic effects of Friend MuLV: mapping of the effects to different regions of the viral genome. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):851–859. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90800-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockert E., DeLeo A. B., O'Donnell P. V., Obata Y., Old L. J. G(AKSL2): a new cell surface antigen of the mouse related to the dualtropic mink cell focus-inducing class of murine leukemia virus detected by naturally occurring antibody. J Exp Med. 1979 Jan 1;149(1):200–215. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.1.200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockert E., Old L. J., Boyse E. A. The G-IX system. A cell surface allo-antigen associated with murine leukemia virus; implications regarding chromosomal integration of the viral genome. J Exp Med. 1971 Jun 1;133(6):1334–1355. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.6.1334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., Arnstein P., Parks W. P., Lennette E. H., Huebner R. J. A type-C virus in human rhabdomyosarcoma cells after inoculation into NIH Swiss mice treated with antithymocyte serum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):859–862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troxler D. H., Yuan E., Linemeyer D., Ruscetti S., Scolnick E. M. Helper-independent mink cell focus-inducing strains of Friend murine type-C virus: potential relationship to the origin of replication-defective spleen focus-forming virus. J Exp Med. 1978 Sep 1;148(3):639–653. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.3.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tung J. S., Vitetta E. S., Fleissner E., Boyse E. A. Biochemical evidence linking the GIX thymocyte surface antigen to the gp69/71 envelope glycoprotein of murine leukemia virus. J Exp Med. 1975 Jan 1;141(1):198–205. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.1.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff L., Scolnick E., Ruscetti S. Envelope gene of the Friend spleen focus-forming virus: deletion and insertions in 3' gp70/p15E-encoding region have resulted in unique features in the primary structure of its protein product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4718–4722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]