Abstract
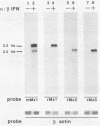
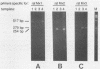
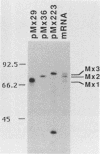
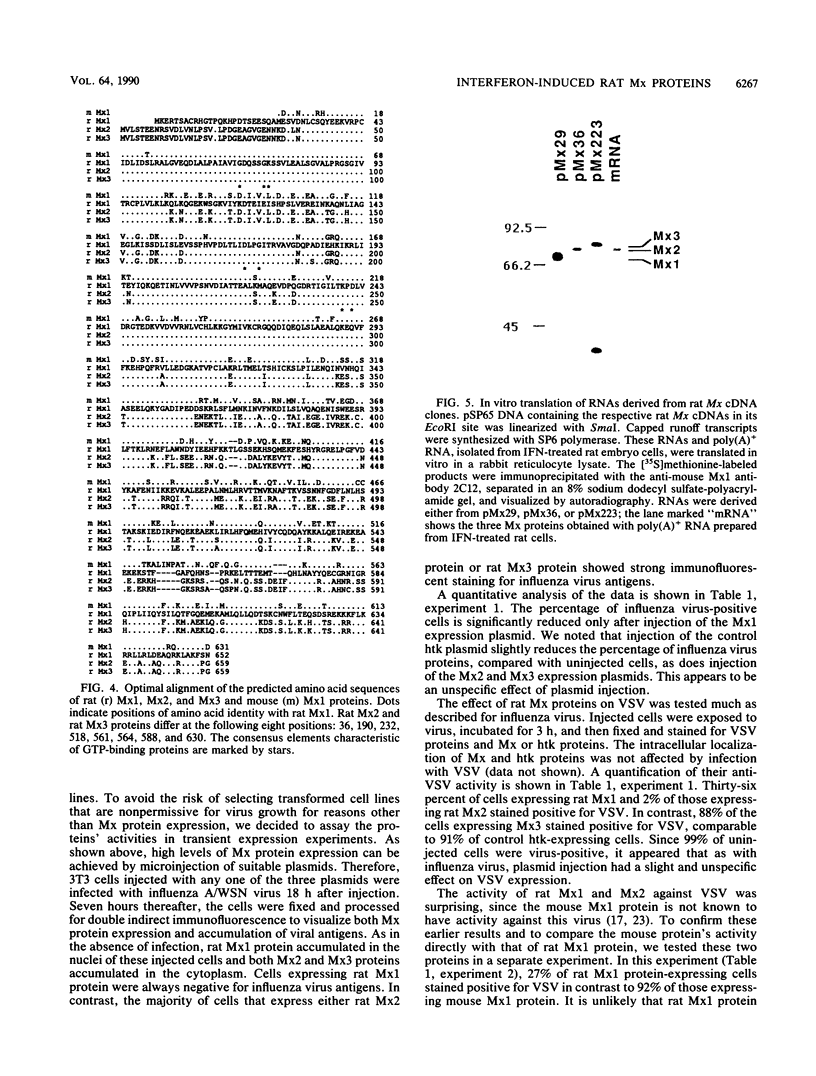
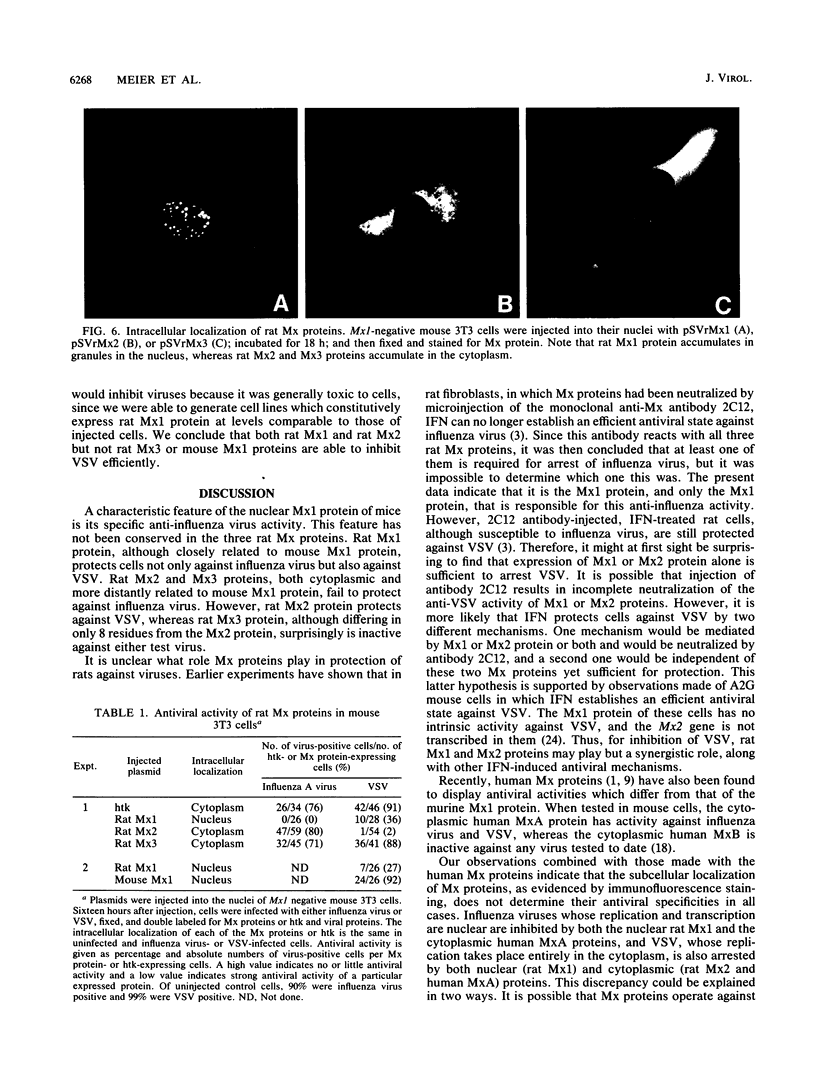
Upon stimulation with alpha/beta interferon, rat cells synthesize three Mx proteins. Sequence analysis of corresponding cDNAs reveals that these three proteins are derived from three distinct genes. One of the rat cDNAs is termed Mx1 because it is most closely related to the mouse Mx1 cDNA and because it codes for a nuclear protein that, like the mouse Mx1 protein, inhibits influenza virus growth. However, this protein differs from mouse Mx1 protein, in that it also inhibits vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV), a rhabdovirus. A second rat cDNA is more closely related to the mouse Mx2 cDNA and directs the synthesis of a cytoplasmic protein that inhibits VSV but not influenza virus. The third rat cDNA codes for a cytoplasmic protein that differs from the second one in only eight positions and has no detectable activity against either virus. These results indicate that rat Mx proteins have antiviral specificities not anticipated from the analysis of the murine Mx1 protein.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebi M., Fäh J., Hurt N., Samuel C. E., Thomis D., Bazzigher L., Pavlovic J., Haller O., Staeheli P. cDNA structures and regulation of two interferon-induced human Mx proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5062–5072. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnheiter H., Dubois-Dalcq M., Lazzarini R. A. Direct visualization of protein transport and processing in the living cell by microinjection of specific antibodies. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):99–109. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90195-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnheiter H., Haller O. Antiviral state against influenza virus neutralized by microinjection of antibodies to interferon-induced Mx proteins. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1315–1320. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02946.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnheiter H., Skuntz S., Noteborn M., Chang S., Meier E. Transgenic mice with intracellular immunity to influenza virus. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):51–61. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90239-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnheiter H., Staeheli P. Expression of interferon dependent resistance to influenza virus in mouse embryo cells. Arch Virol. 1983;76(2):127–137. doi: 10.1007/BF01311696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chebath J., Benech P., Revel M., Vigneron M. Constitutive expression of (2'-5') oligo A synthetase confers resistance to picornavirus infection. Nature. 1987 Dec 10;330(6148):587–588. doi: 10.1038/330587a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haller O., Arnheiter H., Horisberger M. A., Gresser I., Lindenmann J. Interaction between interferon and host genes in antiviral defense. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;350:558–565. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb20657.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haller O. Inborn resistance of ice to orthomyxoviruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1981;92:25–52. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68069-4_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horisberger M. A., McMaster G. K., Zeller H., Wathelet M. G., Dellis J., Content J. Cloning and sequence analyses of cDNAs for interferon- and virus-induced human Mx proteins reveal that they contain putative guanine nucleotide-binding sites: functional study of the corresponding gene promoter. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1171–1181. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1171-1181.