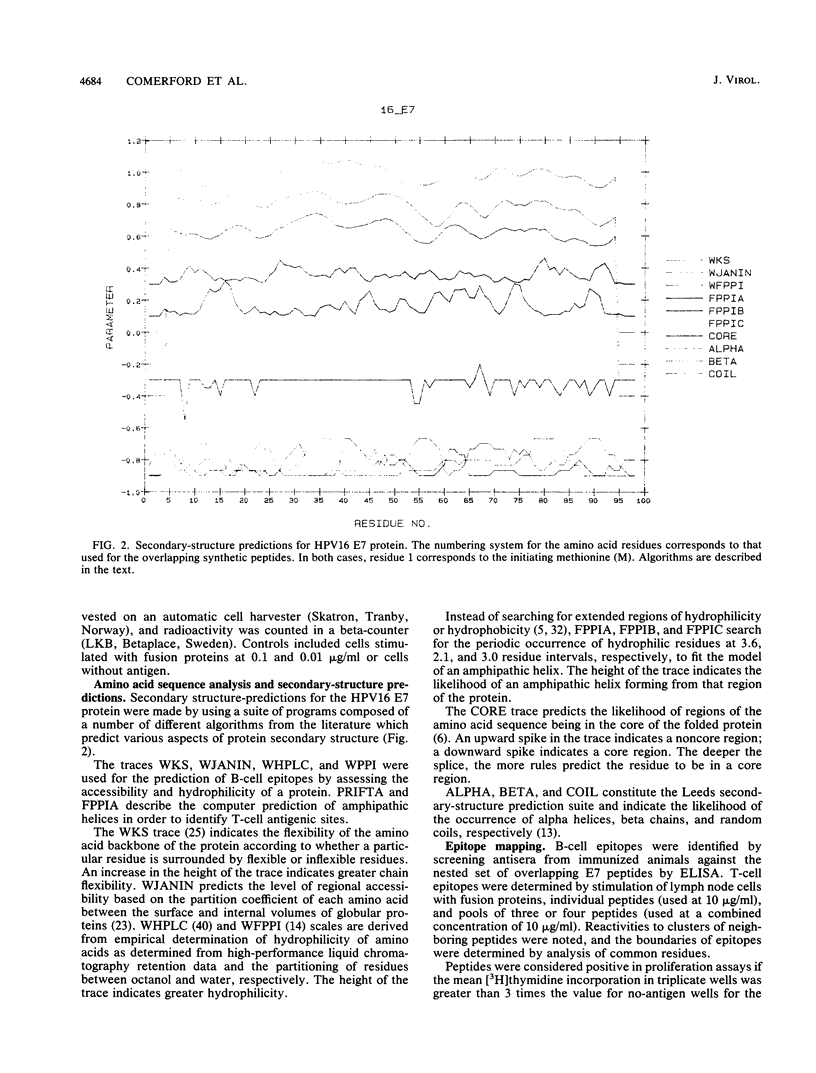
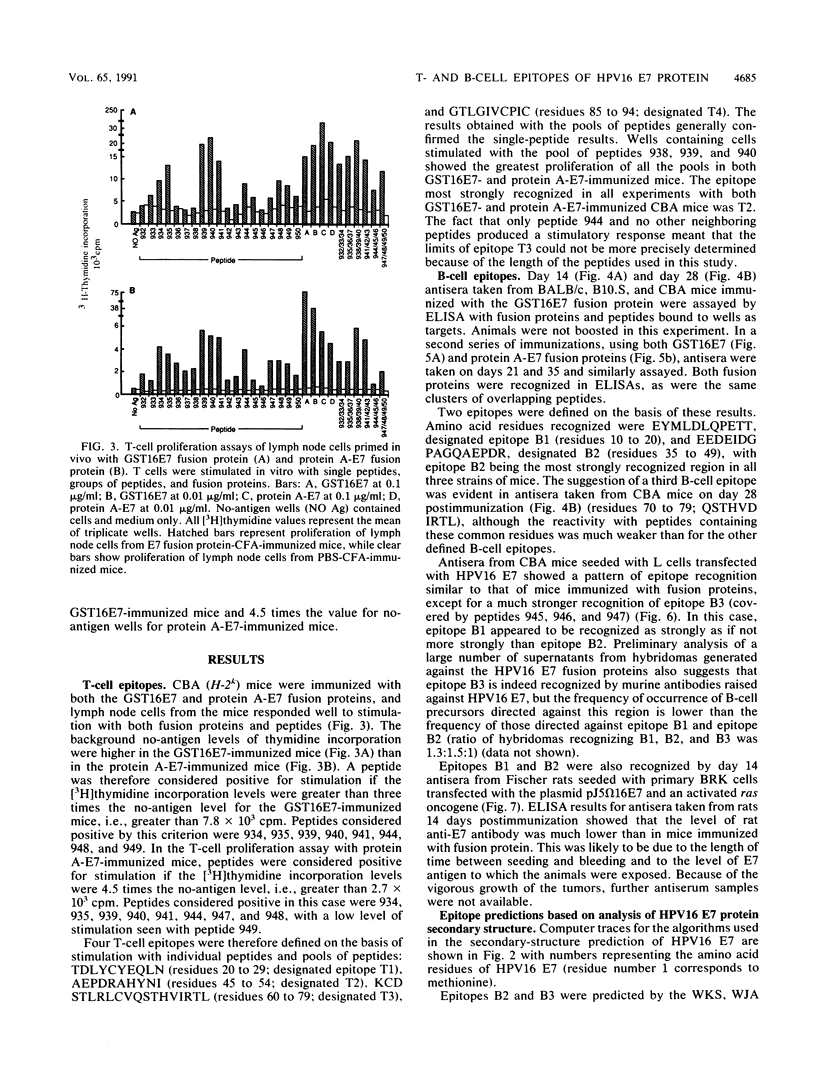
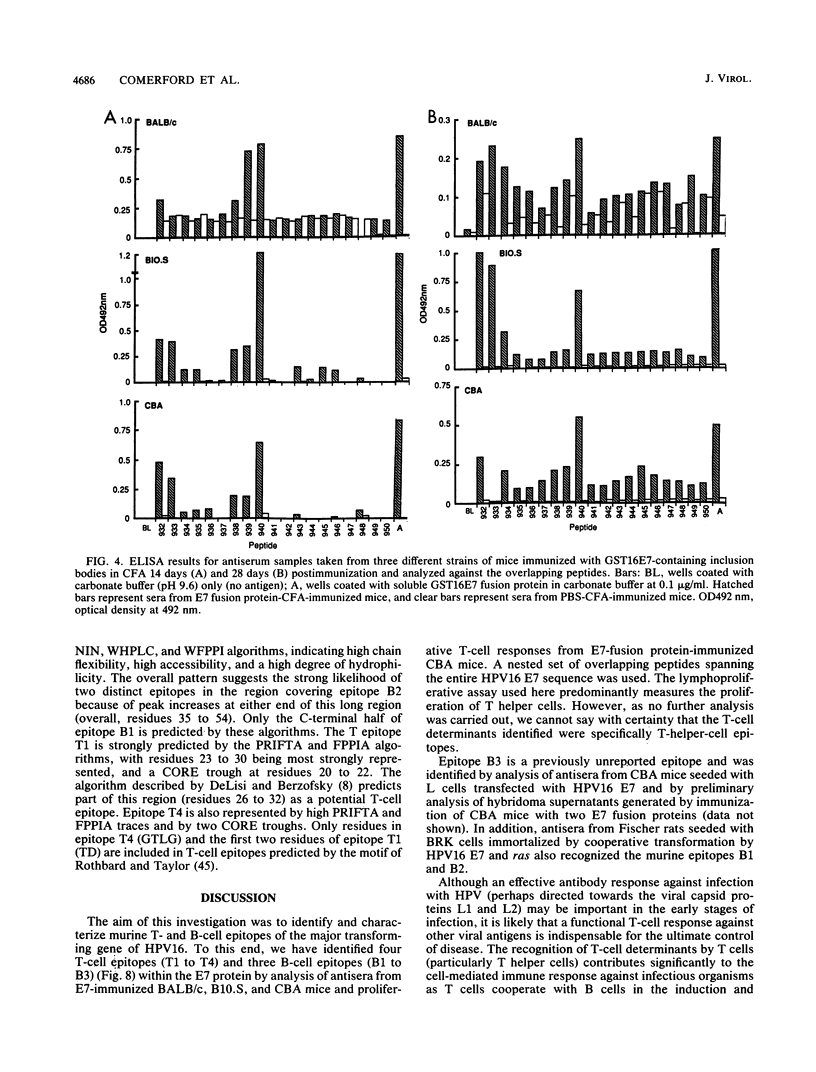
Abstract
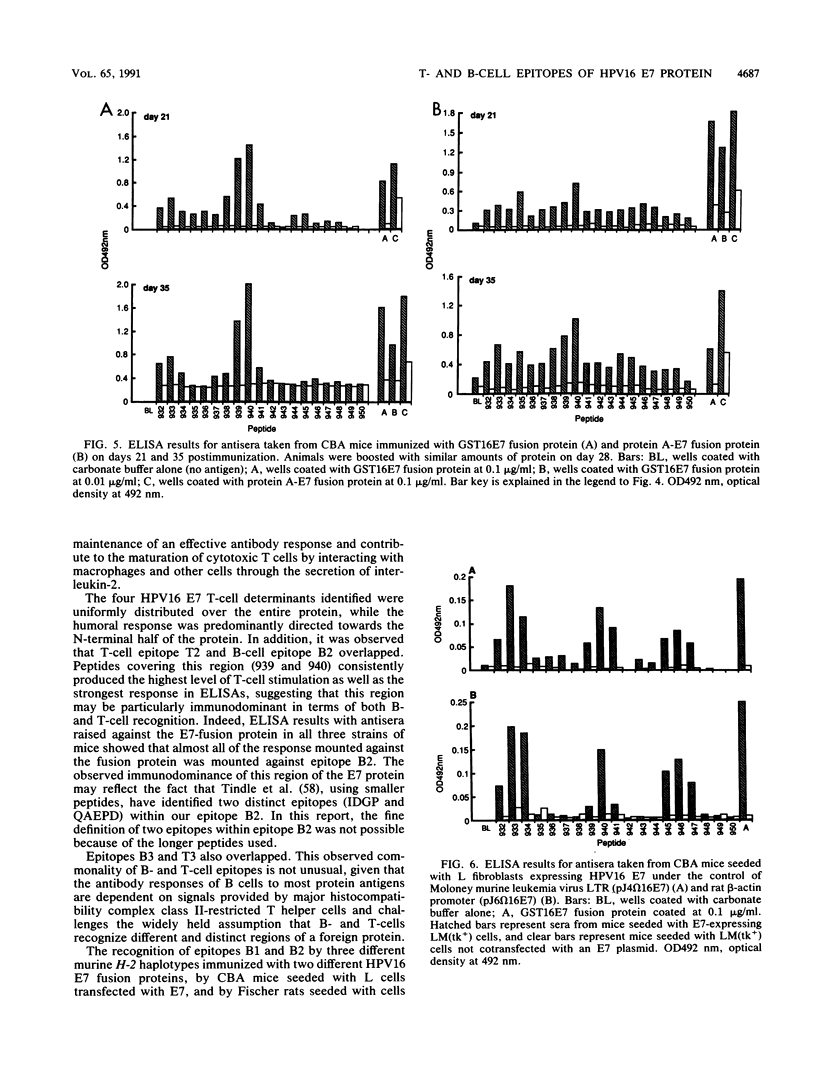
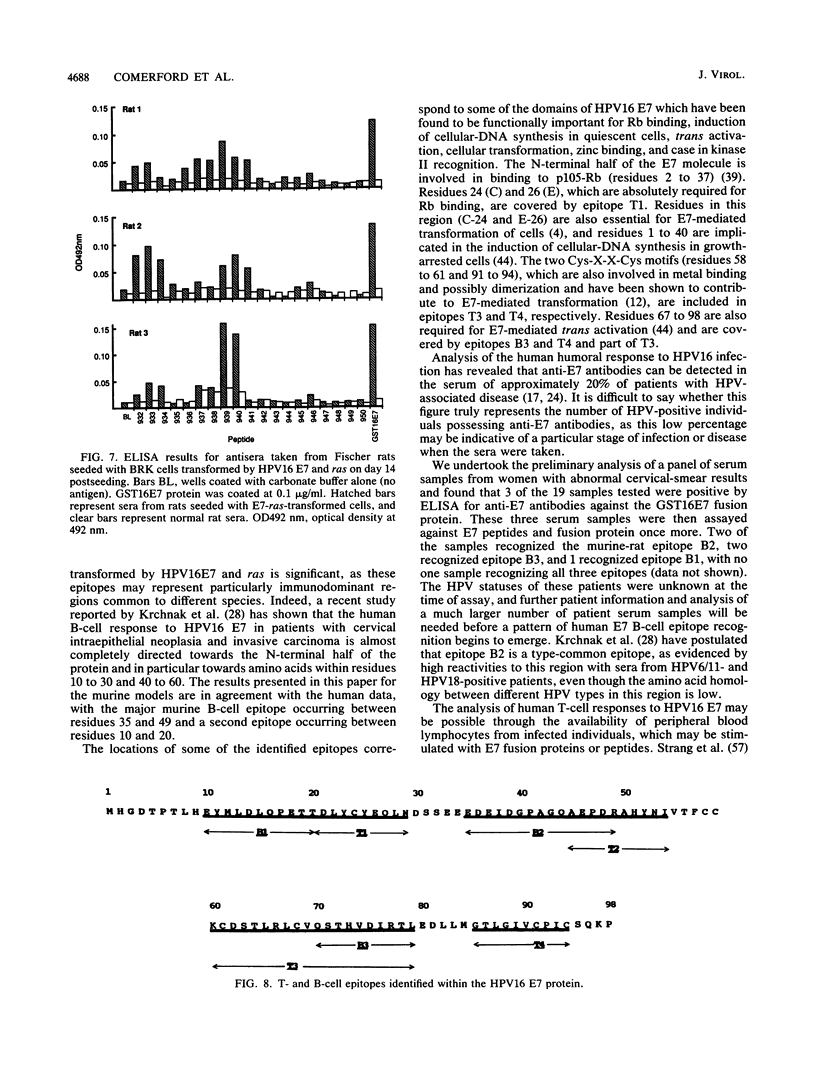
There is strong evidence implicating human papillomavirus type 16 (HPV16) in the genesis of human genital cancer. Viral DNA has been identified in invasive carcinoma of the uterine cervix and in cell lines derived from cervical carcinomas. These sequences are actively transcribed, and translation products corresponding to the early (E)-region genes have been identified. The most abundant viral protein is the E7 protein, which has been shown to possess transforming activity for both established and primary cells. In addition, it has been shown to bind to a cellular tumor suppressor, the retinoblastoma gene product (pRb-105). In view of these properties, we have undertaken the immunological analysis of this protein and have identified four T-cell epitopes and three B-cell epitopes by using a series of overlapping peptides spanning the entire HPV16 E7 sequence. Two of the B-cell epitopes were recognized by antisera from mice with three different murine (H-2) haplotypes (k, d, and s) immunized with two different E7 fusion proteins and from Fischer rats seeded with baby rat kidney cells transformed by HPV16 E7 and ras. A third B-cell epitope was recognized by antisera from CBA mice seeded with HPV16 E7-expressing L cells. Two regions of the protein contain common B- and T-cell epitopes, one of which appears to be particularly immunodominant.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chapes S. K., Gooding L. R. Evidence for the involvement of cytolytic macrophages in rejection of SV40-induced tumors. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):2192–2198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. P., Thomas E. K., Hu S. L., Hellström I., Hellström K. E. Human papillomavirus type 16 nucleoprotein E7 is a tumor rejection antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):110–114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesters P. M., Vousden K. H., Edmonds C., McCance D. J. Analysis of human papillomavirus type 16 open reading frame E7 immortalizing function in rat embryo fibroblast cells. J Gen Virol. 1990 Feb;71(Pt 2):449–453. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-2-449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornette J. L., Cease K. B., Margalit H., Spouge J. L., Berzofsky J. A., DeLisi C. Hydrophobicity scales and computational techniques for detecting amphipathic structures in proteins. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 5;195(3):659–685. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90189-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crampin J., Nicholson B. H., Robson B. Protein folding and heterogeneity inside globular proteins. Nature. 