Abstract
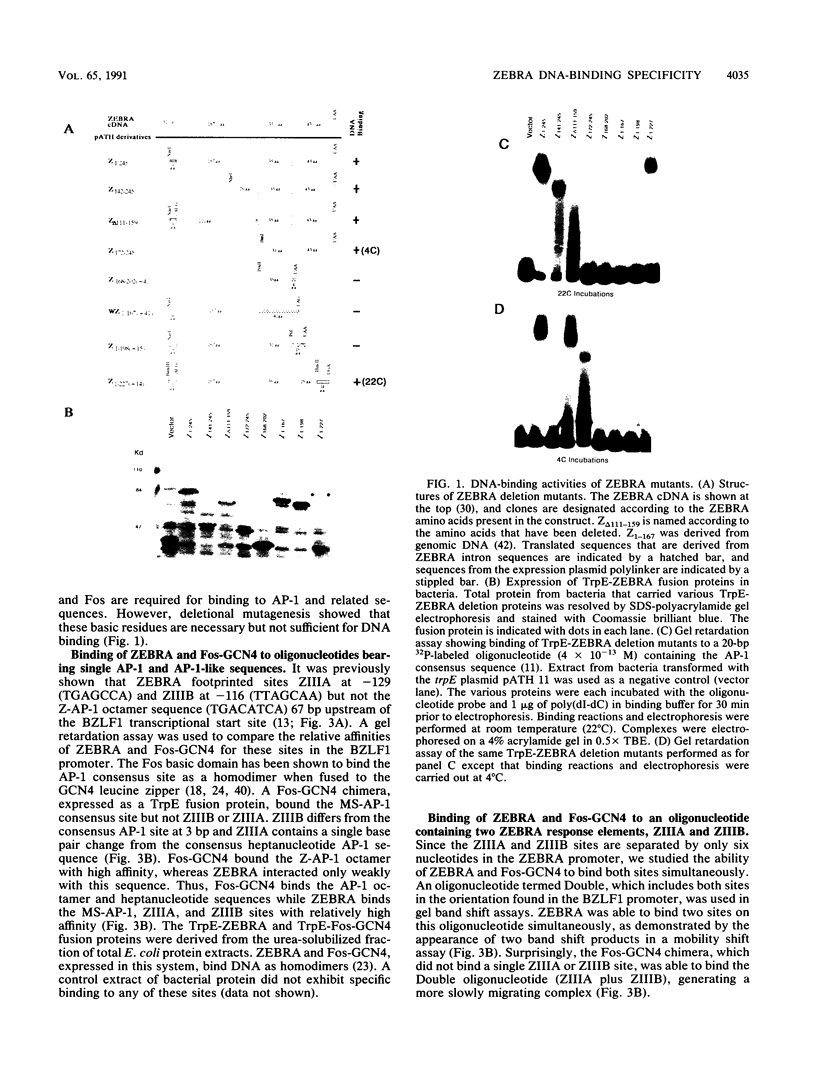
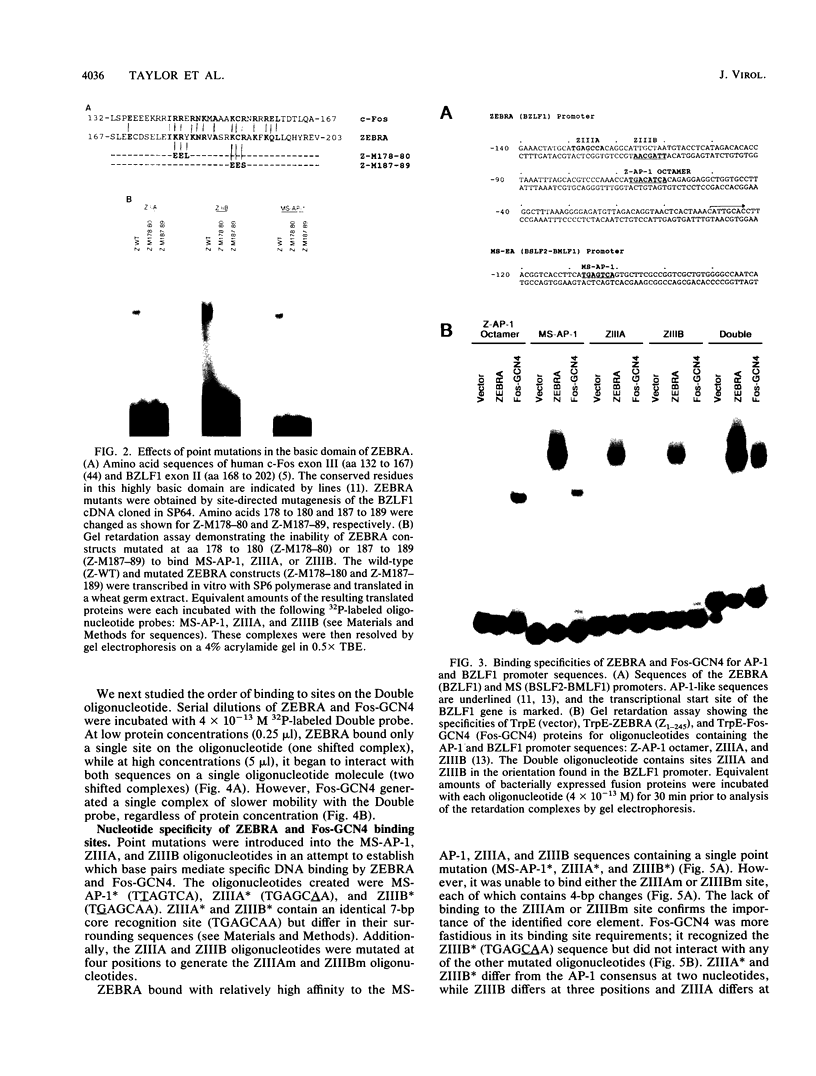
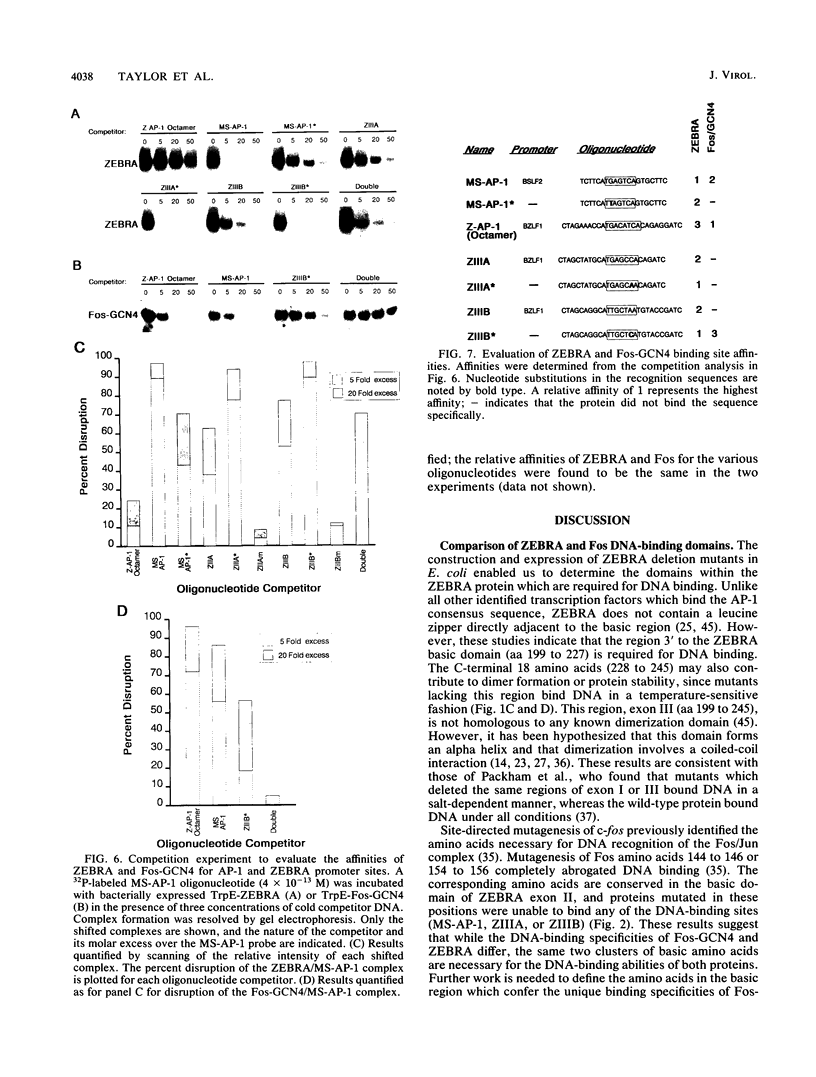
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) encodes a protein, ZEBRA, which enables the virus to switch from a latent to a lytic life cycle. The basic domain of ZEBRA is homologous to the Fos/Jun oncogene family, and both proteins bind the canonical AP-1 site (TGAGTCA). However, ZEBRA does not contain a leucine zipper dimerization domain which has been shown to be necessary for DNA binding of Fos/Jun proteins. Additionally, ZEBRA binds to sites which deviate from the AP-1 consensus sequence. Thus, it was of interest to define the domain of the ZEBRA protein required for DNA binding. We have determined by mutagenesis that ZEBRA residues 172 to 227, representing the basic domain and a putative dimerization domain, are required for specific binding to AP-1 and divergent sites. Mutagenesis of the basic amino acids 178 to 180 or 187 to 189 abrogates ZEBRA binding to all DNA target sequences. These residues are conserved in Fos and are also necessary for Fos DNA-binding activity. We have found that a Fos-GCN4 chimera and ZEBRA have different cognate binding specificities. The autoregulated BZLF1 promoter contains three divergent AP-1 sequences, ZIIIA (TGAGCCA), ZIIIB (TTAGCAA), and Z-AP-1-octamer (TGACATCA). ZEBRA binds with high specificity to ZIIIA and ZIIIB but weakly to the Z-AP-1 octamer. Conversely, the Fos-GCN4 chimera recognizes only the Z-AP-1 octamer. ZEBRA binds the ZIIIA and ZIIIB sites together in a noncooperative fashion, while Fos-GCN4 binds these sites as a higher-order complex. Additionally, we have found that flanking sequences influence binding of Fos-GCN4 to a degenerate AP-1 site (TGAGCAA). The characteristic binding specificities of ZEBRA and cellular AP-1 proteins suggest that they differentially affect viral and cellular transcription.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Allegretto E. A., Okino S. T., Hattori K., Boyle W. J., Hunter T., Karin M. Oncogene jun encodes a sequence-specific trans-activator similar to AP-1. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):166–171. doi: 10.1038/332166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Hattori K., Smeal T., Karin M. The jun proto-oncogene is positively autoregulated by its product, Jun/AP-1. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):875–885. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90143-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M., Bodescot M., Perricaudet M., Farrell P. Epstein-Barr virus gene expression in P3HR1-superinfected Raji cells. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3120–3132. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3120-3132.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. N., Dong D. L., Hayward G. S., Hayward S. D. The Epstein-Barr virus Zta transactivator: a member of the bZIP family with unique DNA-binding specificity and a dimerization domain that lacks the characteristic heptad leucine zipper motif. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3358–3369. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3358-3369.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Gruffat H., Chevallier-Greco A., Buisson M., Sergeant A. The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) early promoter DR contains a cis-acting element responsive to the EBV transactivator EB1 and an enhancer with constitutive and inducible activities. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):607–614. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.607-614.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chevallier-Greco A., Manet E., Chavrier P., Mosnier C., Daillie J., Sergeant A. Both Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-encoded trans-acting factors, EB1 and EB2, are required to activate transcription from an EBV early promoter. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3243–3249. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04635.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch P. J., Hoeffler J. P., Jameson J. L., Habener J. F. Cyclic AMP and phorbol ester-stimulated transcription mediated by similar DNA elements that bind distinct proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7922–7926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Rowe D. T., Rooney C. M., Kouzarides T. Epstein-Barr virus BZLF1 trans-activator specifically binds to a consensus AP-1 site and is related to c-fos. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):127–132. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03356.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flemington E., Speck S. H. Autoregulation of Epstein-Barr virus putative lytic switch gene BZLF1. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1227–1232. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1227-1232.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flemington E., Speck S. H. Evidence for coiled-coil dimer formation by an Epstein-Barr virus transactivator that lacks a heptad repeat of leucine residues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9459–9463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flemington E., Speck S. H. Identification of phorbol ester response elements in the promoter of Epstein-Barr virus putative lytic switch gene BZLF1. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1217–1226. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1217-1226.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gradoville L., Grogan E., Taylor N., Miller G. Differences in the extent of activation of Epstein-Barr virus replicative gene expression among four nonproducer cell lines stably transformed by oriP/BZLF1 plasmids. Virology. 1990 Oct;178(2):345–354. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90331-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschmidt W., Sugden B. Identification and characterization of oriLyt, a lytic origin of DNA replication of Epstein-Barr virus. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):427–433. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90028-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardwick J. M., Lieberman P. M., Hayward S. D. A new Epstein-Barr virus transactivator, R, induces expression of a cytoplasmic early antigen. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2274–2284. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2274-2284.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holley-Guthrie E. A., Quinlivan E. B., Mar E. C., Kenney S. The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) BMRF1 promoter for early antigen (EA-D) is regulated by the EBV transactivators, BRLF1 and BZLF1, in a cell-specific manner. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3753–3759. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3753-3759.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Struhl K. GCN4, a eukaryotic transcriptional activator protein, binds as a dimer to target DNA. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2781–2784. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02573.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney S., Kamine J., Holley-Guthrie E., Lin J. C., Mar E. C., Pagano J. The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) BZLF1 immediate-early gene product differentially affects latent versus productive EBV promoters. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1729–1736. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1729-1736.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney S., Kamine J., Markovitz D., Fenrick R., Pagano J. An Epstein-Barr virus immediate-early gene product trans-activates gene expression from the human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1652–1656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouzarides T., Ziff E. Leucine zippers of fos, jun and GCN4 dictate dimerization specificity and thereby control DNA binding. Nature. 1989 Aug 17;340(6234):568–571. doi: 10.1038/340568a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The DNA binding domain of the rat liver nuclear protein C/EBP is bipartite. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1681–1688. doi: 10.1126/science.2494700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Mitchell P., Tjian R. Purified transcription factor AP-1 interacts with TPA-inducible enhancer elements. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90612-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman P. M., Berk A. J. In vitro transcriptional activation, dimerization, and DNA-binding specificity of the Epstein-Barr virus Zta protein. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2560–2568. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2560-2568.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman P. M., Hardwick J. M., Sample J., Hayward G. S., Hayward S. D. The zta transactivator involved in induction of lytic cycle gene expression in Epstein-Barr virus-infected lymphocytes binds to both AP-1 and ZRE sites in target promoter and enhancer regions. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1143–1155. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1143-1155.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luka J., Kallin B., Klein G. Induction of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) cycle in latently infected cells by n-butyrate. Virology. 1979 Apr 15;94(1):228–231. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90455-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manet E., Gruffat H., Trescol-Biemont M. C., Moreno N., Chambard P., Giot J. F., Sergeant A. Epstein-Barr virus bicistronic mRNAs generated by facultative splicing code for two transcriptional trans-activators. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1819–1826. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03576.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabeppu Y., Nathans D. The basic region of Fos mediates specific DNA binding. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3833–3841. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08561.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabeppu Y., Ryder K., Nathans D. DNA binding activities of three murine Jun proteins: stimulation by Fos. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):907–915. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90146-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuberg M., Adamkiewicz J., Hunter J. B., Müller R. A Fos protein containing the Jun leucine zipper forms a homodimer which binds to the AP1 binding site. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):243–245. doi: 10.1038/341243a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuberg M., Schuermann M., Hunter J. B., Müller R. Two functionally different regions in Fos are required for the sequence-specific DNA interaction of the Fos/Jun protein complex. Nature. 1989 Apr 13;338(6216):589–590. doi: 10.1038/338589a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea E. K., Rutkowski R., Kim P. S. Evidence that the leucine zipper is a coiled coil. Science. 1989 Jan 27;243(4890):538–542. doi: 10.1126/science.2911757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packham G., Economou A., Rooney C. M., Rowe D. T., Farrell P. J. Structure and function of the Epstein-Barr virus BZLF1 protein. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2110–2116. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2110-2116.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Voulalas P. J., Franza B. R., Jr, Curran T. Fos and Jun bind cooperatively to the AP-1 site: reconstitution in vitro. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1687–1699. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risse G., Jooss K., Neuberg M., Brüller H. J., Müller R. Asymmetrical recognition of the palindromic AP1 binding site (TRE) by Fos protein complexes. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3825–3832. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08560.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellers J. W., Struhl K. Changing fos oncoprotein to a jun-independent DNA binding protein with GCN4 dimerization specificity by swapping "leucine zippers". Nature. 1989 Sep 7;341(6237):74–76. doi: 10.1038/341074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada K., Shimizu N., Sakuma S., Ono Y. trans activation of the latent Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) genome after transfection of the EBV DNA fragment. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):1016–1022. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.1016-1022.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor N., Countryman J., Rooney C., Katz D., Miller G. Expression of the BZLF1 latency-disrupting gene differs in standard and defective Epstein-Barr viruses. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1721–1728. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1721-1728.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urier G., Buisson M., Chambard P., Sergeant A. The Epstein-Barr virus early protein EB1 activates transcription from different responsive elements including AP-1 binding sites. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1447–1453. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03527.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson C. R., Sigler P. B., McKnight S. L. Scissors-grip model for DNA recognition by a family of leucine zipper proteins. Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):911–916. doi: 10.1126/science.2683088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Straaten F., Müller R., Curran T., Van Beveren C., Verma I. M. Complete nucleotide sequence of a human c-onc gene: deduced amino acid sequence of the human c-fos protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3183–3187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H., O'Neill F. J., Freese U. K., Hecker E. Persisting oncogenic herpesvirus induced by the tumour promotor TPA. Nature. 1978 Mar 23;272(5651):373–375. doi: 10.1038/272373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]