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horisberger M. A., Staeheli P., Haller O. Interferon induces a unique protein in mouse cells bearing a gene for resistance to influenza virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1910–1914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konkel D. A., Tilghman S. M., Leder P. The sequence of the chromosomal mouse beta-globin major gene: homologies in capping, splicing and poly(A) sites. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1125–1132. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90040-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Melton D. A. In vitro RNA synthesis with SP6 RNA polymerase. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:397–415. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55027-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krug R. M., Shaw M., Broni B., Shapiro G., Haller O. Inhibition of influenza viral mRNA synthesis in cells expressing the interferon-induced Mx gene product. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):201–206. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.201-206.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier E., Fäh J., Grob M. S., End R., Staeheli P., Haller O. A family of interferon-induced Mx-related mRNAs encodes cytoplasmic and nuclear proteins in rat cells. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2386–2393. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2386-2393.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T., Horisberger M. A. Combined action of mouse alpha and beta interferons in influenza virus-infected macrophages carrying the resistance gene Mx. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):709–716. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.709-716.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noteborn M., Arnheiter H., Richter-Mann L., Browning H., Weissmann C. Transport of the murine Mx protein into the nucleus is dependent on a basic carboxy-terminal sequence. J Interferon Res. 1987 Oct;7(5):657–669. doi: 10.1089/jir.1987.7.657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obar R. A., Collins C. A., Hammarback J. A., Shpetner H. S., Vallee R. B. Molecular cloning of the microtubule-associated mechanochemical enzyme dynamin reveals homology with a new family of GTP-binding proteins. Nature. 1990 Sep 20;347(6290):256–261. doi: 10.1038/347256a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovic J., Zürcher T., Haller O., Staeheli P. Resistance to influenza virus and vesicular stomatitis virus conferred by expression of human MxA protein. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3370–3375. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3370-3375.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. H., Raymond C. K., Gilbert T., O'Hara P. J., Stevens T. H. A putative GTP binding protein homologous to interferon-inducible Mx proteins performs an essential function in yeast protein sorting. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1063–1074. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90070-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staeheli P., Dreiding P., Haller O., Lindenmann J. Polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies to the interferon-inducible protein Mx of influenza virus-resistant mice. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1821–1825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staeheli P., Haller O., Boll W., Lindenmann J., Weissmann C. Mx protein: constitutive expression in 3T3 cells transformed with cloned Mx cDNA confers selective resistance to influenza virus. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):147–158. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90493-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staeheli P. Interferon-induced proteins and the antiviral state. Adv Virus Res. 1990;38:147–200. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60862-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staeheli P., Sutcliffe J. G. Identification of a second interferon-regulated murine Mx gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4524–4528. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]