1978 Apr 6;272(5653):558–560. doi: 10.1038/272558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crook T., Morgenstern J. P., Crawford L., Banks L. Continued expression of HPV-16 E7 protein is required for maintenance of the transformed phenotype of cells co-transformed by HPV-16 plus EJ-ras. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):513–519. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03405.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLisi C., Berzofsky J. A. T-cell antigenic sites tend to be amphipathic structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):7048–7052. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.7048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson N., Howley P. M., Münger K., Harlow E. The human papilloma virus-16 E7 oncoprotein is able to bind to the retinoblastoma gene product. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):934–937. doi: 10.1126/science.2537532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürst M., Gissmann L., Ikenberg H., zur Hausen H. A papillomavirus DNA from a cervical carcinoma and its prevalence in cancer biopsy samples from different geographic regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3812–3815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürst M., Kleinheinz A., Hotz M., Gissmann L. The physical state of human papillomavirus type 16 DNA in benign and malignant genital tumours. J Gen Virol. 1985 Jul;66(Pt 7):1515–1522. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-7-1515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds C., Vousden K. H. A point mutational analysis of human papillomavirus type 16 E7 protein. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2650–2656. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2650-2656.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay C. A., Hinds P. W., Levine A. J. The p53 proto-oncogene can act as a suppressor of transformation. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1083–1093. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90045-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frazer I. H., Medley G., Crapper R. M., Brown T. C., Mackay I. R. Association between anorectal dysplasia, human papillomavirus, and human immunodeficiency virus infection in homosexual men. Lancet. 1986 Sep 20;2(8508):657–660. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90168-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway D. A., Jenison S. A. Characterization of the humoral immune response to genital papillomaviruses. Mol Biol Med. 1990 Feb;7(1):59–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gissmann L., Wolnik L., Ikenberg H., Koldovsky U., Schnürch H. G., zur Hausen H. Human papillomavirus types 6 and 11 DNA sequences in genital and laryngeal papillomas and in some cervical cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):560–563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpert R., Fruchter R. G., Sedlis A., Butt K., Boyce J. G., Sillman F. H. Human papillomavirus and lower genital neoplasia in renal transplant patients. Obstet Gynecol. 1986 Aug;68(2):251–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghten R. A. General method for the rapid solid-phase synthesis of large numbers of peptides: specificity of antigen-antibody interaction at the level of individual amino acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5131–5135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang H. J., Yee J. K., Shew J. Y., Chen P. L., Bookstein R., Friedmann T., Lee E. Y., Lee W. H. Suppression of the neoplastic phenotype by replacement of the RB gene in human cancer cells. Science. 1988 Dec 16;242(4885):1563–1566. doi: 10.1126/science.3201247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janin J. Surface and inside volumes in globular proteins. Nature. 1979 Feb 8;277(5696):491–492. doi: 10.1038/277491a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jochmus-Kudielka I., Schneider A., Braun R., Kimmig R., Koldovsky U., Schneweis K. E., Seedorf K., Gissmann L. Antibodies against the human papillomavirus type 16 early proteins in human sera: correlation of anti-E7 reactivity with cervical cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1989 Nov 15;81(22):1698–1704. doi: 10.1093/jnci/81.22.1698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kast W. M., Offringa R., Peters P. J., Voordouw A. C., Meloen R. H., van der Eb A. J., Melief C. J. Eradication of adenovirus E1-induced tumors by E1A-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):603–614. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchner H. Immunobiology of human papillomavirus infection. Prog Med Virol. 1986;33:1–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krchnák V., Vágner J., Suchánková A., Krcmár M., Ritterová L., Vonka V. Synthetic peptides derived from E7 region of human papillomavirus type 16 used as antigens in ELISA. J Gen Virol. 1990 Nov;71(Pt 11):2719–2724. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-11-2719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronenberg M., Siu G., Hood L. E., Shastri N. The molecular genetics of the T-cell antigen receptor and T-cell antigen recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:529–591. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.002525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathe R., Kieny M. P., Gerlinger P., Clertant P., Guizani I., Cuzin F., Chambon P. Tumour prevention and rejection with recombinant vaccinia. 