Abstract
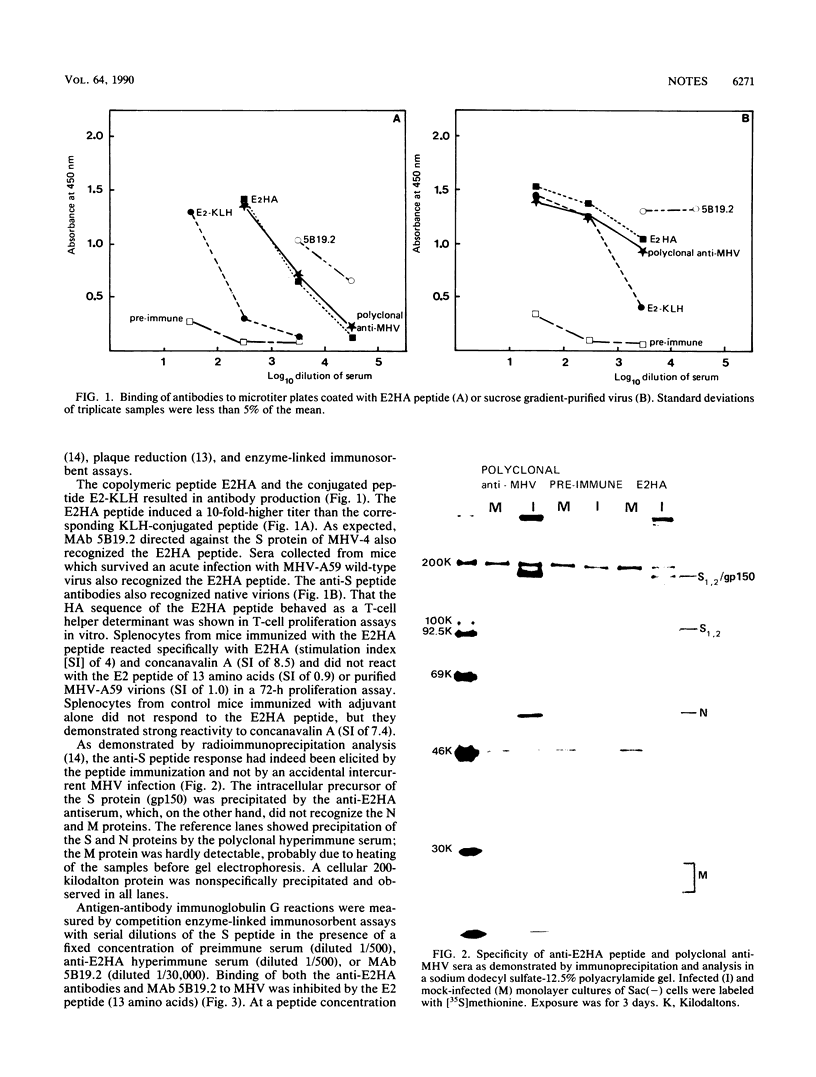
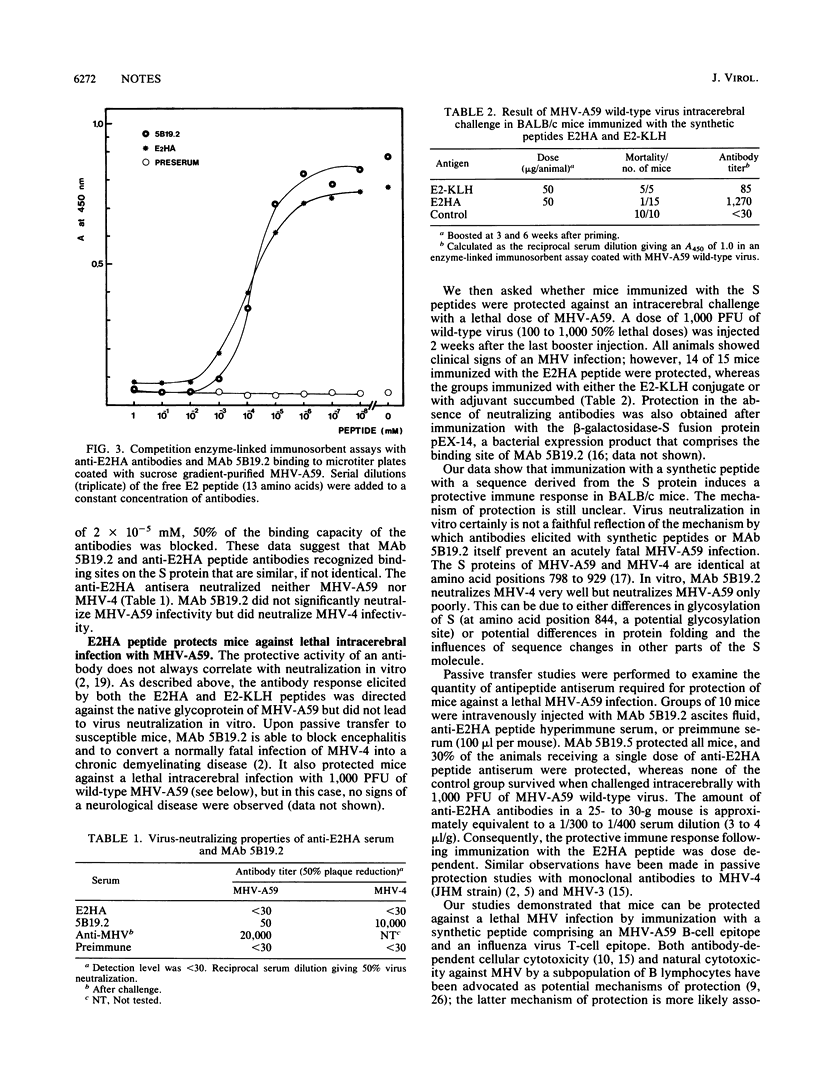
The coronavirus spike protein S is responsible for important biological activities including virus neutralization by antibody, cell attachment, and cell fusion. Recently, we have elucidated the amino acid sequence of an S determinant common in murine coronaviruses (W. Luytjes, D. Geerts, W. Posthumus, R. Meloen, and W. Spaan, J. Virol. 63:1408-1412, 1989). A monoclonal antibody directed to this determinant (MAb 5B19.2) protected mice against acute fatal infection. In this study, BALB/c mice were immunized with a synthetic peptide of 13 amino acids corresponding to the binding site of MAb 5B19.2, which was either extended with an amino acid sequence of influenza virus hemagglutinin or conjugated to keyhole limpet hemocyanin. Both immunogens induced S-specific antibodies in mice, but only the hemagglutinin-peptide construct protected them against lethal challenge. In contrast to mouse hepatitis virus type 4 (MHV-4), MHV-A59 was not neutralized in vitro by MAb 5B19.2. Neither MHV-A59 nor MHV-4 was neutralized in vitro by antibodies comprising by the synthetic peptides. Our results demonstrated that antibodies elicited with a synthetic peptide comprising a B-cell epitope and a T-helper cell determinant can protect mice against an acute fetal mouse hepatitis virus infection.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borras-Cuesta F., Petit-Camurdan A., Fedon Y. Engineering of immunogenic peptides by co-linear synthesis of determinants recognized by B and T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Aug;17(8):1213–1215. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier M. J., Lewicki H. A., Talbot P. J., Knobler R. L. Murine hepatitis virus-4 (strain JHM)-induced neurologic disease is modulated in vivo by monoclonal antibody. Virology. 1984 Jan 30;132(2):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90033-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins A. R., Knobler R. L., Powell H., Buchmeier M. J. Monoclonal antibodies to murine hepatitis virus-4 (strain JHM) define the viral glycoprotein responsible for attachment and cell--cell fusion. Virology. 1982 Jun;119(2):358–371. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90095-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalziel R. G., Lampert P. W., Talbot P. J., Buchmeier M. J. Site-specific alteration of murine hepatitis virus type 4 peplomer glycoprotein E2 results in reduced neurovirulence. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):463–471. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.463-471.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming J. O., Shubin R. A., Sussman M. A., Casteel N., Stohlman S. A. Monoclonal antibodies to the matrix (E1) glycoprotein of mouse hepatitis virus protect mice from encephalitis. Virology. 1989 Jan;168(1):162–167. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90415-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming J. O., Stohlman S. A., Harmon R. C., Lai M. M., Frelinger J. A., Weiner L. P. Antigenic relationships of murine coronaviruses: analysis using monoclonal antibodies to JHM (MHV-4) virus. Virology. 1983 Dec;131(2):296–307. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90498-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullick W. J., Downward J., Waterfield M. D. Antibodies to the autophosphorylation sites of the epidermal growth factor receptor protein-tyrosine kinase as probes of structure and function. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2869–2877. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04016.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackett C. J., Hurwitz J. L., Dietzschold B., Gerhard W. A synthetic decapeptide of influenza virus hemagglutinin elicits helper T cells with the same fine recognition specificities as occur in response to whole virus. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2):1391–1394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes K. V., Welsh R. M., Haspel M. V. Natural cytotoxicity against mouse hepatitis virus-infected target cells. I. Correlation of cytotoxicity with virus binding to leukocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 15;136(4):1446–1453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes M. J., Callow K. A., Childs R. A., Tyrrell D. A. Antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity against coronavirus 229E-infected cells. Br J Exp Pathol. 1986 Aug;67(4):581–586. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz J. L., Herber-Katz E., Hackett C. J., Gerhard W. Characterization of the murine TH response to influenza virus hemagglutinin: evidence for three major specificities. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):3371–3377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keck J. G., Hogue B. G., Brian D. A., Lai M. M. Temporal regulation of bovine coronavirus RNA synthesis. Virus Res. 1988 Mar;9(4):343–356. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(88)90093-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koolen M. J., Love S., Wouda W., Calafat J., Horzinek M. C., van der Zeijst B. A. Induction of demyelination by a temperature-sensitive mutant of the coronavirus MHV-A59 is associated with restriction of viral replication in the brain. J Gen Virol. 1987 Mar;68(Pt 3):703–714. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-3-703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koolen M. J., Osterhaus A. D., Siebelink K. H., Horzinek M. C., van der Zeijst B. A. Monoclonal antibodies to the three classes of mouse hepatitis virus strain A59 proteins. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1984;173:115–116. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-9373-7_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecomte J., Cainelli-Gebara V., Mercier G., Mansour S., Talbot P. J., Lussier G., Oth D. Protection from mouse hepatitis virus type 3-induced acute disease by an anti-nucleoprotein monoclonal antibody. Brief report. Arch Virol. 