Abstract
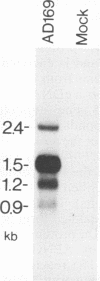
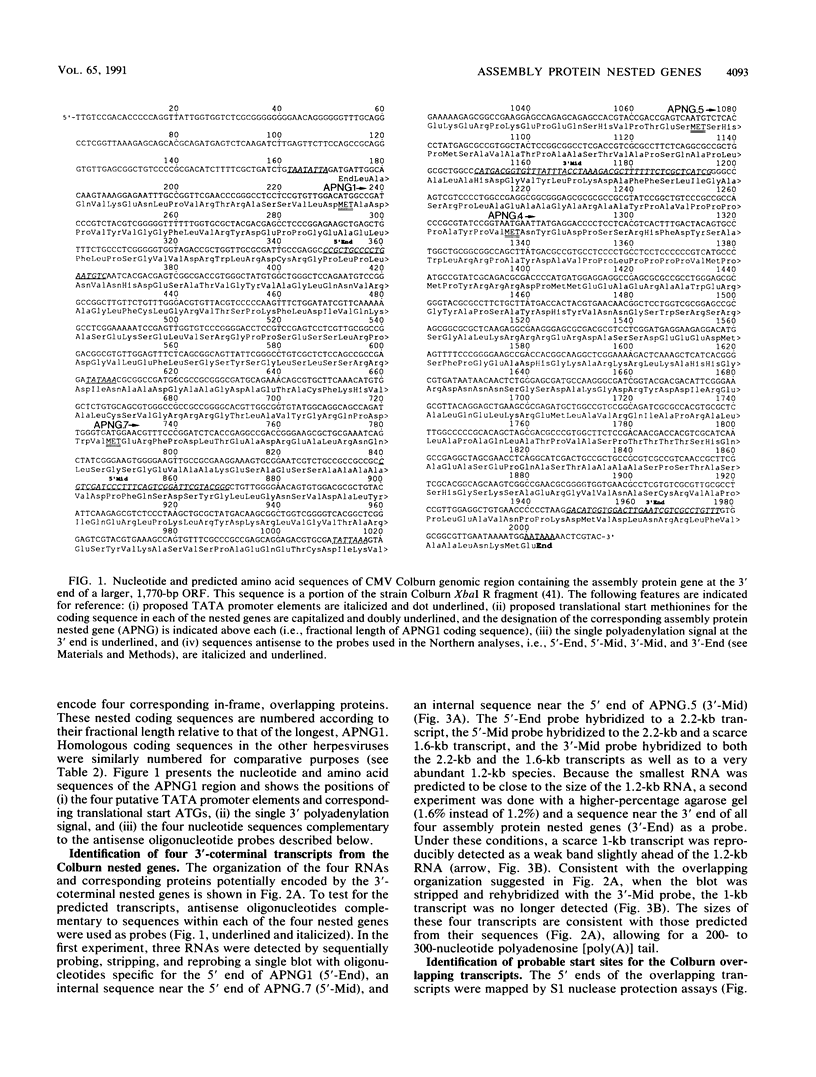
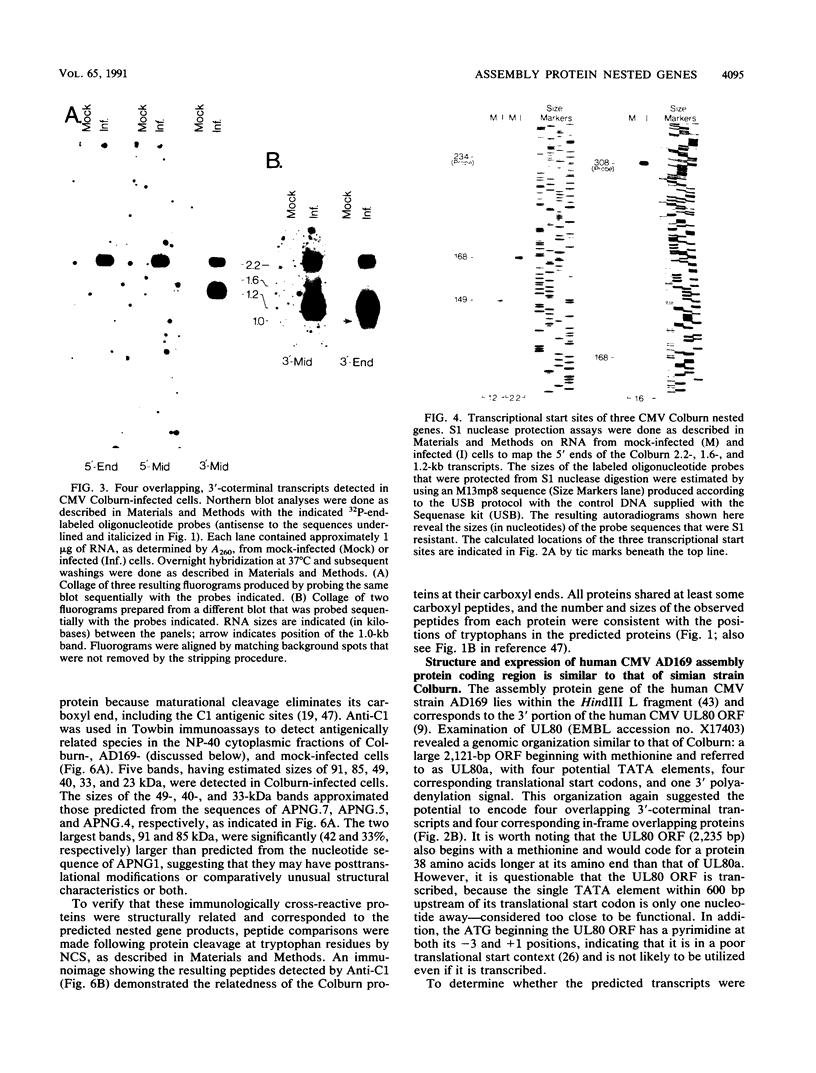
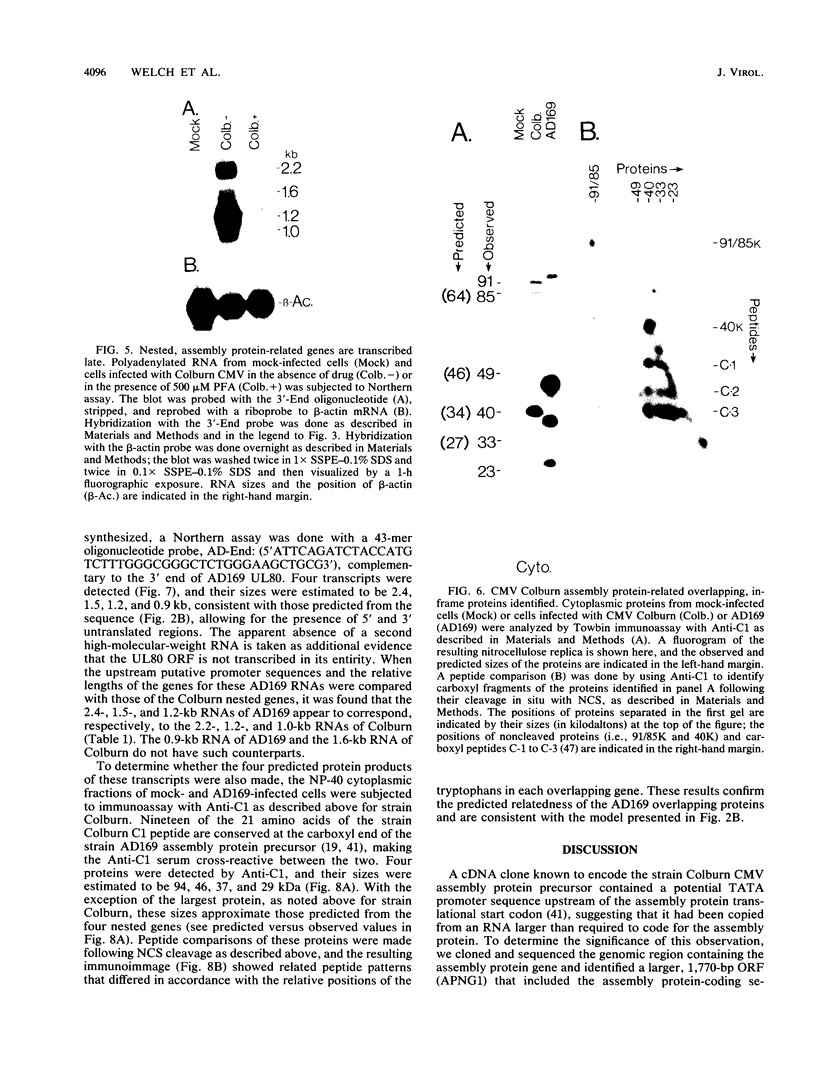
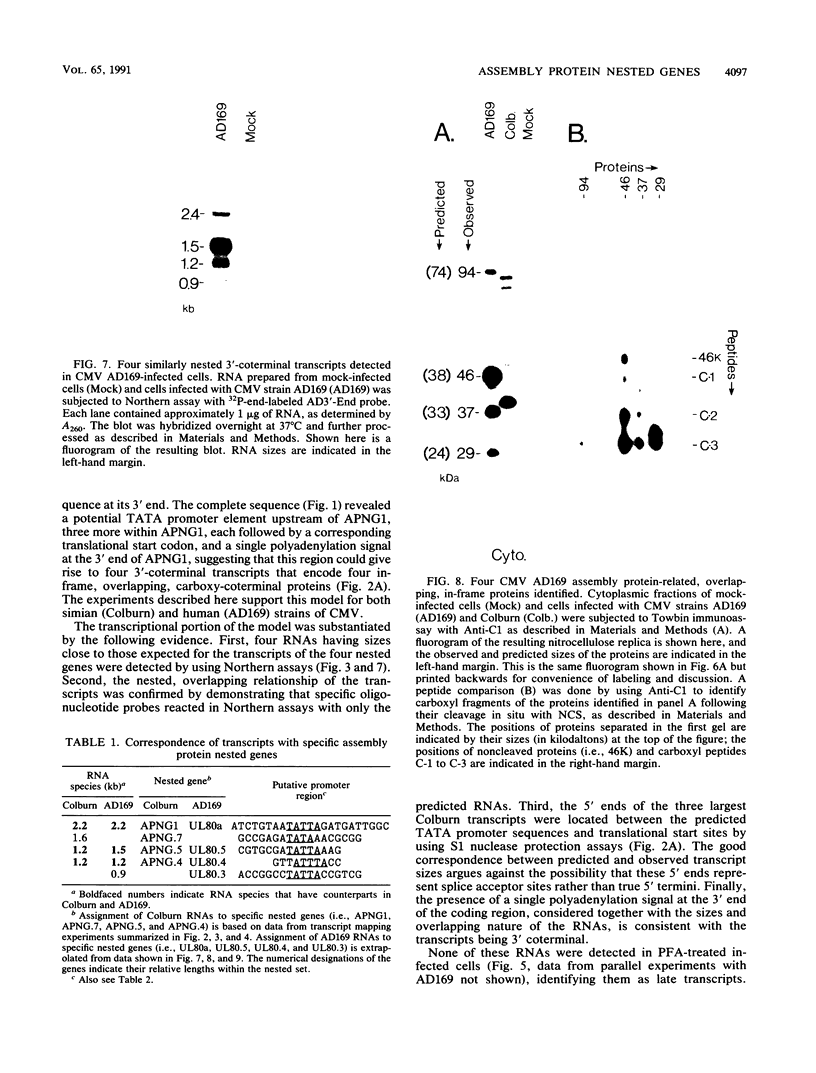
The genomic region encoding the assembly protein of simian cytomegalovirus (CMV) strain Colburn has been cloned, sequenced, and found to be organized as a nested set of four in-frame, 3'-coterminal genes, each with its own TATA promoter element and translational start codon, and all using a single 3' polyadenylation signal. The 3' end of the longest open reading frame (1.770 bp) was identical to the 930-bp sequence coding for the assembly protein precursor, as determined from a cDNA clone. The assembly protein coding region of human CMV strain AD169 was similarly organized, suggesting that both viral genomes could give rise to four independently transcribed 3'-coterminal RNAs coding for four overlapping, in-frame, carboxy-coterminal proteins. These predictions were tested and confirmed. Four mRNAs corresponding in size and sequence to those predicted were identified in both human and simian CMV-infected cells by using transcript-specific antisense oligonucleotide probes in Northern (RNA blot) assays. The 5' ends of the three largest of these Colburn transcripts were determined by S1 nuclease protection assays and found to map between the anticipated TATA sequences and corresponding translational start codons. The four predicted overlapping proteins were identified by immunoassays in lysates of simian and human CMV-infected cells by using an antiserum specific for the carboxyl end of the assembly protein precursor. The structural relationship of both sets of proteins was verified by comparing their peptide patterns following protein cleavage at tryptophan residues by N-chlorosuccinimide. The similar organization of the homologous coding regions in other herpesviruses into at least two nested, in-frame, 3'-coterminal genes is discussed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anders D. G., Irmiere A., Gibson W. Identification and characterization of a major early cytomegalovirus DNA-binding protein. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):253–262. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.253-262.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benko D. M., Gibson W. Primate cytomegalovirus glycoproteins: lectin-binding properties and sensitivities to glycosidases. J Virol. 1986 Sep;59(3):703–713. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.3.703-713.