1987 Apr 30-May 6Nature. 326(6116):878–880. doi: 10.1038/326878a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malejczyk J., Majewski S., Jablonska S., Rogozinski T. T., Orth G. Abrogated NK-cell lysis of human papillomavirus (HPV)-16-bearing keratinocytes in patients with pre-cancerous and cancerous HPV-induced anogenital lesions. Int J Cancer. 1989 Feb 15;43(2):209–214. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910430206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margalit H., Spouge J. L., Cornette J. L., Cease K. B., Delisi C., Berzofsky J. A. Prediction of immunodominant helper T cell antigenic sites from the primary sequence. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2213–2229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlashewski G., Schneider J., Banks L., Jones N., Murray A., Crawford L. Human papillomavirus type 16 DNA cooperates with activated ras in transforming primary cells. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1741–1746. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02426.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCance D. J., Singer A., Campion M. J. DNA hybridisation of cervical smears. Lancet. 1985 Mar 2;1(8427):514–514. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92109-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCance D. J., Walker P. G., Dyson J. L., Coleman D. V., Singer A. Presence of human papillomavirus DNA sequences in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Sep 17;287(6395):784–788. doi: 10.1136/bmj.287.6395.784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. C., Spence A., Smith M. The distal transcription signals of the herpesvirus tk gene share a common hexanucleotide control sequence. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90321-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morison W. L. Viral warts, herpes simplex and herpes zoster in patients with secondary immune deficiencies and neoplasms. Br J Dermatol. 1975 Jun;92(6):625–630. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1975.tb03141.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullis K. B., Faloona F. A. Specific synthesis of DNA in vitro via a polymerase-catalyzed chain reaction. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:335–350. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Münger K., Werness B. A., Dyson N., Phelps W. C., Harlow E., Howley P. M. Complex formation of human papillomavirus E7 proteins with the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor gene product. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4099–4105. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08594.