1987;97(1-2):123–130. doi: 10.1007/BF01310740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luytjes W., Geerts D., Posthumus W., Meloen R., Spaan W. Amino acid sequence of a conserved neutralizing epitope of murine coronaviruses. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1408–1412. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1408-1412.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luytjes W., Sturman L. S., Bredenbeek P. J., Charite J., van der Zeijst B. A., Horzinek M. C., Spaan W. J. Primary structure of the glycoprotein E2 of coronavirus MHV-A59 and identification of the trypsin cleavage site. Virology. 1987 Dec;161(2):479–487. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90142-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrifield R. B. Solid-phase peptide synthesis. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1969;32:221–296. doi: 10.1002/9780470122778.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmaljohn A. L., Johnson E. D., Dalrymple J. M., Cole G. A. Non-neutralizing monoclonal antibodies can prevent lethal alphavirus encephalitis. Nature. 1982 May 6;297(5861):70–72. doi: 10.1038/297070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddell S. G., Anderson R., Cavanagh D., Fujiwara K., Klenk H. D., Macnaughton M. R., Pensaert M., Stohlman S. A., Sturman L., van der Zeijst B. A. Coronaviridae. Intervirology. 1983;20(4):181–189. doi: 10.1159/000149390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot P. J., Buchmeier M. J. Antigenic variation among murine coronaviruses: evidence for polymorphism on the peplomer glycoprotein, E2. Virus Res. 1985 Jun;2(4):317–328. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(85)90028-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot P. J., Dionne G., Lacroix M. Vaccination against lethal coronavirus-induced encephalitis with a synthetic decapeptide homologous to a domain in the predicted peplomer stalk. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):3032–3036. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.3032-3036.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot P. J., Salmi A. A., Knobler R. L., Buchmeier M. J. Topographical mapping of epitopes on the glycoproteins of murine hepatitis virus-4 (strain JHM): correlation with biological activities. Virology. 1984 Jan 30;132(2):250–260. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90032-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wege H., Siddell S., ter Meulen V. The biology and pathogenesis of coronaviruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1982;99:165–200. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68528-6_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh R. M., Haspel M. V., Parker D. C., Holmes K. V. Natural cytotoxicity against mouse hepatitis virus-infected cells. II. A cytotoxic effector cell with a B lymphocyte phenotype. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 15;136(4):1454–1460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]