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benko D. M., Haltiwanger R. S., Hart G. W., Gibson W. Virion basic phosphoprotein from human cytomegalovirus contains O-linked N-acetylglucosamine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2573–2577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun D. K., Roizman B., Pereira L. Characterization of post-translational products of herpes simplex virus gene 35 proteins binding to the surfaces of full capsids but not empty capsids. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):142–153. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.142-153.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Taussig R., Kustu S., Botstein D. The secreted form of invertase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is synthesized from mRNA encoding a signal sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;3(3):439–447. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.3.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo R., Will H., Hernandez N., Schaller H. Signals regulating hepatitis B surface antigen transcription. Nature. 1983 Sep 22;305(5932):336–338. doi: 10.1038/305336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colberg-Poley A. M., Santomenna L. D. Selective induction of chromosomal gene expression by human cytomegalovirus. Virology. 1988 Sep;166(1):217–228. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90163-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Scott J. E. The complete DNA sequence of varicella-zoster virus. J Gen Virol. 1986 Sep;67(Pt 9):1759–1816. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-9-1759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrichs W. E., Grose C. Varicella-zoster virus p32/p36 complex is present in both the viral capsid and the nuclear matrix of the infected cell. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):155–164. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.155-164.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson W., Hunter T., Cogen B., Eckhart W. Altered virion proteins of a temperature-sensitive mutant of polyoma virus, ts59. Virology. 1977 Jul 1;80(1):21–41. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90378-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
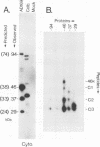
- Gibson W., Marcy A. I., Comolli J. C., Lee J. Identification of precursor to cytomegalovirus capsid assembly protein and evidence that processing results in loss of its carboxy-terminal end. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1241–1249. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1241-1249.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson W. Protease-facilitated transfer of high-molecular-weight proteins during electrotransfer to nitrocellulose. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90147-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson W., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. 