Abstract
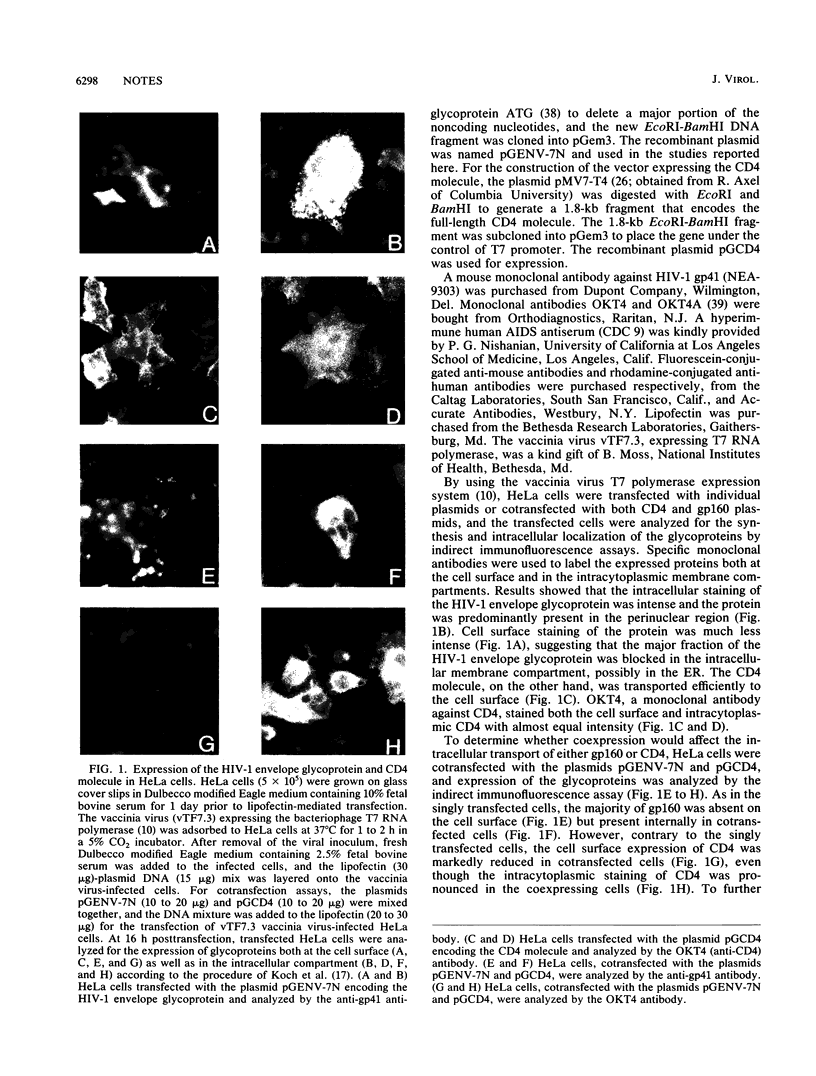
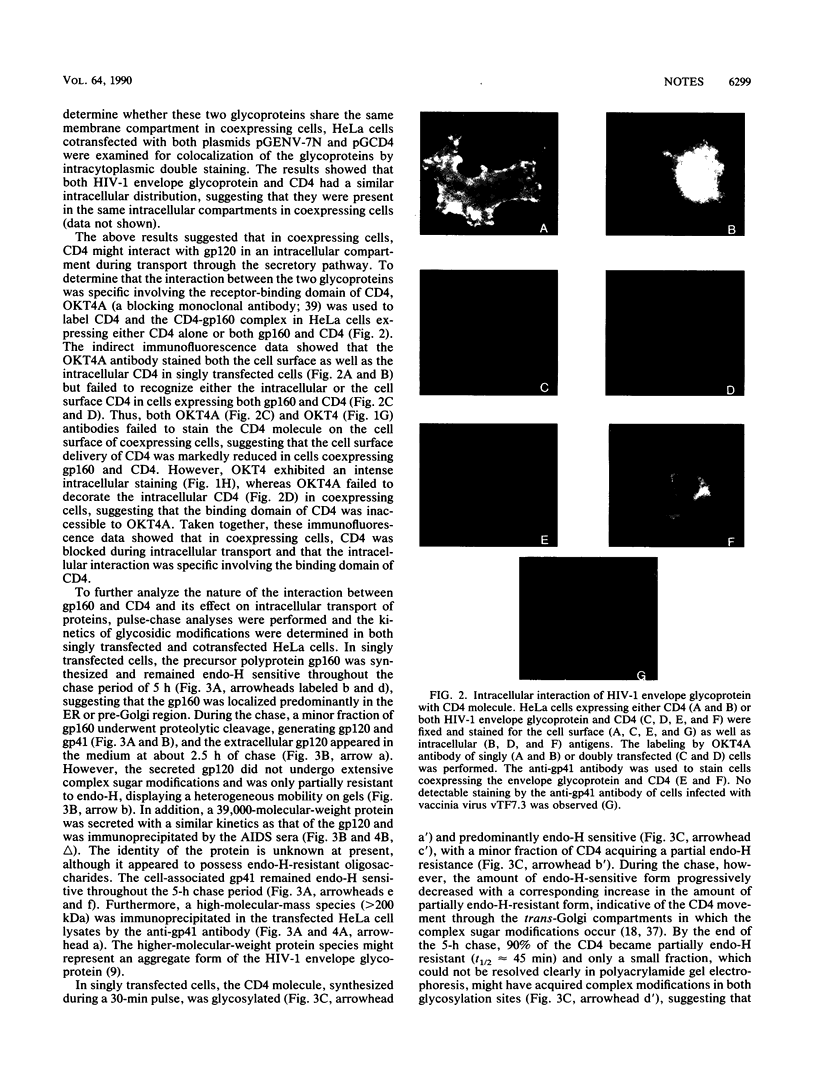
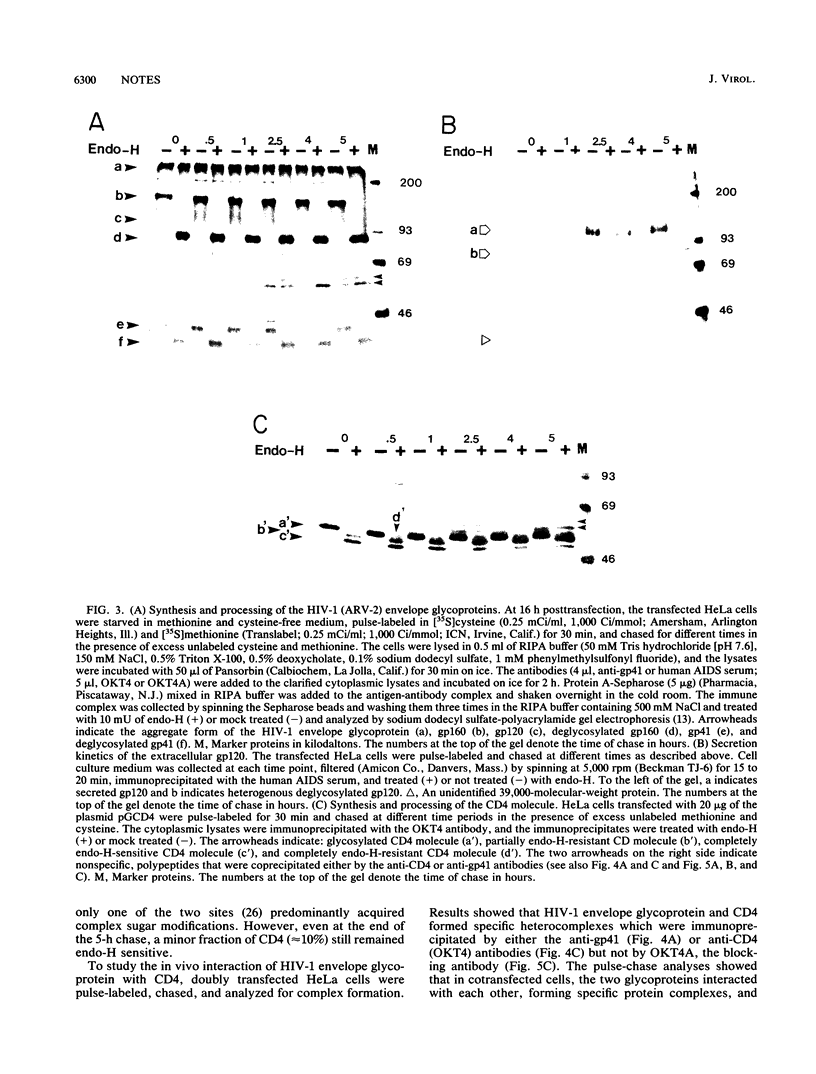
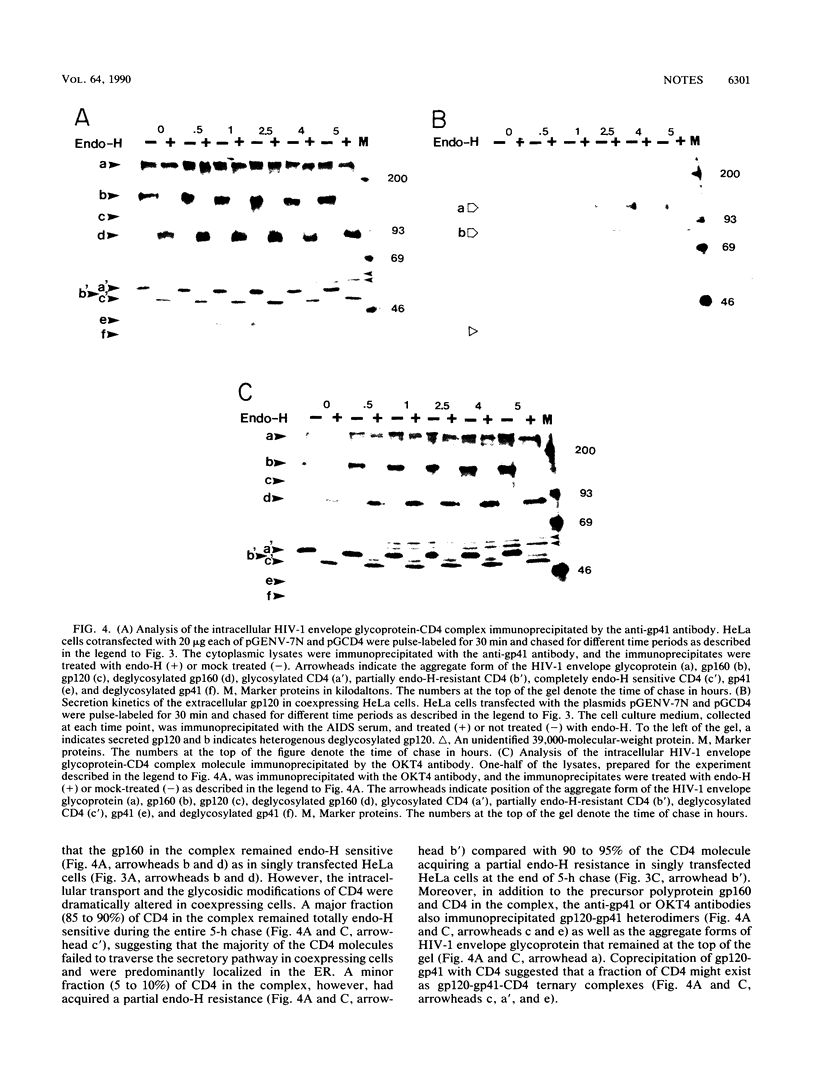
The envelope glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) plays a major role in the down-regulation of its receptor, CD4. Using a transient-expression system, we investigated the interaction of the HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein with CD4 during their movement through the intracellular membrane traffic. In singly transfected cells, the envelope glyprotein gp160 was synthesized, glycosylated, and localized predominantly in the endoplasmic reticulum. Only a minor fraction of gp160 was proteolytically cleaved, producing gp120 and gp41, and gp120 was secreted into the medium. On the other hand, the CD4 molecule, when expressed alone, was properly glycosylated and transported efficiently to the cell surface. However, when gp160 and CD4 were coexpressed in the same cell, the cell surface delivery of CD4 was greatly reduced. In coexpressing cells, CD4 formed a specific intracellular complex with gp160 as both proteins could be immunoprecipitated by antibodies against either the gp160 or CD4 (OKT4) but not by OKT4A, a blocking antibody against CD4. The specific gp160-CD4 complex was localized predominantly in the endoplasmic reticulum, and the CD4 in the complex did not acquire endoglycosidase H resistance. The present studies demonstrated that a specific intracellular interaction between gp160 and CD4 was responsible for the cell surface down-regulation of CD4 in cells expressing both the envelope glycoprotein of HIV-1 and its receptor, CD4.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdul Jabbar M., Nayak D. P. Signal processing, glycosylation, and secretion of mutant hemagglutinins of a human influenza virus by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1476–1485. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alizon M., Wain-Hobson S., Montagnier L., Sonigo P. Genetic variability of the AIDS virus: nucleotide sequence analysis of two isolates from African patients. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):63–74. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90860-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan J. S., Coligan J. E., Barin F., McLane M. F., Sodroski J. G., Rosen C. A., Haseltine W. A., Lee T. H., Essex M. Major glycoprotein antigens that induce antibodies in AIDS patients are encoded by HTLV-III. Science. 1985 May 31;228(4703):1091–1094. doi: 10.1126/science.2986290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arthos J., Deen K. C., Chaikin M. A., Fornwald J. A., Sathe G., Sattentau Q. J., Clapham P. R., Weiss R. A., McDougal J. S., Pietropaolo C. Identification of the residues in human CD4 critical for the binding of HIV. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):469–481. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90922-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barin F., McLane M. F., Allan J. S., Lee T. H., Groopman J. E., Essex M. Virus envelope protein of HTLV-III represents major target antigen for antibodies in AIDS patients. Science. 1985 May 31;228(4703):1094–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.2986291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti S., Robert-Guroff M., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C., Moss B. Expression of the HTLV-III envelope gene by a recombinant vaccinia virus. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):535–537. doi: 10.1038/320535a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordonnier A., Montagnier L., Emerman M. Single amino-acid changes in HIV envelope affect viral tropism and receptor binding. Nature. 1989 Aug 17;340(6234):571–574. doi: 10.1038/340571a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crise B., Buonocore L., Rose J. K. CD4 is retained in the endoplasmic reticulum by the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 glycoprotein precursor. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5585–5593. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5585-5593.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalgleish A. G., Beverley P. C., Clapham P. R., Crawford D. H., Greaves M. F., Weiss R. A. The CD4 (T4) antigen is an essential component of the receptor for the AIDS retrovirus. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):763–767. doi: 10.1038/312763a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delwart E. L., Panganiban A. T. Role of reticuloendotheliosis virus envelope glycoprotein in superinfection interference. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):273–280. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.273-280.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earl P. L., Doms R. W., Moss B. Oligomeric structure of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):648–652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Earl P. L., Moss B. Use of a hybrid vaccinia virus-T7 RNA polymerase system for expression of target genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2538–2544. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoxie J. A., Alpers J. D., Rackowski J. L., Huebner K., Haggarty B. S., Cedarbaum A. J., Reed J. C. Alterations in T4 (CD4) protein and mRNA synthesis in cells infected with HIV. Science. 1986 Nov 28;234(4780):1123–1127. doi: 10.1126/science.3095925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S. L., Kosowski S. G., Dalrymple J. M. Expression of AIDS virus envelope gene in recombinant vaccinia viruses. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):537–540. doi: 10.1038/320537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura I., Koga Y., Oh-Hori N., Onodera K., Kimura G., Nomoto K. Depletion of the surface CD4 molecule by the envelope protein of human immunodeficiency virus expressed in a human CD4+ monocytoid cell line. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3748–3754. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3748-3754.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatzmann D., Champagne E., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Guetard D., Hercend T., Gluckman J. C., Montagnier L. T-lymphocyte T4 molecule behaves as the receptor for human retrovirus LAV. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):767–768. doi: 10.1038/312767a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch G. L., Booth C., Wooding F. B. Dissociation and re-assembly of the endoplasmic reticulum in live cells. J Cell Sci. 1988 Dec;91(Pt 4):511–522. doi: 10.1242/jcs.91.4.511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Kornfeld S. Assembly of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:631–664. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski M., Potz J., Basiripour L., Dorfman T., Goh W. C., Terwilliger E., Dayton A., Rosen C., Haseltine W., Sodroski J. Functional regions of the envelope glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Science. 1987 Sep 11;237(4820):1351–1355. doi: 10.1126/science.3629244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landau N. R., Warton M., Littman D. R. The envelope glycoprotein of the human immunodeficiency virus binds to the immunoglobulin-like domain of CD4. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):159–162. doi: 10.1038/334159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasky L. A., Nakamura G., Smith D. H., Fennie C., Shimasaki C., Patzer E., Berman P., Gregory T., Capon D. J. Delineation of a region of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 glycoprotein critical for interaction with the CD4 receptor. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90524-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifson J. D., Feinberg M. B., Reyes G. R., Rabin L., Banapour B., Chakrabarti S., Moss B., Wong-Staal F., Steimer K. S., Engleman E. G. Induction of CD4-dependent cell fusion by the HTLV-III/LAV envelope glycoprotein. Nature. 1986 Oct 23;323(6090):725–728. doi: 10.1038/323725a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifson J. D., Reyes G. R., McGrath M. S., Stein B. S., Engleman E. G. AIDS retrovirus induced cytopathology: giant cell formation and involvement of CD4 antigen. Science. 1986 May 30;232(4754):1123–1127. doi: 10.1126/science.3010463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddon P. J., Dalgleish A. G., McDougal J. S., Clapham P. R., Weiss R. A., Axel R. The T4 gene encodes the AIDS virus receptor and is expressed in the immune system and the brain. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):333–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90590-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddon P. J., Littman D. R., Godfrey M., Maddon D. E., Chess L., Axel R. The isolation and nucleotide sequence of a cDNA encoding the T cell surface protein T4: a new member of the immunoglobulin gene family. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80105-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddon P. J., McDougal J. S., Clapham P. R., Dalgleish A. G., Jamal S., Weiss R. A., Axel R. HIV infection does not require endocytosis of its receptor, CD4. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):865–874. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91241-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure M. O., Marsh M., Weiss R. A. Human immunodeficiency virus infection of CD4-bearing cells occurs by a pH-independent mechanism. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):513–518. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02839.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCune J. M., Rabin L. B., Feinberg M. B., Lieberman M., Kosek J. C., Reyes G. R., Weissman I. L. Endoproteolytic cleavage of gp160 is required for the activation of human immunodeficiency virus. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):55–67. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90487-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougal J. S., Kennedy M. S., Sligh J. M., Cort S. P., Mawle A., Nicholson J. K. Binding of HTLV-III/LAV to T4+ T cells by a complex of the 110K viral protein and the T4 molecule. Science. 1986 Jan 24;231(4736):382–385. doi: 10.1126/science.3001934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modrow S., Hahn B. H., Shaw G. M., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F., Wolf H. Computer-assisted analysis of envelope protein sequences of seven human immunodeficiency virus isolates: prediction of antigenic epitopes in conserved and variable regions. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):570–578. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.570-578.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nayak D. P., Jabbar M. A. Structural domains and organizational conformation involved in the sorting and transport of influenza virus transmembrane proteins. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1989;43:465–501. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.43.100189.002341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson T., Jackson M., Peterson P. A. Short cytoplasmic sequences serve as retention signals for transmembrane proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):707–718. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90105-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pal R., Gallo R. C., Sarngadharan M. G. Processing of the structural proteins of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in the presence of monensin and cerulenin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9283–9286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson A., Seed B. Genetic analysis of monoclonal antibody and HIV binding sites on the human lymphocyte antigen CD4. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):65–72. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90180-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer S. R., Rothman J. E. Biosynthetic protein transport and sorting by the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:829–852. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Päbo S., Weber F., Nilsson T., Schaffner W., Peterson P. A. Structural and functional dissection of an MHC class I antigen-binding adenovirus glycoprotein. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1921–1927. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04445.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Pescador R., Power M. D., Barr P. J., Steimer K. S., Stempien M. M., Brown-Shimer S. L., Gee W. W., Renard A., Randolph A., Levy J. A. Nucleotide sequence and expression of an AIDS-associated retrovirus (ARV-2). Science. 1985 Feb 1;227(4686):484–492. doi: 10.1126/science.2578227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattentau Q. J., Dalgleish A. G., Weiss R. A., Beverley P. C. Epitopes of the CD4 antigen and HIV infection. Science. 1986 Nov 28;234(4780):1120–1123. doi: 10.1126/science.2430333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J., Goh W. C., Rosen C., Campbell K., Haseltine W. A. Role of the HTLV-III/LAV envelope in syncytium formation and cytopathicity. 1986 Jul 31-Aug 6Nature. 322(6078):470–474. doi: 10.1038/322470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein B. S., Gowda S. D., Lifson J. D., Penhallow R. C., Bensch K. G., Engleman E. G. pH-independent HIV entry into CD4-positive T cells via virus envelope fusion to the plasma membrane. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):659–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90542-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson M., Meier C., Mann A. M., Chapman N., Wasiak A. Envelope glycoprotein of HIV induces interference and cytolysis resistance in CD4+ cells: mechanism for persistence in AIDS. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):483–496. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90168-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veronese F. D., DeVico A. L., Copeland T. D., Oroszlan S., Gallo R. C., Sarngadharan M. G. Characterization of gp41 as the transmembrane protein coded by the HTLV-III/LAV envelope gene. Science. 1985 Sep 27;229(4720):1402–1405. doi: 10.1126/science.2994223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willey R. L., Bonifacino J. S., Potts B. J., Martin M. A., Klausner R. D. Biosynthesis, cleavage, and degradation of the human immunodeficiency virus 1 envelope glycoprotein gp160. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9580–9584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willey R. L., Smith D. H., Lasky L. A., Theodore T. S., Earl P. L., Moss B., Capon D. J., Martin M. A. In vitro mutagenesis identifies a region within the envelope gene of the human immunodeficiency virus that is critical for infectivity. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):139–147. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.139-147.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]