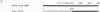Abstract
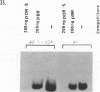
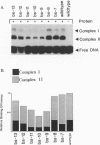
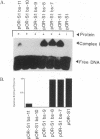
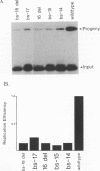
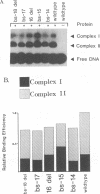
The herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) OriS region resides within a 90-bp sequence that contains two binding sites for the origin-binding protein (OBP), designated sites I and II. A third presumptive OBP-binding site (III) within OriS has strong sequence similarity to sites I and II, but no sequence-specific OBP binding has yet been demonstrated at this site. We have generated mutations in sites I, II, and III and determined their replication efficiencies in a transient in vivo assay in the presence of a helper virus. Mutations in any one of the sites reduced DNA replication significantly. To study the role of OriS sequence elements in site I and the presumptive site III in DNA replication, we have also generated a series of mutations that span from site I across the presumptive binding site III. These mutants were tested for their ability to replicate and for the ability to bind OBP by using gel shift analyses. The results indicate that mutations across site I drastically reduce DNA replication. Triple-base-pair substitution mutations that fall within the crucial OBP-binding domain, 5'-YGYTCGCACT-3' (where Y represents C or T), show a reduced level of OBP binding and DNA replication. Substitution mutations in site I that are outside this crucial binding sequence show a more detrimental effect on DNA replication than on OBP binding. This suggests that these sequences are required for initiation of DNA replication but are not critical for OBP binding. Mutations across the presumptive OBP-binding site III also resulted in a loss in efficiency of DNA replication. These mutations influenced OBP binding to OriS in gel shift assays, even though the mutated sequences are not contained within known OBP-binding sites. Replacement of the wild-type site III with a perfect OBP-binding site I results in a drastic reduction of DNA replication. Thus, our DNA replication assays and in vitro DNA-binding studies suggest that the binding of the origin sequence by OBP is not the only determining factor for initiation of DNA replication in vivo.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumann R. P., Yalamanchili V. R., O'Callaghan D. J. Functional mapping and DNA sequence of an equine herpesvirus 1 origin of replication. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1275–1283. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1275-1283.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramhill D., Kornberg A. A model for initiation at origins of DNA replication. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):915–918. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90102-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLucia A. L., Deb S., Partin K., Tegtmeyer P. Functional interactions of the simian virus 40 core origin of replication with flanking regulatory sequences. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):138–144. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.138-144.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deb S., DeLucia A. L., Baur C. P., Koff A., Tegtmeyer P. Domain structure of the simian virus 40 core origin of replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1663–1670. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deb S., DeLucia A. L., Koff A., Tsui S., Tegtmeyer P. The adenine-thymine domain of the simian virus 40 core origin directs DNA bending and coordinately regulates DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4578–4584. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deb S., Deb S. P. A 269-amino-acid segment with a pseudo-leucine zipper and a helix-turn-helix motif codes for the sequence-specific DNA-binding domain of herpes simplex virus type 1 origin-binding protein. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):2829–2838. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.2829-2838.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deb S., Deb S. P. Analysis of Ori-S sequence of HSV-1: identification of one functional DNA binding domain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 11;17(7):2733–2752. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.7.2733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deb S., Doelberg M. A 67-base-pair segment from the Ori-S region of herpes simplex virus type 1 encodes origin function. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2516–2519. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2516-2519.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deb S., Tsui S., Koff A., DeLucia A. L., Parsons R., Tegtmeyer P. The T-antigen-binding domain of the simian virus 40 core origin of replication. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2143–2149. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2143-2149.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P., Gustafsson C. M., Hammarsten O. The origin binding protein of herpes simplex virus 1 binds cooperatively to the viral origin of replication oris. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17167–17173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P., Lehman I. R. Interaction of origin binding protein with an origin of replication of herpes simplex virus 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):2959–2963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.2959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P., O'Donnell M. E., Mocarski E. S., Lehman I. R. A DNA binding protein specific for an origin of replication of herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6322–6326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel N., Jacob R. J., Honess R. W., Hayward G. S., Locker H., Roizman B. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA. III. Characterization of defective DNA molecules and biological properties of virus populations containing them. J Virol. 1975 Jul;16(1):153–167. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.1.153-167.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkeĺ N., Locker H., Batterson W., Hayward G. S., Roizman B. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA. VI. Defective DNA originates from the S component. J Virol. 1976 Nov;20(2):527–531. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.2.527-531.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez T. R., Dutch R. E., Lehman I. R., Gustafsson C., Elias P. Mutations in a herpes simplex virus type 1 origin that inhibit interaction with origin-binding protein also inhibit DNA replication. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1649–1652. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1649-1652.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaerner H. C., Maichle I. B., Ott A., Schröder C. H. Origin of two different classes of defective HSV-1 Angelotti DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Apr;6(4):1467–1478. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.4.1467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaerner H. C., Ott-Hartmann A., Schatten R., Schröder C. H., Gray C. P. Amplification of a short nucleotide sequence in the repeat units of defective herpes simplex virus type 1 Angelotti DNA. J Virol. 1981 Jul;39(1):75–81. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.1.75-81.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koff A., Tegtmeyer P. Characterization of major recognition sequences for a herpes simplex virus type 1 origin-binding protein. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4096–4103. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4096-4103.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockshon D., Galloway D. A. Cloning and characterization of oriL2, a large palindromic DNA replication origin of herpes simplex virus type 2. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):513–521. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.513-521.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockshon D., Galloway D. A. Sequence and structural requirements of a herpes simplex viral DNA replication origin. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4018–4027. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dalrymple M. A., Davison A. J., Dolan A., Frame M. C., McNab D., Perry L. J., Scott J. E., Taylor P. The complete DNA sequence of the long unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jul;69(Pt 7):1531–1574. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-7-1531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dalrymple M. A., Dolan A., McNab D., Perry L. J., Taylor P., Challberg M. D. Structures of herpes simplex virus type 1 genes required for replication of virus DNA. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):444–453. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.444-453.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocarski E. S., Roizman B. Herpesvirus-dependent amplification and inversion of cell-associated viral thymidine kinase gene flanked by viral a sequences and linked to an origin of viral DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5626–5630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivo P. D., Nelson N. J., Challberg M. D. Herpes simplex virus DNA replication: the UL9 gene encodes an origin-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5414–5418. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaete R. R., Frenkel N. The herpes simplex virus amplicon: a new eucaryotic defective-virus cloning-amplifying vector. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):295–304. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90035-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., Davison A. J. Identification of a varicella-zoster virus origin of DNA replication and its activation by herpes simplex virus type 1 gene products. J Gen Virol. 1986 Aug;67(Pt 8):1613–1623. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-8-1613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., McMonagle E. C. Characterization of the TRS/IRS origin of DNA replication of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1983 Oct 30;130(2):427–438. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90097-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir H. M., Stow N. D. Two binding sites for the herpes simplex virus type 1 UL9 protein are required for efficient activity of the oriS replication origin. J Gen Virol. 1990 Jun;71(Pt 6):1379–1385. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-6-1379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller S. K., Spadaro A., Schaffer J. E., Murray A. W., Maxam A. M., Schaffer P. A. Cloning, sequencing, and functional analysis of oriL, a herpes simplex virus type 1 origin of DNA synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):930–942. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitton J. L., Clements J. B. Replication origins and a sequence involved in coordinate induction of the immediate-early gene family are conserved in an intergenic region of herpes simplex virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 24;12(4):2061–2079. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.4.2061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. A., Nelson N. J., McGeoch D. J., Challberg M. D. Identification of herpes simplex virus type 1 genes required for origin-dependent DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):435–443. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.435-443.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]