8. Characterization and composition of multiple capsid forms of subtypes 1 and 2. J Virol. 1972 Nov;10(5):1044–1052. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.5.1044-1052.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson W., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. Staining and radiolabeling properties of B capsid and virion proteins in polyacrylamide gels. J Virol. 1974 Jan;13(1):155–165. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.1.155-165.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson W. Structural and nonstructural proteins of strain Colburn cytomegalovirus. Virology. 1981 Jun;111(2):516–537. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90354-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Gibson W. Characterization of the mRNA's for the polyoma virus capsid proteins VP1, VP2, and VP3. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):240–253. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.240-253.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irmiere A., Gibson W. Isolation and characterization of a noninfectious virion-like particle released from cells infected with human strains of cytomegalovirus. Virology. 1983 Oct 15;130(1):118–133. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90122-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irmiere A., Gibson W. Isolation of human cytomegalovirus intranuclear capsids, characterization of their protein constituents, and demonstration that the B-capsid assembly protein is also abundant in noninfectious enveloped particles. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):277–283. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.277-283.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroki K., Russnak R., Ganem D. Novel N-terminal amino acid sequence required for retention of a hepatitis B virus glycoprotein in the endoplasmic reticulum. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4459–4466. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käufer N. F., Fried H. M., Schwindinger W. F., Jasin M., Warner J. R. Cycloheximide resistance in yeast: the gene and its protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 25;11(10):3123–3135. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.10.3123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladin B. F., Ihara S., Hampl H., Ben-Porat T. Pathway of assembly of herpesvirus capsids: an analysis using DNA+ temperature-sensitive mutants of pseudorabies virus. Virology. 1982 Jan 30;116(2):544–561. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90147-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Enhanced autoradiographic detection of 32P and 125I using intensifying screens and hypersensitized film. FEBS Lett. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):314–316. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80609-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. Y., Irmiere A., Gibson W. Primate cytomegalovirus assembly: evidence that DNA packaging occurs subsequent to B capsid assembly. Virology. 1988 Nov;167(1):87–96. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90057-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lischwe M. A., Ochs D. A new method for partial peptide mapping using N-chlorosuccinimide/urea and peptide silver staining in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Dec;127(2):453–457. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90203-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littler E., Lawrence G., Liu M. Y., Barrell B. G., Arrand J. R. Identification, cloning, and expression of the major capsid protein gene of human herpesvirus 6. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):714–722. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.714-722.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. Y., Roizman B. The promoter, transcriptional unit, and coding sequence of herpes simplex virus 1 family 35 proteins are contained within and in frame with the UL26 open reading frame. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):206–212. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.206-212.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dalrymple M. A., Davison A. J., Dolan A., Frame M. C., McNab D., Perry L. J., Scott J. E., Taylor P. The complete DNA sequence of the long unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jul;69(Pt 7):1531–1574. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-7-1531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Kent S. B. The pre-S region of hepadnavirus envelope proteins. Adv Virus Res. 1988;34:65–142. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60516-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston V. G., Coates J. A., Rixon F. J. Identification and characterization of a herpes simplex virus gene product required for encapsidation of virus DNA. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1056–1064. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.1056-1064.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy V. B., Dhar R., Weissman S. M. Nucleotides sequence of the genes for the simian virus 40 proteins VP2 and VP3. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 25;253(2):621–630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson L., Gibson W. Primate cytomegalovirus assembly protein: genome location and nucleotide sequence. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):669–676. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.669-676.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozenblatt S., Mulligan R. C., Gorecki M., Roberts B. E., Rich A. Direct biochemical mapping of eukaryotic viral DNA by means of a linked transcription-translation cell-free system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2747–2751. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo R. N., Shaper N. L., Shaper J. H. Bovine beta 1----4-galactosyltransferase: two sets of mRNA transcripts encode two forms of the protein with different amino-terminal domains. In vitro translation experiments demonstrate that both the short and the long forms of the enzyme are type II membrane-bound glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3324–3331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenk P., Pietschmann S., Gelderblom H., Pauli G., Ludwig H., Schenck P. Monoclonal antibodies against herpes simplex virus type 1-infected nuclei defining and localizing the ICP8 protein, 65K DNA-binding protein and polypeptides of the ICP35 family. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jan;69(Pt 1):99–111. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-1-99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenk P., Woods A. S., Gibson W. The 45-kilodalton protein of cytomegalovirus (Colburn) B-capsids is an amino-terminal extension form of the assembly protein. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1525–1529. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1525-1529.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. E., Murialdo H. Morphogenetic genes C and Nu3 overlap in bacteriophage lambda. Nature. 1980 Jan 3;283(5742):30–35. doi: 10.1038/283030a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman G., Bachenheimer S. L. Characterization of intranuclear capsids made by ts morphogenic mutants of HSV-1. Virology. 1988 Apr;163(2):471–480. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90288-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wobbe C. R., Struhl K. Yeast and human TATA-binding proteins have nearly identical DNA sequence requirements for transcription in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):3859–3867. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.3859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweig M., Heilman C. J., Jr, Rabin H., Hampar B. Shared antigenic determinants between two distinct classes of proteins in cells infected with herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):644–652. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.644-652.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]