Abstract
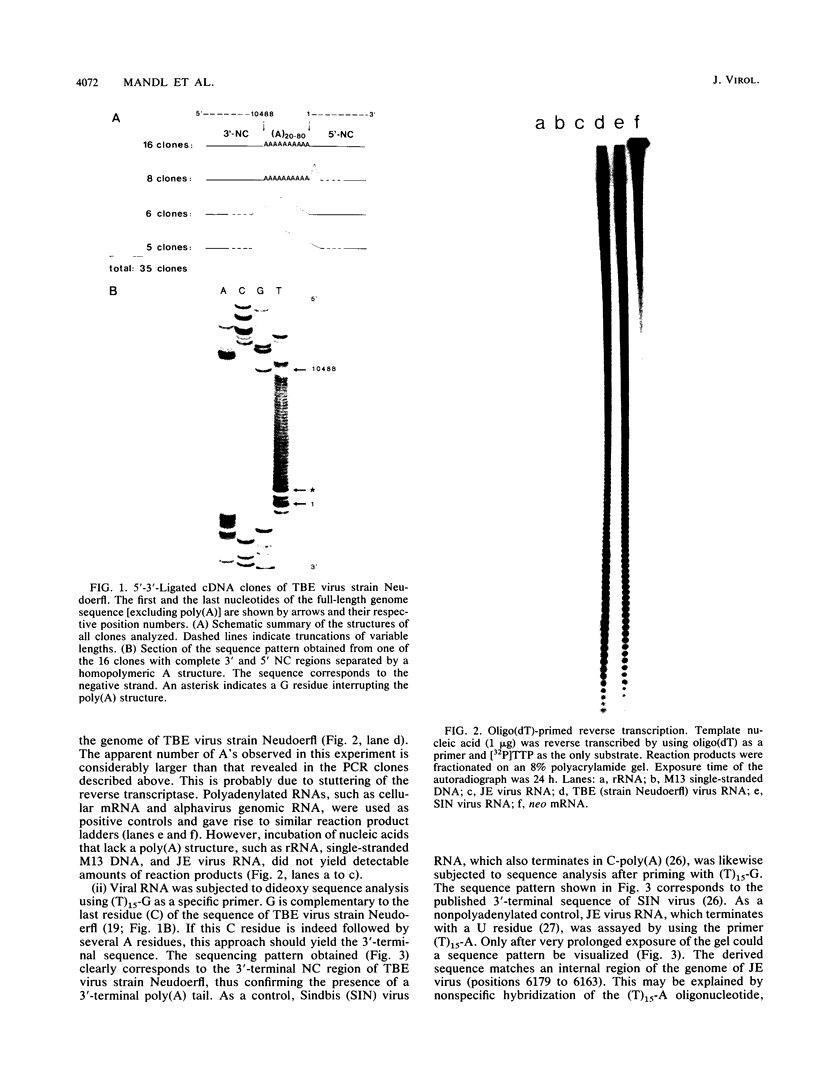
A poly(A) tail was identified on the 3' end of the prototype tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) virus strain Neudoerfl. This is in contrast to the general lack of poly(A) in the genomic RNAs of mosquito-borne flaviviruses analyzed so far. Analysis of several closely related strains of TBE virus, however, revealed the existence of two different types of 3' noncoding (NC) regions. One type (represented by strain Neudoerfl) is only 114 nucleotides long and carries a 3'-terminal poly(A) structure. This was also found in several TBE virus strains isolated from different geographic regions over a period of almost 30 years. The other type (represented by strain Hypr) is 461 nucleotides long and not polyadenylated. The sequence homology between the two types of TBE virus 3' NC regions terminates at a specific position 81 nucleotides after the stop codon. The second type of 3' NC region more closely resembles the common flavivirus pattern, including the potential for the formation of a 3'-terminal hairpin structure. However, it lacks primary sequence elements that are conserved among other flavivirus genomes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brinton M. A., Dispoto J. H. Sequence and secondary structure analysis of the 5'-terminal region of flavivirus genome RNA. Virology. 1988 Feb;162(2):290–299. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90468-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinton M. A., Fernandez A. V., Dispoto J. H. The 3'-nucleotides of flavivirus genomic RNA form a conserved secondary structure. Virology. 1986 Aug;153(1):113–121. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90012-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calisher C. H., Karabatsos N., Dalrymple J. M., Shope R. E., Porterfield J. S., Westaway E. G., Brandt W. E. Antigenic relationships between flaviviruses as determined by cross-neutralization tests with polyclonal antisera. J Gen Virol. 1989 Jan;70(Pt 1):37–43. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-1-37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers T. J., Hahn C. S., Galler R., Rice C. M. Flavivirus genome organization, expression, and replication. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1990;44:649–688. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.44.100190.003245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleaves G. R., Dubin D. T. Methylation status of intracellular dengue type 2 40 S RNA. Virology. 1979 Jul 15;96(1):159–165. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90181-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dominguez G., Wang C. Y., Frey T. K. Sequence of the genome RNA of rubella virus: evidence for genetic rearrangement during togavirus evolution. Virology. 1990 Jul;177(1):225–238. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90476-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faragher S. G., Dalgarno L. Regions of conservation and divergence in the 3' untranslated sequences of genomic RNA from Ross River virus isolates. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jul 20;190(2):141–148. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90287-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grange T., Bouloy M., Girard M. Stable secondary structures at the 3'-end of the genome of yellow fever virus (17 D vaccine strain). FEBS Lett. 1985 Aug 19;188(1):159–163. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80895-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guirakhoo F., Radda A. C., Heinz F. X., Kunz C. Evidence for antigenic stability of tick-borne encephalitis virus by the analysis of natural isolates. J Gen Virol. 1987 Mar;68(Pt 3):859–864. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-3-859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn C. S., Dalrymple J. M., Strauss J. H., Rice C. M. Comparison of the virulent Asibi strain of yellow fever virus with the 17D vaccine strain derived from it. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):2019–2023. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.2019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn C. S., Hahn Y. S., Rice C. M., Lee E., Dalgarno L., Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H. Conserved elements in the 3' untranslated region of flavivirus RNAs and potential cyclization sequences. J Mol Biol. 1987 Nov 5;198(1):33–41. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90455-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinz F. X. Epitope mapping of flavivirus glycoproteins. Adv Virus Res. 1986;31:103–168. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60263-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinz F. X., Kunz C. Homogeneity of the structural glycoprotein from European isolates of tick-borne encephalitis virus: comparison with other flaviviruses. J Gen Virol. 1981 Dec;57(Pt 2):263–274. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-57-2-263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzmann H., Heinz F. X., Mandl C. W., Guirakhoo F., Kunz C. A single amino acid substitution in envelope protein E of tick-borne encephalitis virus leads to attenuation in the mouse model. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):5156–5159. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.5156-5159.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandl C. W., Heinz F. X., Kunz C. Sequence of the structural proteins of tick-borne encephalitis virus (western subtype) and comparative analysis with other flaviviruses. Virology. 1988 Sep;166(1):197–205. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90161-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandl C. W., Heinz F. X., Puchhammer-Stöckl E., Kunz C. Sequencing the termini of capped viral RNA by 5'-3' ligation and PCR. Biotechniques. 1991 Apr;10(4):484–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandl C. W., Heinz F. X., Stöckl E., Kunz C. Genome sequence of tick-borne encephalitis virus (Western subtype) and comparative analysis of nonstructural proteins with other flaviviruses. Virology. 1989 Nov;173(1):291–301. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90246-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers G., Rümenapf T., Thiel H. J. Ubiquitin in a togavirus. Nature. 1989 Oct 12;341(6242):491–491. doi: 10.1038/341491a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitayaphan S., Grant J. A., Chang G. J., Trent D. W. Nucleotide sequence of the virulent SA-14 strain of Japanese encephalitis virus and its attenuated vaccine derivative, SA-14-14-2. Virology. 1990 Aug;177(2):541–552. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90519-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pletnev A. G., Yamshchikov V. F., Blinov V. M. Nucleotide sequence of the genome and complete amino acid sequence of the polyprotein of tick-borne encephalitis virus. Virology. 1990 Jan;174(1):250–263. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90073-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss E. G., Rice C. M., Strauss J. H. Complete nucleotide sequence of the genomic RNA of Sindbis virus. Virology. 1984 Feb;133(1):92–110. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90428-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takegami T., Washizu M., Yasui K. Nucleotide sequence at the 3' end of Japanese encephalitis virus genomic RNA. Virology. 1986 Jul 30;152(2):483–486. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90152-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G., Castle E. Analysis of structural properties which possibly are characteristic for the 3'-terminal sequence of the genome RNA of flaviviruses. J Gen Virol. 1986 Jun;67(Pt 6):1183–1188. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-6-1183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G., Wengler G., Gross H. J. Studies on virus-specific nucleic acids synthesized in vertebrate and mosquito cells infected with flaviviruses. Virology. 1978 Sep;89(2):423–437. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90185-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G., Wengler G. Terminal sequences of the genome and replicative-from RNA of the flavivirus West Nile virus: absence of poly(A) and possible role in RNA replication. Virology. 1981 Sep;113(2):544–555. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90182-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westaway E. G., Brinton M. A., Gaidamovich SYa, Horzinek M. C., Igarashi A., Käriäinen L., Lvov D. K., Porterfield J. S., Russell P. K., Trent D. W. Flaviviridae. Intervirology. 1985;24(4):183–192. doi: 10.1159/000149642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westaway E. G. Flavivirus replication strategy. Adv Virus Res. 1987;33:45–90. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60316-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. L., Jr, Tinoco I., Jr A dynamic programming algorithm for finding alternative RNA secondary structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):299–315. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmern D., Kaesberg P. 3'-terminal nucleotide sequence of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA determined by reverse transcriptase and chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4257–4261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]