Abstract
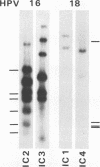
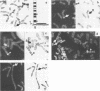
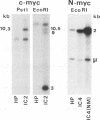
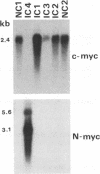
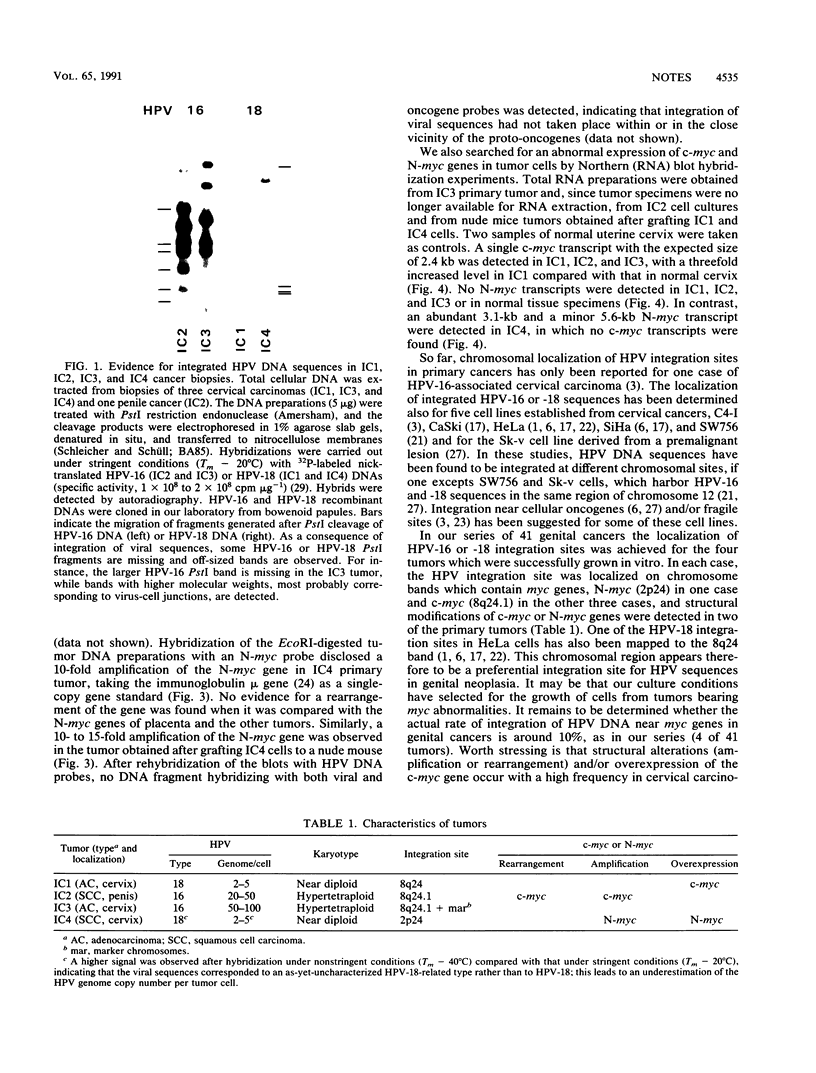
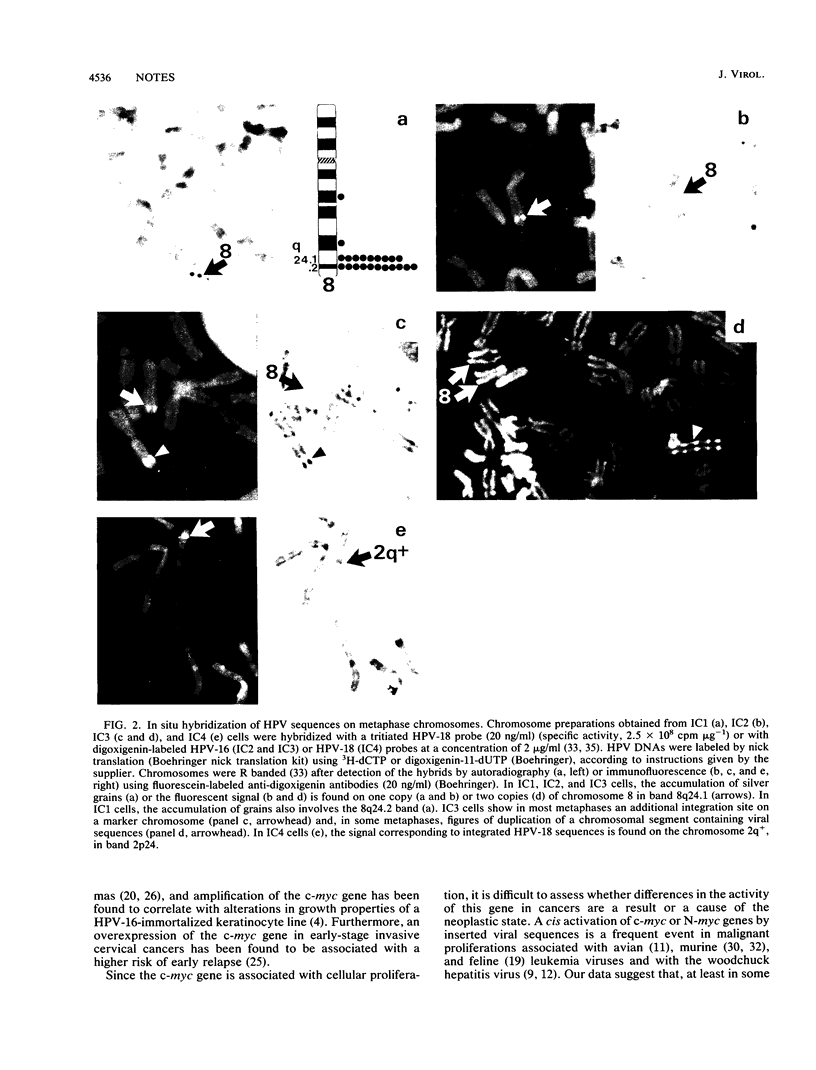
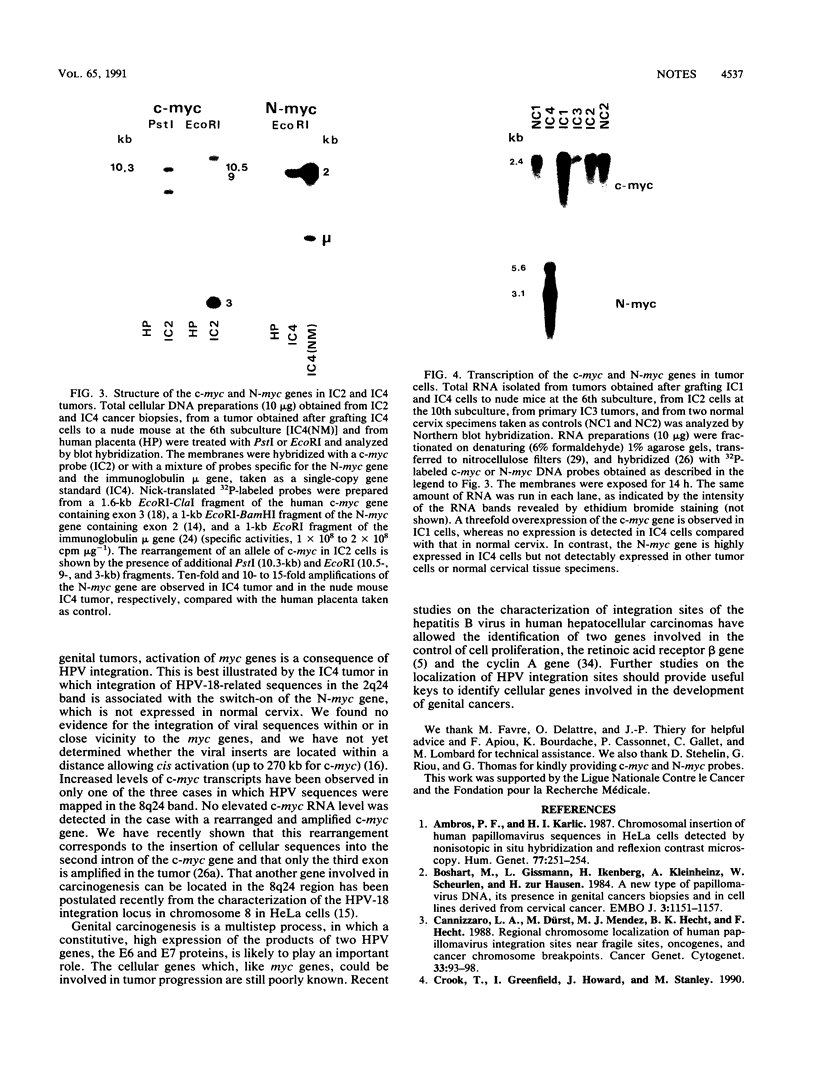
DNA sequences of specific human papillomavirus (HPV) types are found integrated in the cell genome in most invasive genital carcinomas. We have determined the chromosomal localization of integrated HPV type 16 (HPV-16) or HPV-18 genomes in genital cancers by in situ hybridization experiments. In three cancers, HPV sequences were localized in chromosome band 8q24.1, in which the c-myc gene is mapped, and in one cancer HPV sequences were localized in chromosome band 2p24, which contains the N-myc gene. In three of the four cases, the proto-oncogene located near integrated viral sequences was found to be structurally altered and/or overexpressed. These data indicate that HPV genomes are preferentially integrated near myc genes in invasive genital cancers and support the hypothesis that integration plays a part in tumor progression via an activation of cellular oncogenes.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambros P. F., Karlic H. I. Chromosomal insertion of human papillomavirus 18 sequences in HeLa cells detected by nonisotopic in situ hybridization and reflection contrast microscopy. Hum Genet. 1987 Nov;77(3):251–254. doi: 10.1007/BF00284479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Gissmann L., Ikenberg H., Kleinheinz A., Scheurlen W., zur Hausen H. A new type of papillomavirus DNA, its presence in genital cancer biopsies and in cell lines derived from cervical cancer. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1151–1157. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01944.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannizzaro L. A., Dürst M., Mendez M. J., Hecht B. K., Hecht F. Regional chromosome localization of human papillomavirus integration sites near fragile sites, oncogenes, and cancer chromosome breakpoints. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1988 Jul 1;33(1):93–98. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(88)90054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürst M., Croce C. M., Gissmann L., Schwarz E., Huebner K. Papillomavirus sequences integrate near cellular oncogenes in some cervical carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1070–1074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürst M., Gissmann L., Ikenberg H., zur Hausen H. A papillomavirus DNA from a cervical carcinoma and its prevalence in cancer biopsy samples from different geographic regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3812–3815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürst M., Kleinheinz A., Hotz M., Gissmann L. The physical state of human papillomavirus type 16 DNA in benign and malignant genital tumours. J Gen Virol. 