Abstract
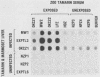
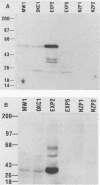
Callitrichid hepatitis (CH) is an acute, frequently fatal viral hepatitis which affects members of the primate family Callitrichidae (R. J. Montali, E. C. Ramsay, C. B. Stephensen, M. Worley, J. A. Davis, and K. V. Holmes, J. Infect. Dis. 160:759-765, 1989; E. C. Ramsay, R. J. Montali, M. Worley, C. B. Stephensen, and K. V. Holmes, J. Zoo Wildlife Med. 20:178-183, 1989). Outbreaks of the disease occur in zoos and animal parks. In this study, CH-specific antigens were identified in the livers of infected animals by using immune sera from primates with CH and CH-exposed asymptomatic animals. Three CH-specific antigens with apparent molecular masses of 34, 54, and 65 kDa were identified. A polyclonal antiserum was raised against the 54-kDa antigen. These antigens were not found in the livers of uninfected animals and may be viral proteins. Our results suggest that at least five of the six outbreaks of CH considered here were caused by the same virus or by an antigenically related virus.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akatsuka T., Tohmatsu J., Abe K., Shikata T., Ishikawa T., Nakajima K., Yoshihara N., Odaka T. Non-A, non-B hepatitis related AN6520 Ag is a normal cellular protein mainly expressed in liver. II. J Med Virol. 1986 Sep;20(1):43–56. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890200107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C., Pedersen J., Underwood J. R., Gust I., Toh B. H. Autoantibodies to intermediate filaments in acute viral hepatitis A, B and non-A, non-B are directed against vimentin. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1986 Jan;19(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda T., Honda Y., Hanawa M., Yamada E., Ono Y., Shikata T., Shimizu Y. K. Production of antibodies directed against microtubular aggregates in hepatocytes of chimpanzees with non-A, non-B hepatitis. J Gen Virol. 1989 Jun;70(Pt 6):1401–1407. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-6-1401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montali R. J., Ramsay E. C., Stephensen C. B., Worley M., Davis J. A., Holmes K. V. A new transmissible viral hepatitis of marmosets and tamarins. J Infect Dis. 1989 Nov;160(5):759–765. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.5.759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu Y. K., Oomura M., Abe K., Uno M., Yamada E., Ono Y., Shikata T. Production of antibody associated with non-A, non-B hepatitis in a chimpanzee lymphoblastoid cell line established by in vitro transformation with Epstein-Barr virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):2138–2142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.2138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]