Abstract
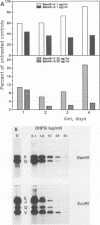
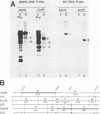
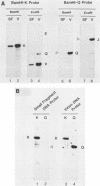
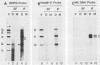
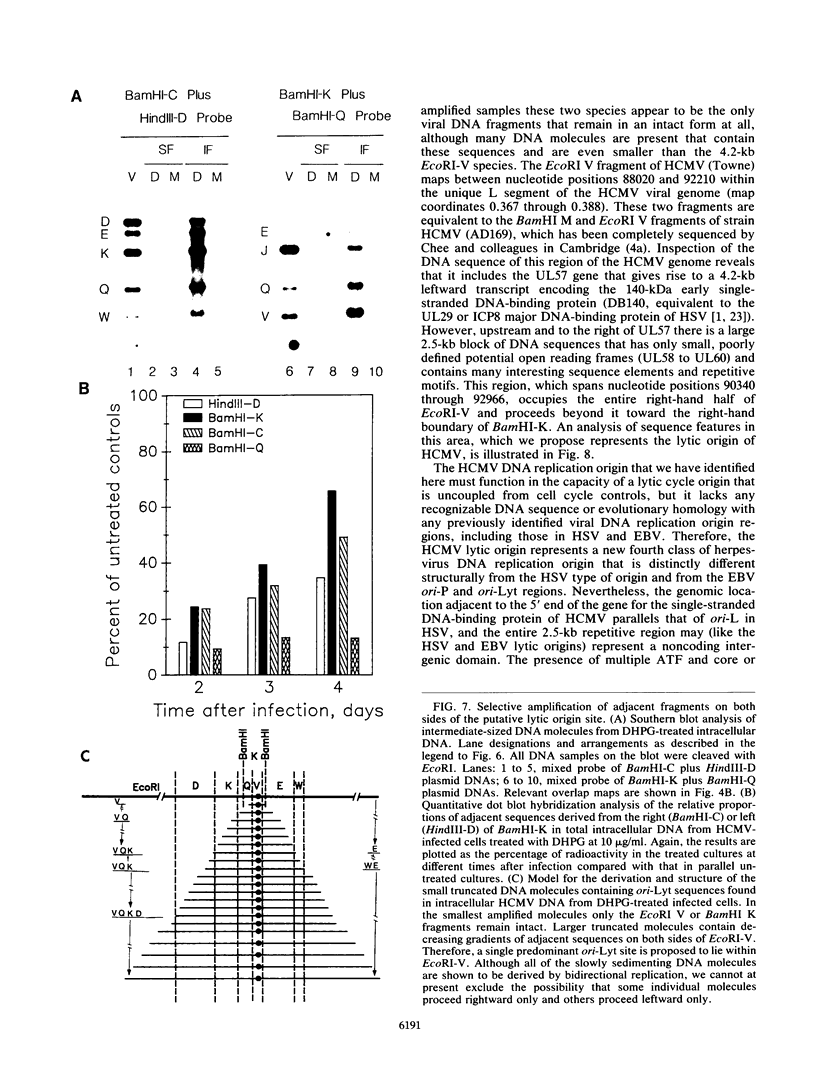
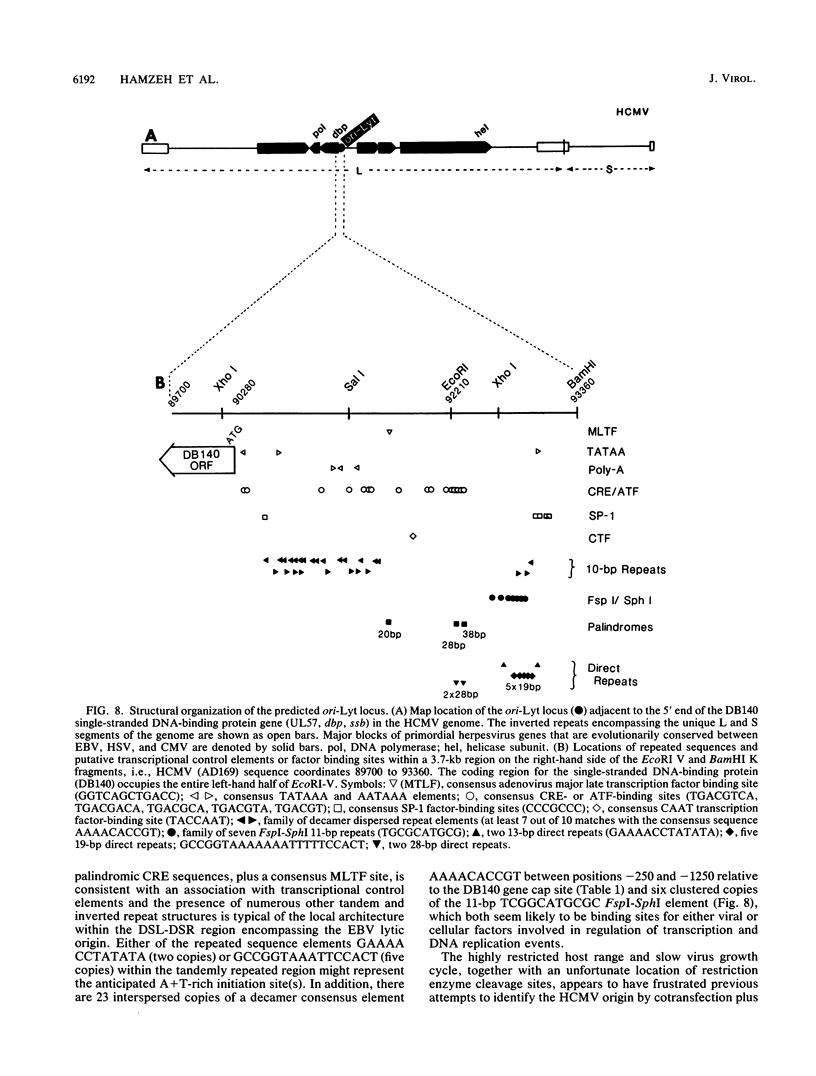
Infection with human cytomegalovirus in the presence of the antiviral nucleotide analog ganciclovir results in continuing low-level viral DNA synthesis and the accumulation of relatively small fragments of double-stranded progency DNA. These fragments consistently proved to represent amplification of sequences from only one small section of the viral genome (EcoRI-V) lying near the center of the unique L segment. Further mapping revealed that the viral sequences represented in these fragments occurred in gradients of abundance that decreased in both directions from a point near 0.35 to 0.4 map unit. The proportion of amplified sequences increased with both time after infection and dosage of ganciclovir used. We conclude that the primary lytic cycle replication origin of human cytomegalovirus lies within a 3- to 4-kb region immediately upstream and to the right of the promoter for the single-stranded DNA-binding protein (DB140). The amplified origin-containing DNA molecules appeared to arise by continuing rounds of bidirectional initiation on truncated fragments of the genome that were generated as a result of chain termination effects induced by the incorporation of ganciclovir into the viral DNA. Inspection of the DNA sequence in the vicinity of ori-Lyt revealed a large complex upstream region that may be a noncoding intergenic domain and that bears no homology to any previously described herpesvirus origin. This 2.5-kb region includes many duplicated and inverted sequences, together with consensus CRE/ATF and other transcription factor-binding sites, and an interesting set of 23 copies of an interspersed decamer consensus element AAAACACCGT that is also conserved at the equivalent locus in simian cytomegalovirus. This work represents the first identification of an origin domain in a cytomegalovirus genome and is the first demonstration of a bidirectional mechanism for any herpesvirus lytic cycle origin.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anders D. G., Gibson W. Location, transcript analysis, and partial nucleotide sequence of the cytomegalovirus gene encoding an early DNA-binding protein with similarities to ICP8 of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1364–1372. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1364-1372.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biron K. K., Stanat S. C., Sorrell J. B., Fyfe J. A., Keller P. M., Lambe C. U., Nelson D. J. Metabolic activation of the nucleoside analog 9-[( 2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethoxy]methyl)guanine in human diploid fibroblasts infected with human cytomegalovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2473–2477. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg M. D. A method for identifying the viral genes required for herpesvirus DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9094–9098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg M. D., Kelly T. J. Animal virus DNA replication. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:671–717. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chee M. S., Bankier A. T., Beck S., Bohni R., Brown C. M., Cerny R., Horsnell T., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Kouzarides T., Martignetti J. A. Analysis of the protein-coding content of the sequence of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;154:125–169. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74980-3_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chittenden T., Lupton S., Levine A. J. Functional limits of oriP, the Epstein-Barr virus plasmid origin of replication. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):3016–3025. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.3016-3025.