1985 Jul;66(Pt 7):1515–1522. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-7-1515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fourel G., Trepo C., Bougueleret L., Henglein B., Ponzetto A., Tiollais P., Buendia M. A. Frequent activation of N-myc genes by hepadnavirus insertion in woodchuck liver tumours. Nature. 1990 Sep 20;347(6290):294–298. doi: 10.1038/347294a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritsch E. F., Lawn R. M., Maniatis T. Molecular cloning and characterization of the human beta-like globin gene cluster. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):959–972. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90087-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward W. S., Neel B. G., Astrin S. M. Activation of a cellular onc gene by promoter insertion in ALV-induced lymphoid leukosis. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):475–480. doi: 10.1038/290475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu T., Möröy T., Etiemble J., Louise A., Trépo C., Tiollais P., Buendia M. A. Activation of c-myc by woodchuck hepatitis virus insertion in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):627–635. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90221-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl N. E., Legouy E., DePinho R. A., Nisen P. D., Smith R. K., Gee C. E., Alt F. W. Human N-myc is closely related in organization and nucleotide sequence to c-myc. Nature. 1986 Jan 2;319(6048):73–77. doi: 10.1038/319073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazo P. A., DiPaolo J. A., Popescu N. C. Amplification of the integrated viral transforming genes of human papillomavirus 18 and its 5'-flanking cellular sequence located near the myc protooncogene in HeLa cells. Cancer Res. 1989 Aug 1;49(15):4305–4310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazo P. A., Lee J. S., Tsichlis P. N. Long-distance activation of the Myc protooncogene by provirus insertion in Mlvi-1 or Mlvi-4 in rat T-cell lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):170–173. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mincheva A., Gissmann L., zur Hausen H. Chromosomal integration sites of human papillomavirus DNA in three cervical cancer cell lines mapped by in situ hybridization. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1987;176(5):245–256. doi: 10.1007/BF00190531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modjtahedi N., Lavialle C., Poupon M. F., Landin R. M., Cassingena R., Monier R., Brison O. Increased level of amplification of the c-myc oncogene in tumors induced in nude mice by a human breast carcinoma cell line. Cancer Res. 1985 Sep;45(9):4372–4379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neil J. C., Hughes D., McFarlane R., Wilkie N. M., Onions D. E., Lees G., Jarrett O. Transduction and rearrangement of the myc gene by feline leukaemia virus in naturally occurring T-cell leukaemias. 1984 Apr 26-May 2Nature. 308(5962):814–820. doi: 10.1038/308814a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ocadiz R., Sauceda R., Cruz M., Graef A. M., Gariglio P. High correlation between molecular alterations of the c-myc oncogene and carcinoma of the uterine cervix. Cancer Res. 1987 Aug 1;47(15):4173–4177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popescu N. C., Amsbaugh S. C., DiPaolo J. A. Human papillomavirus type 18 DNA is integrated at a single chromosome site in cervical carcinoma cell line SW756. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1682–1685. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1682-1685.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popescu N. C., DiPaolo J. A., Amsbaugh S. C. Integration sites of human papillomavirus 18 DNA sequences on HeLa cell chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1987;44(1):58–62. doi: 10.1159/000132342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popescu N. C., Zimonjic D., DiPaolo J. A. Viral integration, fragile sites, and proto-oncogenes in human neoplasia. Hum Genet. 1990 Apr;84(5):383–386. doi: 10.1007/BF00195804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravetch J. V., Siebenlist U., Korsmeyer S., Waldmann T., Leder P. Structure of the human immunoglobulin mu locus: characterization of embryonic and rearranged J and D genes. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):583–591. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90400-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riou G., Barrois M., Lê M. G., George M., Le Doussal V., Haie C. C-myc proto-oncogene expression and prognosis in early carcinoma of the uterine cervix. Lancet. 1987 Apr 4;1(8536):761–763. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92795-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sastre-Garau X., Schneider-Maunoury S., Couturier J., Orth G. Human papillomavirus type 16 DNA is integrated into chromosome region 12q14-q15 in a cell line derived from a vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1990 Feb;44(2):243–251. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(90)90053-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider-Gädicke A., Schwarz E. Different human cervical carcinoma cell lines show similar transcription patterns of human papillomavirus type 18 early genes. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2285–2292. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04496.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider-Maunoury S., Croissant O., Orth G. Integration of human papillomavirus type 16 DNA sequences: a possible early event in the progression of genital tumors. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3295–3298. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3295-3298.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selten G., Cuypers H. T., Zijlstra M., Melief C., Berns A. Involvement of c-myc in MuLV-induced T cell lymphomas in mice: frequency and mechanisms of activation. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3215–3222. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02281.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M., Green H. Enzymatic cross-linking of involucrin and other proteins by keratinocyte particulates in vitro. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):677–683. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90216-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viegas-Pequignot E., Dutrillaux B., Magdelenat H., Coppey-Moisan M. Mapping of single-copy DNA sequences on human chromosomes by in situ hybridization with biotinylated probes: enhancement of detection sensitivity by intensified-fluorescence digital-imaging microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):582–586. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J., Chenivesse X., Henglein B., Bréchot C. Hepatitis B virus integration in a cyclin A gene in a hepatocellular carcinoma. Nature. 1990 Feb 8;343(6258):555–557. doi: 10.1038/343555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabel B. U., Naylor S. L., Sakaguchi A. Y., Bell G. I., Shows T. B. High-resolution chromosomal localization of human genes for amylase, proopiomelanocortin, somatostatin, and a DNA fragment (D3S1) by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6932–6936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Thé H., Marchio A., Tiollais P., Dejean A. A novel steroid thyroid hormone receptor-related gene inappropriately expressed in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):667–670. doi: 10.1038/330667a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Lohuizen M., Breuer M., Berns A. N-myc is frequently activated by proviral insertion in MuLV-induced T cell lymphomas. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):133–136. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03357.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H. Papillomaviruses in anogenital cancer as a model to understand the role of viruses in human cancers. Cancer Res. 1989 Sep 1;49(17):4677–4681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]