Abstract
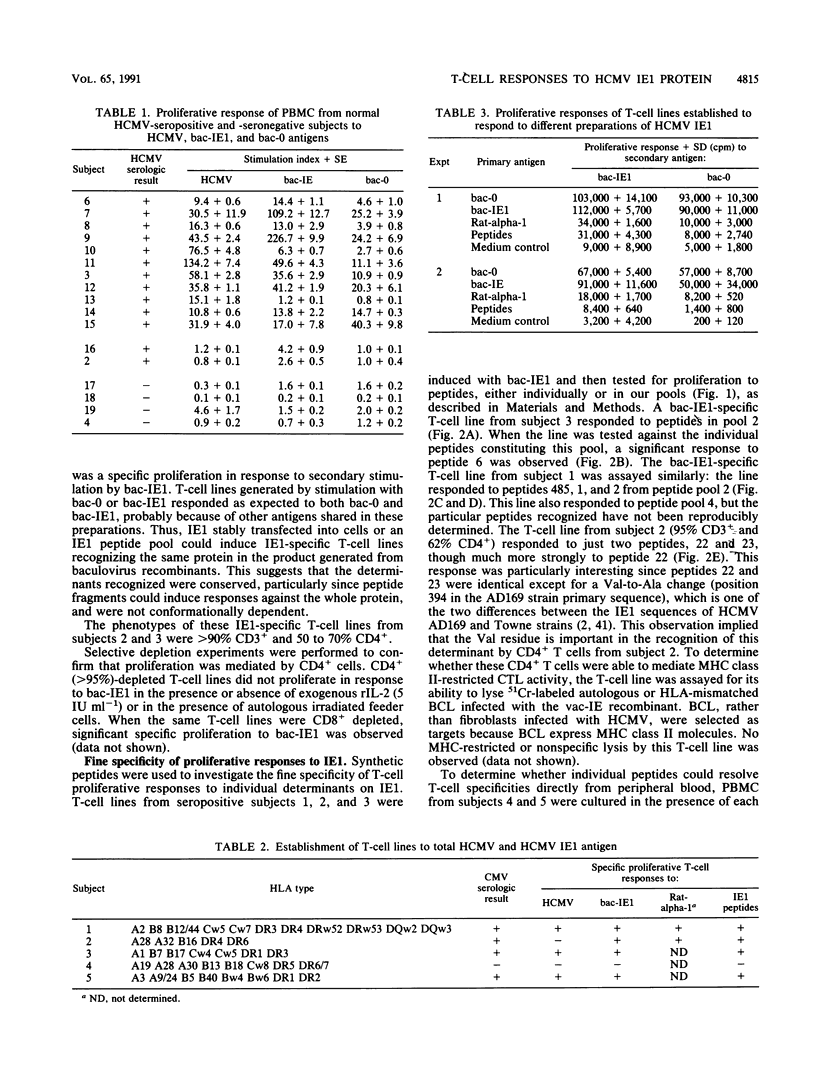
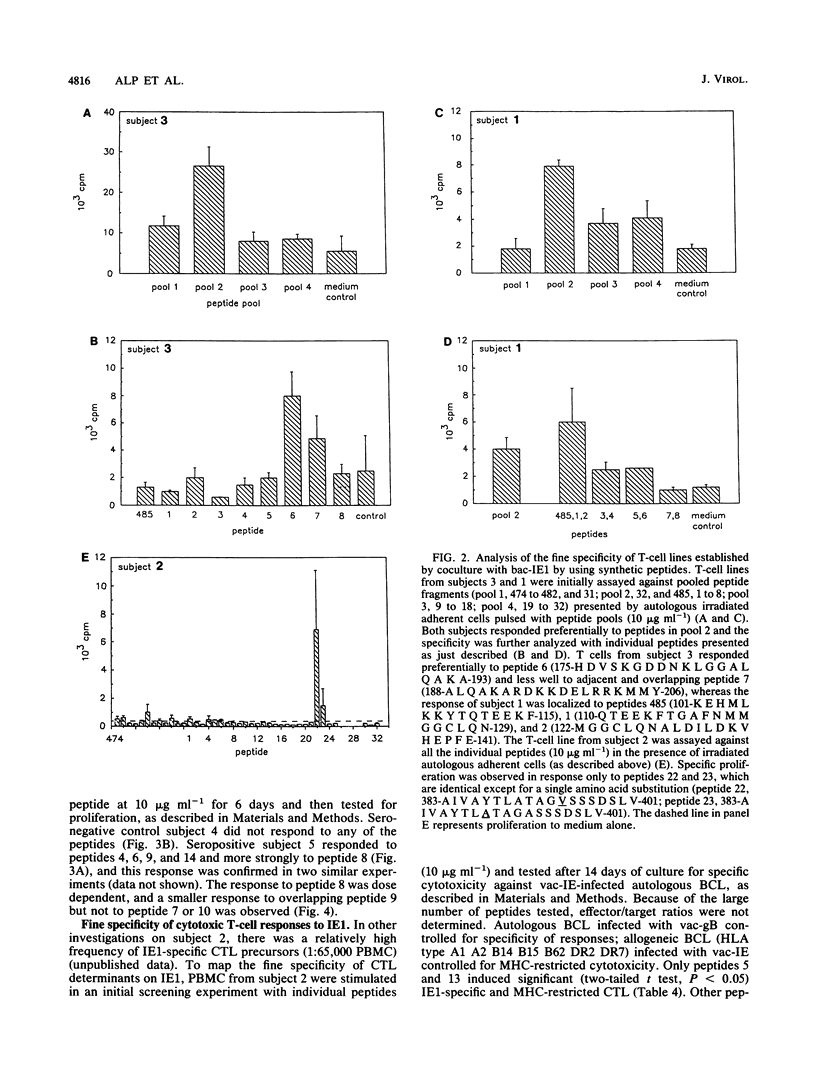
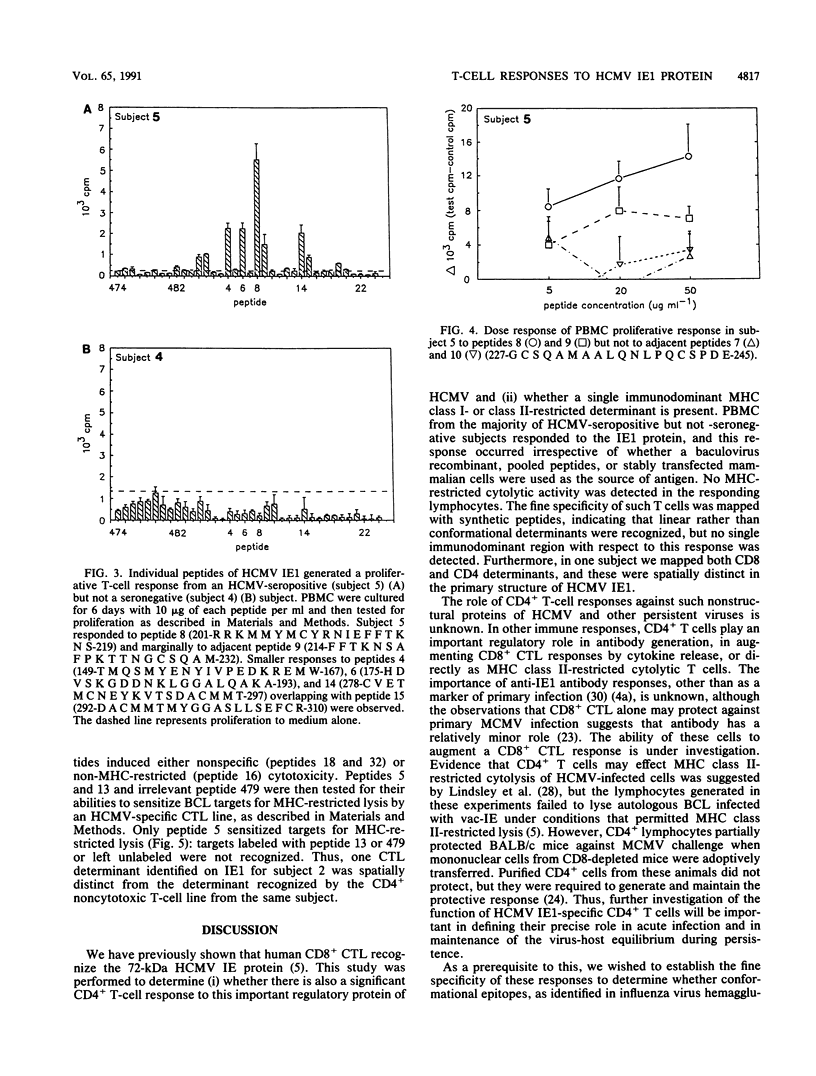
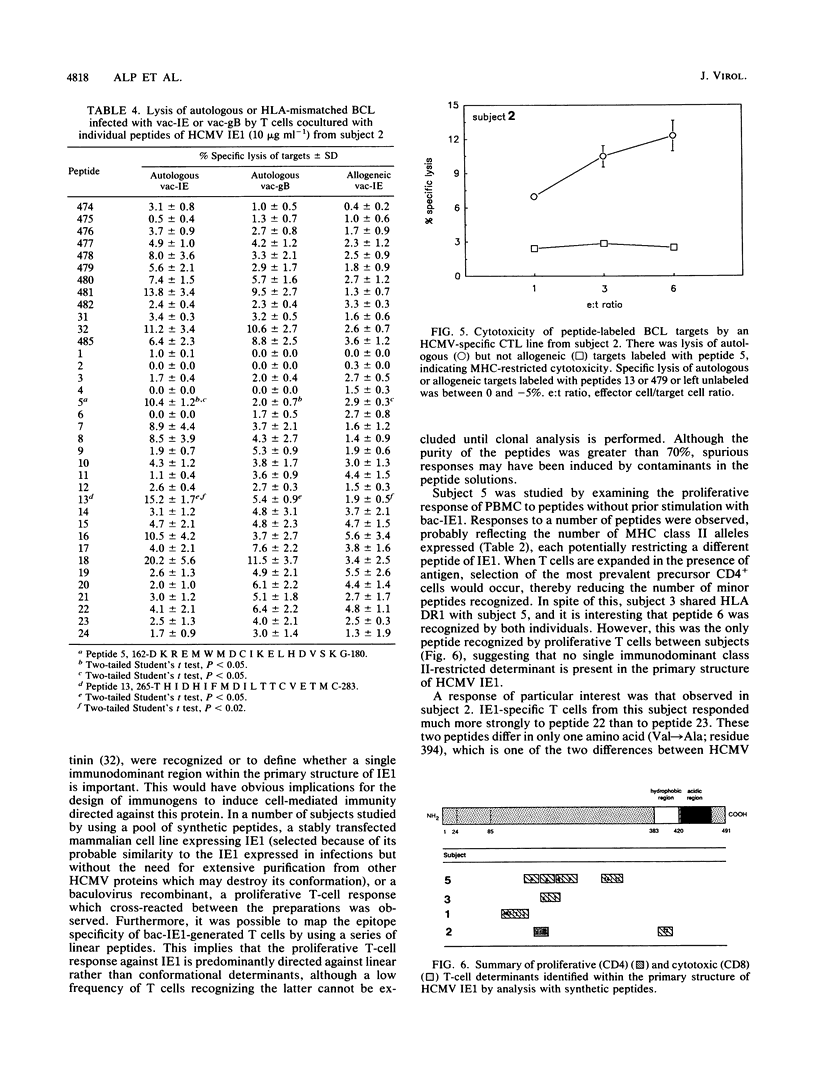
Cell-mediated immunity is important in maintaining the virus-host equilibrium in persistent human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infection. The HCMV 72-kDa major immediate early 1 protein (IE1) is a target for CD8+ cytotoxic T cells in humans, as is the equivalent 89-kDa protein in mouse. Less is known about responses against this protein by CD4+ T cells, which may be important as direct effector cells or helper cells for antibody and CD8+ responses. Proliferative-T-cell responses to HCMV IE1 were studied in normal seropositive subjects. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells from 85% of seropositive subjects proliferated in response to HCMV from infected fibroblasts, and of these, 73% responded to recombinant baculovirus IE1. Responding cells were predominantly CD3+ CD4+. IE1 antigen preparations, including baculovirus recombinant protein, transfected rat cell nuclei, and synthetic peptides, induced IE1-specific T-cell lines which cross-reacted between the preparations. The fine specificity of these IE1-specific T-cell lines was studied by using overlapping synthetic peptides encompassing the entire sequence of the IE1 protein. The regions of the IE1 molecule recognized were identified and these varied between individuals, possibly reflecting differences in major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II haplotype. In one subject, the peptide specificities of proliferative and MHC class I-restricted cytotoxic determinants on IE1 were spatially distinct. Thus, no single immunodominant T-cell determinant within HCMV IE1 was identified, suggesting that multiple peptides or a region of the 72-kDa IE1 protein would be required to induce specific T-cell responses in humans.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adorini L., Ullrich S. J., Appella E., Fuchs S. Inhibition by brefeldin A of presentation of exogenous protein antigens to MHC class II-restricted T cells. Nature. 1990 Jul 5;346(6279):63–66. doi: 10.1038/346063a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akrigg A., Wilkinson G. W., Oram J. D. The structure of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. Virus Res. 1985 Mar;2(2):107–121. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(85)90242-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanton R. A., Tevethia M. J. Immunoprecipitation of virus-specific immediate-early and early polypeptides from cells lytically infected with human cytomegalovirus strain AD 169. Virology. 1981 Jul 15;112(1):262–273. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90631-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boom R., Geelen J. L., Sol C. J., Raap A. K., Minnaar R. P., Klaver B. P., van der Noordaa J. Establishment of a rat cell line inducible for the expression of human cytomegalovirus immediate-early gene products by protein synthesis inhibition. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):851–859. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.851-859.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borysiewicz L. K., Graham S., Hickling J. K., Mason P. D., Sissons J. G. Human cytomegalovirus-specific cytotoxic T cells: their precursor frequency and stage specificity. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Feb;18(2):269–275. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borysiewicz L. K., Hickling J. K., Graham S., Sinclair J., Cranage M. P., Smith G. L., Sissons J. G. Human cytomegalovirus-specific cytotoxic T cells. Relative frequency of stage-specific CTL recognizing the 72-kD immediate early protein and glycoprotein B expressed by recombinant vaccinia viruses. J Exp Med. 1988 Sep 1;168(3):919–931. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.3.919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borysiewicz L. K., Morris S., Page J. D., Sissons J. G. Human cytomegalovirus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes: requirements for in vitro generation and specificity. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Oct;13(10):804–809. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830131005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chee M. S., Bankier A. T., Beck S., Bohni R., Brown C. M., Cerny R., Horsnell T., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Kouzarides T., Martignetti J. A. Analysis of the protein-coding content of the sequence of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;154:125–169. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74980-3_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen B. P., Madrigal A., Parham P. Cytotoxic T cell recognition of an endogenous class I HLA peptide presented by a class II HLA molecule. J Exp Med. 1990 Sep 1;172(3):779–788. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.3.779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cranage M. P., Kouzarides T., Bankier A. T., Satchwell S., Weston K., Tomlinson P., Barrell B., Hart H., Bell S. E., Minson A. C. Identification of the human cytomegalovirus glycoprotein B gene and induction of neutralizing antibodies via its expression in recombinant vaccinia virus. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):3057–3063. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04606.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Val M., Volkmer H., Rothbard J. B., Jonjić S., Messerle M., Schickedanz J., Reddehase M. J., Koszinowski U. H. Molecular basis for cytolytic T-lymphocyte recognition of the murine cytomegalovirus immediate-early protein pp89. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):3965–3972. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.3965-3972.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. Trans activation of transcription by herpes virus products: requirement for two HSV-1 immediate-early polypeptides for maximum activity. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3135–3141. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02270.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geelen J. L., Boom R., Klaver G. P., Minnaar R. P., Feltkamp M. C., van Milligen F. J., Sol C. J., van der Noordaa J. Transcriptional activation of the major immediate early transcription unit of human cytomegalovirus by heat-shock, arsenite and protein synthesis inhibitors. J Gen Virol. 1987 Nov;68(Pt 11):2925–2931. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-11-2925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotch F. M., Nixon D. F., Alp N., McMichael A. J., Borysiewicz L. K. High frequency of memory and effector gag specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes in HIV seropositive individuals. Int Immunol. 1990;2(8):707–712. doi: 10.1093/intimm/2.8.707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guagliardi L. E., Koppelman B., Blum J. S., Marks M. S., Cresswell P., Brodsky F. M. Co-localization of molecules involved in antigen processing and presentation in an early endocytic compartment. Nature. 1990 Jan 11;343(6254):133–139. doi: 10.1038/343133a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding C. V., Unanue E. R., Slot J. W., Schwartz A. L., Geuze H. J. Functional and ultrastructural evidence for intracellular formation of major histocompatibility complex class II-peptide complexes during antigen processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5553–5557. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghten R. A., Chang W. C., Li C. H. Human beta-endorphin: synthesis and characterization of analogs iodinated and tritiated at tyrosine residues 1 and 27. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1980 Oct;16(4):311–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1980.tb02592.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghten R. A. General method for the rapid solid-phase synthesis of large numbers of peptides: specificity of antigen-antibody interaction at the level of individual amino acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5131–5135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghten R. A., Ostresh J. M., Klipstein F. A. Chemical synthesis of an octadecapeptide with the biological and immunological properties of human heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Nov 15;145(1):157–162. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08535.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn G., Knust E., Schmolla H., Sarre T., Nelson J. A., McDougall J. K., Fleckenstein B. Predominant immediate-early transcripts of human cytomegalovirus AD 169. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):363–370. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.363-370.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonjić S., Pavić I., Lucin P., Rukavina D., Koszinowski U. H. Efficacious control of cytomegalovirus infection after long-term depletion of CD8+ T lymphocytes. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5457–5464. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5457-5464.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonjić S., del Val M., Keil G. M., Reddehase M. J., Koszinowski U. H. A nonstructural viral protein expressed by a recombinant vaccinia virus protects against lethal cytomegalovirus infection. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1653–1658. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1653-1658.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klavinskis L. S., Whitton J. L., Joly E., Oldstone M. B. Vaccination and protection from a lethal viral infection: identification, incorporation, and use of a cytotoxic T lymphocyte glycoprotein epitope. Virology. 1990 Oct;178(2):393–400. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90336-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koszinowski U. H., Keil G. M., Schwarz H., Schickedanz J., Reddehase M. J. A nonstructural polypeptide encoded by immediate-early transcription unit 1 of murine cytomegalovirus is recognized by cytolytic T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1987 Jul 1;166(1):289–294. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.1.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koszinowski U. H., Reddehase M. J., Keil G. M., Schickedanz J. Host immune response to cytomegalovirus: products of transfected viral immediate-early genes are recognized by cloned cytolytic T lymphocytes. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):2054–2058. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.2054-2058.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsley M. D., Torpey D. J., 3rd, Rinaldo C. R., Jr HLA-DR-restricted cytotoxicity of cytomegalovirus-infected monocytes mediated by Leu-3-positive T cells. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 15;136(8):3045–3051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. D., Leszczynski J., Zaia J. A., Flournoy N., Newton B., Snydman D. R., Wright G. G., Levin M. J., Thomas E. D. Prevention of cytomegalovirus infection by cytomegalovirus immune globulin after marrow transplantation. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Apr;98(4):442–446. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-98-4-442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelson-Fiske S., Horodniceanu F., Guillon J. C. Immediate early antigens in human cytomegalovirus infected cells. Nature. 1977 Dec 15;270(5638):615–617. doi: 10.1038/270615a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milich D. R. Genetic and molecular basis for T- and B-cell recognition of hepatitis B viral antigens. Immunol Rev. 1987 Oct;99:71–103. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1987.tb01173.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills K. H., Skehel J. J., Thomas D. B. Conformational-dependent recognition of influenza virus hemagglutinin by murine T helper clones. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Mar;16(3):276–280. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neefjes J. J., Stollorz V., Peters P. J., Geuze H. J., Ploegh H. L. The biosynthetic pathway of MHC class II but not class I molecules intersects the endocytic route. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):171–183. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90224-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuchtern J. G., Biddison W. E., Klausner R. D. Class II MHC molecules can use the endogenous pathway of antigen presentation. Nature. 1990 Jan 4;343(6253):74–76. doi: 10.1038/343074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall R. E., Young D. F. Solid matrix-antibody-antigen complexes induce antigen-specific CD8+ cells that clear a persistent paramyxovirus infection. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):719–726. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.719-726.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddehase M. J., Mutter W., Münch K., Bühring H. J., Koszinowski U. H. CD8-positive T lymphocytes specific for murine cytomegalovirus immediate-early antigens mediate protective immunity. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3102–3108. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3102-3108.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddehase M. J., Rothbard J. B., Koszinowski U. H. A pentapeptide as minimal antigenic determinant for MHC class I-restricted T lymphocytes. Nature. 1989 Feb 16;337(6208):651–653. doi: 10.1038/337651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier R. D., Gnann J. W., Jr, Landes R., Lockshin C., Richman D., McCutchan A., Kennedy C., Oldstone M. B., Nelson J. A. T cell recognition of HIV synthetic peptides in a natural infection. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 15;142(4):1166–1176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stagno S., Pass R. F., Dworsky M. E., Henderson R. E., Moore E. G., Walton P. D., Alford C. A. Congenital cytomegalovirus infection: The relative importance of primary and recurrent maternal infection. N Engl J Med. 1982 Apr 22;306(16):945–949. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198204223061601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Stinski M. F. Autoregulation of the human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early gene. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):676–682. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.676-682.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F., Thomsen D. R., Stenberg R. M., Goldstein L. C. Organization and expression of the immediate early genes of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):1–14. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.1-14.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi H., Takeshita T., Morein B., Putney S., Germain R. N., Berzofsky J. A. Induction of CD8+ cytotoxic T cells by immunization with purified HIV-1 envelope protein in ISCOMs. Nature. 1990 Apr 26;344(6269):873–875. doi: 10.1038/344873a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tevethia S. S., Lewis M., Tanaka Y., Milici J., Knowles B., Maloy W. L., Anderson R. Dissection of H-2Db-restricted cytotoxic T-lymphocyte epitopes on simian virus 40 T antigen by the use of synthetic peptides and H-2Dbm mutants. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1192–1200. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1192-1200.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend A., Ohlén C., Bastin J., Ljunggren H. G., Foster L., Kärre K. Association of class I major histocompatibility heavy and light chains induced by viral peptides. Nature. 1989 Aug 10;340(6233):443–448. doi: 10.1038/340443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahren B., Robèrt K. H., Nordlund S. Conditions for cytomegalovirus stimulation of lymphocytes. Scand J Immunol. 1981;13(6):581–586. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1981.tb00172.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wreghitt T. G., Hicks J., Gray J. J., O'Connor C. Development of a competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detecting cytomegalovirus antibody. J Med Virol. 1986 Feb;18(2):119–129. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890180204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zanten J., van der Giessen M., van der Voort L. H., van Son W. J., van der Bij W., The T. H. Cytomegalovirus-specific antibodies to an immediate early antigen and a late membrane antigen and their possible role in controlling secondary cytomegalovirus infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Jan;83(1):102–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05596.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