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker J. M., Guo D., Hodges R. S. New hydrophilicity scale derived from high-performance liquid chromatography peptide retention data: correlation of predicted surface residues with antigenicity and X-ray-derived accessible sites. Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 23;25(19):5425–5432. doi: 10.1021/bi00367a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfister H. Biology and biochemistry of papillomaviruses. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1984;99:111–181. doi: 10.1007/BFb0027716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps W. C., Yee C. L., Münger K., Howley P. M. The human papillomavirus type 16 E7 gene encodes transactivation and transformation functions similar to those of adenovirus E1A. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):539–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90570-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirisi L., Yasumoto S., Feller M., Doniger J., DiPaolo J. A. Transformation of human fibroblasts and keratinocytes with human papillomavirus type 16 DNA. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1061–1066. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1061-1066.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawls J. A., Pusztai R., Green M. Chemical synthesis of human papillomavirus type 16 E7 oncoprotein: autonomous protein domains for induction of cellular DNA synthesis and for trans activation. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6121–6129. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6121-6129.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothbard J. B., Taylor W. R. A sequence pattern common to T cell epitopes. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):93–100. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02787.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Phelps W. C., Zhang Y. L., Barbosa M. Quantitative keratinocyte assay detects two biological activities of human papillomavirus DNA and identifies viral types associated with cervical carcinoma. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3181–3187. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03185.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider V., Kay S., Lee H. M. Immunosuppression as a high-risk factor in the development of condyloma acuminatum and squamous neoplasia of the cervix. Acta Cytol. 1983 May-Jun;27(3):220–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seedorf K., Krämmer G., Dürst M., Suhai S., Röwekamp W. G. Human papillomavirus type 16 DNA sequence. Virology. 1985 Aug;145(1):181–185. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90214-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seedorf K., Oltersdorf T., Krämmer G., Röwekamp W. Identification of early proteins of the human papilloma viruses type 16 (HPV 16) and type 18 (HPV 18) in cervical carcinoma cells. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):139–144. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04731.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih C., Weinberg R. A. Isolation of a transforming sequence from a human bladder carcinoma cell line. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):161–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smotkin D. Virology of human papillomavirus. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 1989 Mar;32(1):117–126. doi: 10.1097/00003081-198903000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer E. S., Andersen H. K. Clinically evident, non-terminal infections with herpesviruses and the wart virus in immunosuppressed renal allograft recipients. Br Med J. 1970 Aug 1;3(5717):251–254. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5717.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storey A., Pim D., Murray A., Osborn K., Banks L., Crawford L. Comparison of the in vitro transforming activities of human papillomavirus types. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1815–1820. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03013.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strang G., Hickling J. K., McIndoe G. A., Howland K., Wilkinson D., Ikeda H., Rothbard J. B. Human T cell responses to human papillomavirus type 16 L1 and E6 synthetic peptides: identification of T cell determinants, HLA-DR restriction and virus type specificity. J Gen Virol. 1990 Feb;71(Pt 2):423–431. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-2-423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tindle R. W., Smith J. A., Geysen H. M., Selvey L. A., Frazer I. H. Identification of B epitopes in human papillomavirus type 16 E7 open reading frame protein. J Gen Virol. 1990 Jun;71(Pt 6):1347–1354. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-6-1347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Sweet R., Sim G. K., Wold B., Pellicer A., Lacy E., Maniatis T., Silverstein S., Axel R. Transformation of mammalian cells with genes from procaryotes and eucaryotes. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasumoto S., Burkhardt A. L., Doniger J., DiPaolo J. A. Human papillomavirus type 16 DNA-induced malignant transformation of NIH 3T3 cells. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):572–577. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.572-577.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabeau M., Stanley K. K. Enhanced expression of cro-beta-galactosidase fusion proteins under the control of the PR promoter of bacteriophage lambda. EMBO J. 1982;1(10):1217–1224. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb00016.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]