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crute J. J., Tsurumi T., Zhu L. A., Weller S. K., Olivo P. D., Challberg M. D., Mocarski E. S., Lehman I. R. Herpes simplex virus 1 helicase-primase: a complex of three herpes-encoded gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2186–2189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Aquila R. T., Hayward G. S., Summers W. C. Physical mapping of the human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) (Towne) DNA polymerase gene: DNA-mediated transfer of a genetic marker for an HCMV gene. Virology. 1989 Jul;171(1):312–316. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90546-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P., Lehman I. R. Interaction of origin binding protein with an origin of replication of herpes simplex virus 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):2959–2963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.2959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freese U. K., Laux G., Hudewentz J., Schwarz E., Bornkamm G. W. Two distant clusters of partially homologous small repeats of Epstein-Barr virus are transcribed upon induction of an abortive or lytic cycle of the virus. J Virol. 1983 Dec;48(3):731–743. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.3.731-743.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel N., Jacob R. J., Honess R. W., Hayward G. S., Locker H., Roizman B. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA. III. Characterization of defective DNA molecules and biological properties of virus populations containing them. J Virol. 1975 Jul;16(1):153–167. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.1.153-167.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkeĺ N., Locker H., Batterson W., Hayward G. S., Roizman B. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA. VI. Defective DNA originates from the S component. J Virol. 1976 Nov;20(2):527–531. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.2.527-531.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedmann A., Becker Y. Circular and circular-linear DNA molecules of herpes simplex virus. J Gen Virol. 1977 Oct;37(1):205–208. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-37-1-205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahn T. A., Schildkraut C. L. The Epstein-Barr virus origin of plasmid replication, oriP, contains both the initiation and termination sites of DNA replication. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):527–535. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90433-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geelen J. L., Walig C., Wertheim P., van der Noordaa J. Human cytomegalovirus DNA. I. Molecular weight and infectivity. J Virol. 1978 Jun;26(3):813–816. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.3.813-816.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray C. P., Kaerner H. C. Sequence of the putative origin of replication in the UL region of herpes simplex virus type 1 ANG DNA. J Gen Virol. 1984 Dec;65(Pt 12):2109–2119. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-12-2109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschmidt W., Sugden B. Identification and characterization of oriLyt, a lytic origin of DNA replication of Epstein-Barr virus. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):427–433. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90028-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handeli S., Klar A., Meuth M., Cedar H. Mapping replication units in animal cells. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):909–920. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90329-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudewentz J., Delius H., Freese U. K., Zimber U., Bornkamm G. W. Two distant regions of the Epstein-Barr virus genome with sequence homologies have the same orientation and involve small tandem repeats. EMBO J. 1982;1(1):21–26. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01118.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob R. J., Morse L. S., Roizman B. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA. XII. Accumulation of head-to-tail concatemers in nuclei of infected cells and their role in the generation of the four isomeric arrangements of viral DNA. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):448–457. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.448-457.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jean J. H., Blankenship M. L., Ben-Porat T. Replication of herpesvirus DNA. I. Electron microscopic analysis of replicative structures. Virology. 1977 Jun 15;79(2):281–291. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90355-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaerner H. C., Ott-Hartmann A., Schatten R., Schröder C. H., Gray C. P. Amplification of a short nucleotide sequence in the repeat units of defective herpes simplex virus type 1 Angelotti DNA. J Virol. 1981 Jul;39(1):75–81. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.1.75-81.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemble G. W., McCormick A. L., Pereira L., Mocarski E. S. A cytomegalovirus protein with properties of herpes simplex virus ICP8: partial purification of the polypeptide and map position of the gene. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3143–3151. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3143-3151.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick B. A., Huang E. S., Pagano J. S. Analysis of cytomegalovirus genomes with restriction endonucleases Hin D III and EcoR-1. J Virol. 1976 Jun;18(3):1095–1105. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.3.1095-1105.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koff A., Tegtmeyer P. Characterization of major recognition sequences for a herpes simplex virus type 1 origin-binding protein. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4096–4103. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4096-4103.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaFemina R. L., Hayward G. S. Replicative forms of human cytomegalovirus DNA with joined termini are found in permissively infected human cells but not in non-permissive Balb/c-3T3 mouse cells. J Gen Virol. 1983 Feb;64(Pt 2):373–389. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-2-373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman P. M., Hardwick J. M., Sample J., Hayward G. S., Hayward S. D. The zta transactivator involved in induction of lytic cycle gene expression in Epstein-Barr virus-infected lymphocytes binds to both AP-1 and ZRE sites in target promoter and enhancer regions. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1143–1155. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1143-1155.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locker H., Frenkel N., Halliburton I. Structure and expression of class II defective herpes simplex virus genomes encoding infected cell polypeptide number 8. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):574–593. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.574-593.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockshon D., Galloway D. A. Cloning and characterization of oriL2, a large palindromic DNA replication origin of herpes simplex virus type 2. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):513–521. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.513-521.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks J. R., Spector D. H. Fusion of the termini of the murine cytomegalovirus genome after infection. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):24–28. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.24-28.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dalrymple M. A., Dolan A., McNab D., Perry L. J., Taylor P., Challberg M. D. Structures of herpes simplex virus type 1 genes required for replication of virus DNA. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):444–453. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.444-453.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivo P. D., Nelson N. J., Challberg M. D. Herpes simplex virus DNA replication: the UL9 gene encodes an origin-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5414–5418. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlins D. R., Milman G., Hayward S. D., Hayward G. S. Sequence-specific DNA binding of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen (EBNA-1) to clustered sites in the plasmid maintenance region. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):859–868. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90282-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reardon J. E. Herpes simplex virus type 1 and human DNA polymerase interactions with 2'-deoxyguanosine 5'-triphosphate analogues. Kinetics of incorporation into DNA and induction of inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):19039–19044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisman D., Yates J., Sugden B. A putative origin of replication of plasmids derived from Epstein-Barr virus is composed of two cis-acting components. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1822–1832. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuster R. C., Rubenstein A. J., Wallace D. C. Mitochondrial DNA in anucleate human blood cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Sep 30;155(3):1360–1365. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81291-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F., Mocarski E. S., Thomsen D. R. DNA of human cytomegalovirus: size heterogeneity and defectiveness resulting from serial undiluted passage. J Virol. 1979 Jul;31(1):231–239. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.1.231-239.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D. Localization of an origin of DNA replication within the TRS/IRS repeated region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome. EMBO J. 1982;1(7):863–867. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01261.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., McMonagle E. C. Characterization of the TRS/IRS origin of DNA replication of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1983 Oct 30;130(2):427–438. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90097-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen D. R., Stinski M. F. Cloning of the human cytomegalovirus genome as endonuclease XbaI fragments. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90077-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir H. M., Calder J. M., Stow N. D. Binding of the herpes simplex virus type 1 UL9 gene product to an origin of viral DNA replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 25;17(4):1409–1425. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.4.1409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller S. K., Spadaro A., Schaffer J. E., Murray A. W., Maxam A. M., Schaffer P. A. Cloning, sequencing, and functional analysis of oriL, a herpes simplex virus type 1 origin of DNA synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):930–942. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. A., Nelson N. J., McGeoch D. J., Challberg M. D. Identification of herpes simplex virus type 1 genes required for origin-dependent DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):435–443. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.435-443.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wysokenski D. A., Yates J. L. Multiple EBNA1-binding sites are required to form an EBNA1-dependent enhancer and to activate a minimal replicative origin within oriP of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2657–2666. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2657-2666.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. L., Warren N., Sugden B. Stable replication of plasmids derived from Epstein-Barr virus in various mammalian cells. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):812–815. doi: 10.1038/313812a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J., Warren N., Reisman D., Sugden B. A cis-acting element from the Epstein-Barr viral genome that permits stable replication of recombinant plasmids in latently infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3806–3810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]