Abstract
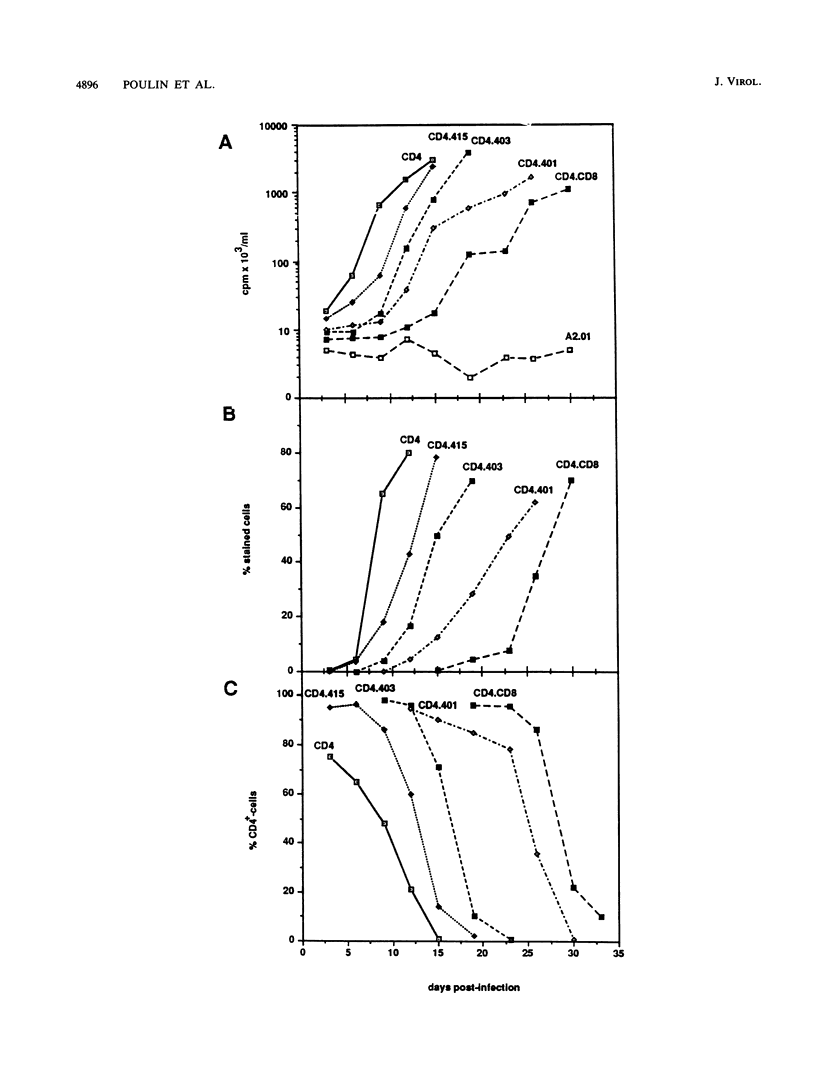
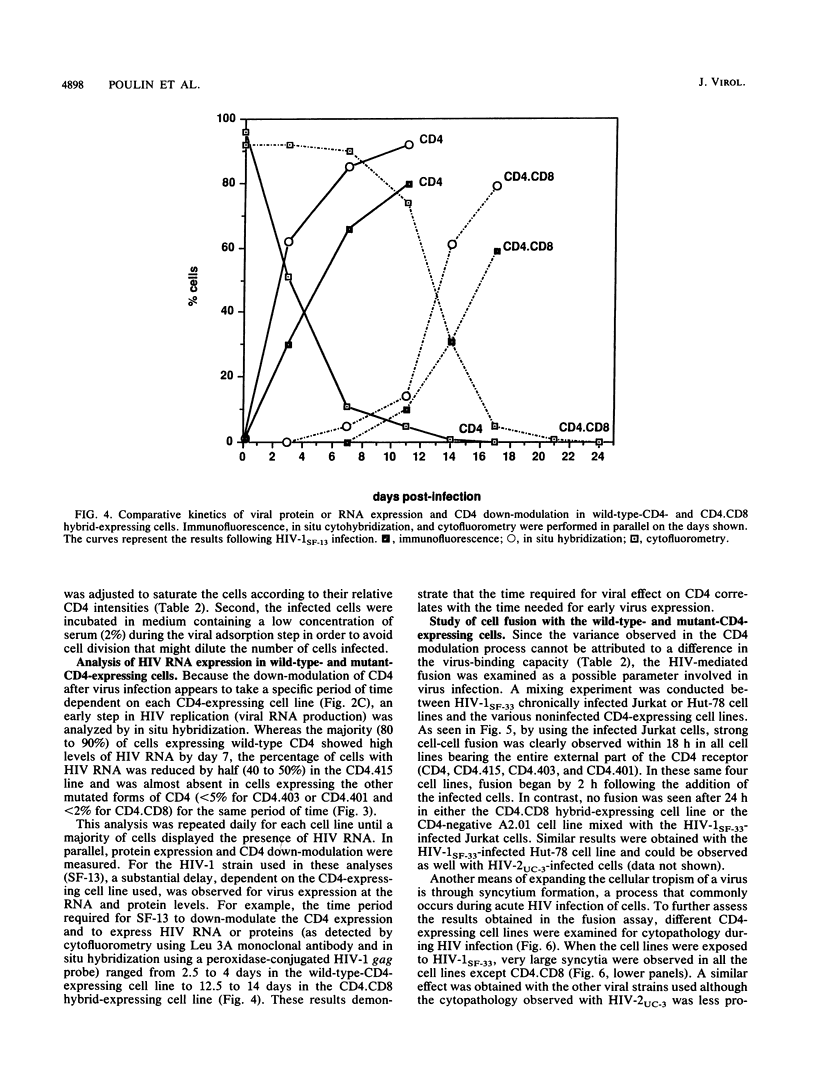
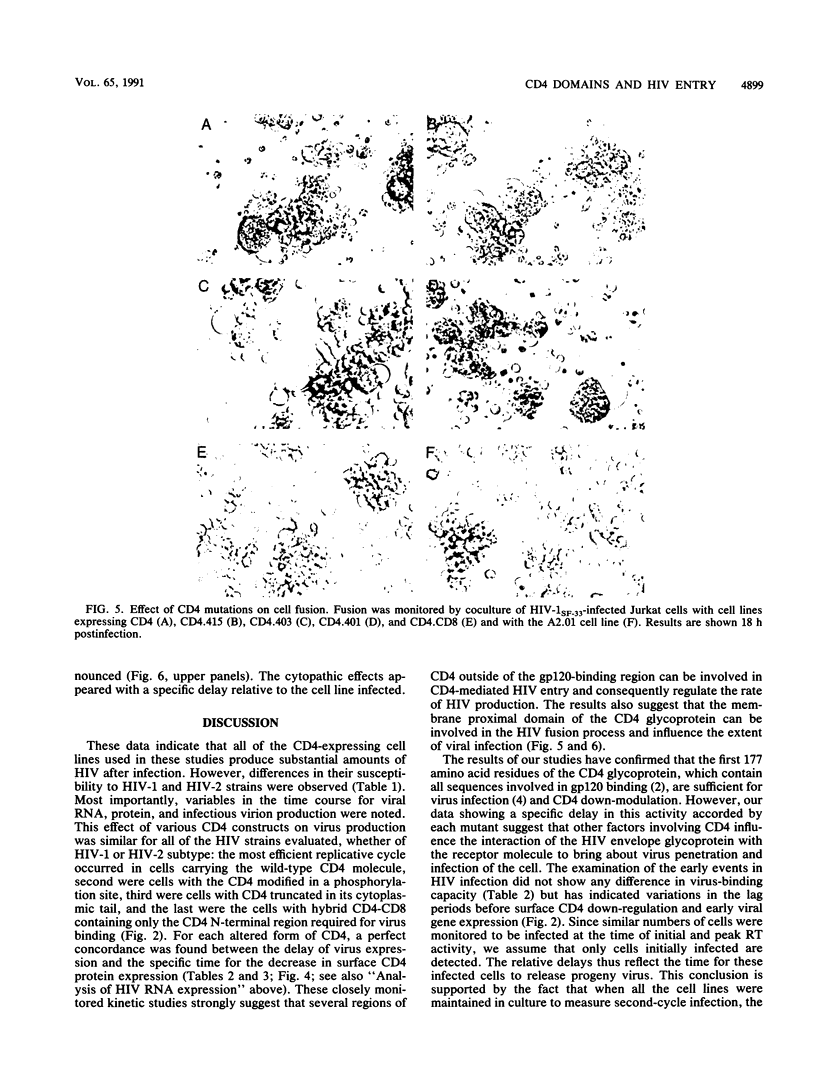
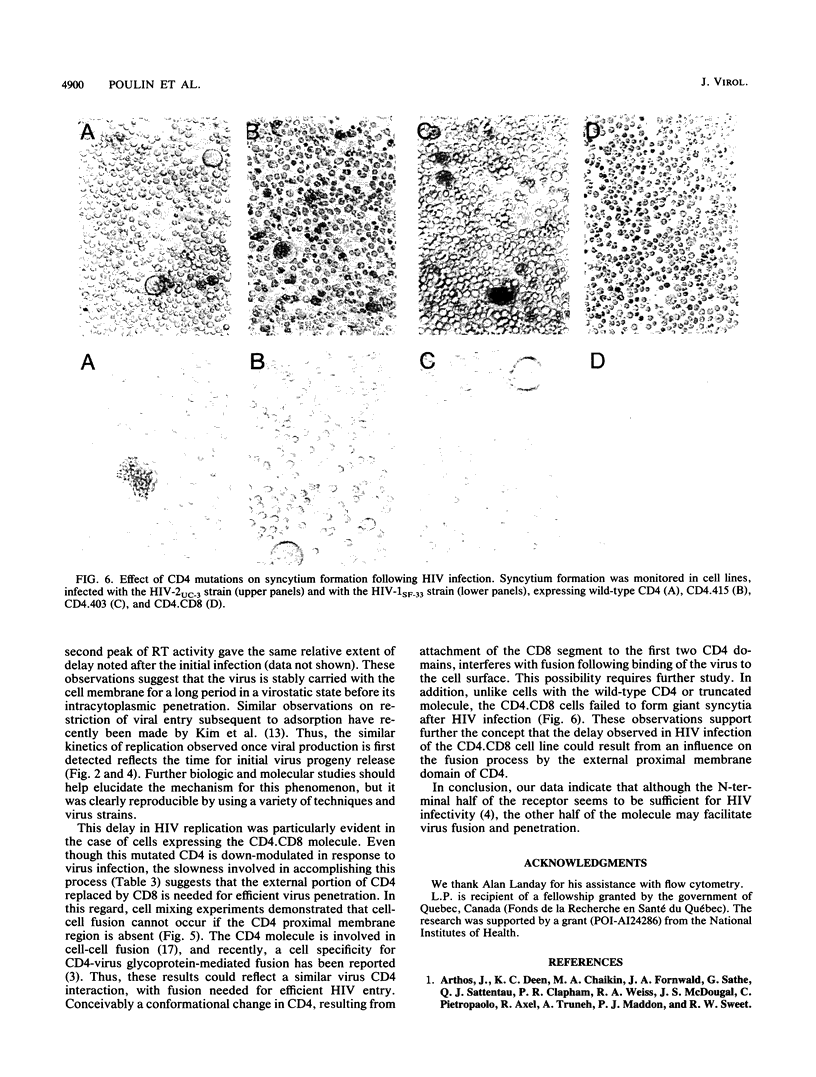
The human immunodefiency virus (HIV) uses the human CD4 glycoprotein as a receptor for infection of susceptible cells. Cells expressing a series of mutated forms of the CD4 gene have shown a variability in their ability to support replication of three HIV type 1 (HIV-1) and three HIV-2 strains. Moreover, when different stages of virus production were examined by a variety of assays, a consistent delay was observed in all cell lines containing CD4 mutants compared with those with intact full-length CD4. Cells expressing the CD4.415 mutant (modified at the serine 415 corresponding to a phosphorylation site of the cytoplasmic domain) showed only a minimal effect on virus replication. Cells expressing CD4.403 and CD4.401 mutants (lacking the whole cytoplasmic domain) manifested a moderate delay in production of virus progeny. The most substantial effect on HIV replication was observed in cells expressing a chimeric hybrid containing sequences corresponding to the first 177 residues of the N-terminal CD4 fused to CD8 sequences encoding the hinge, transmembrane, and cytoplasmic domains of the human CD8. Furthermore, in a cell-to-cell contact assay, fusion was absent when the CD4 proximal membrane domain was replaced by the CD8 counterpart. In addition, a strong correlation between the down-modulation of the surface CD4 and HIV expression was observed. These observations suggest that in addition to the known binding region, other domains of CD4 could play an important role in regulating HIV entry of cells.
Full text
PDF
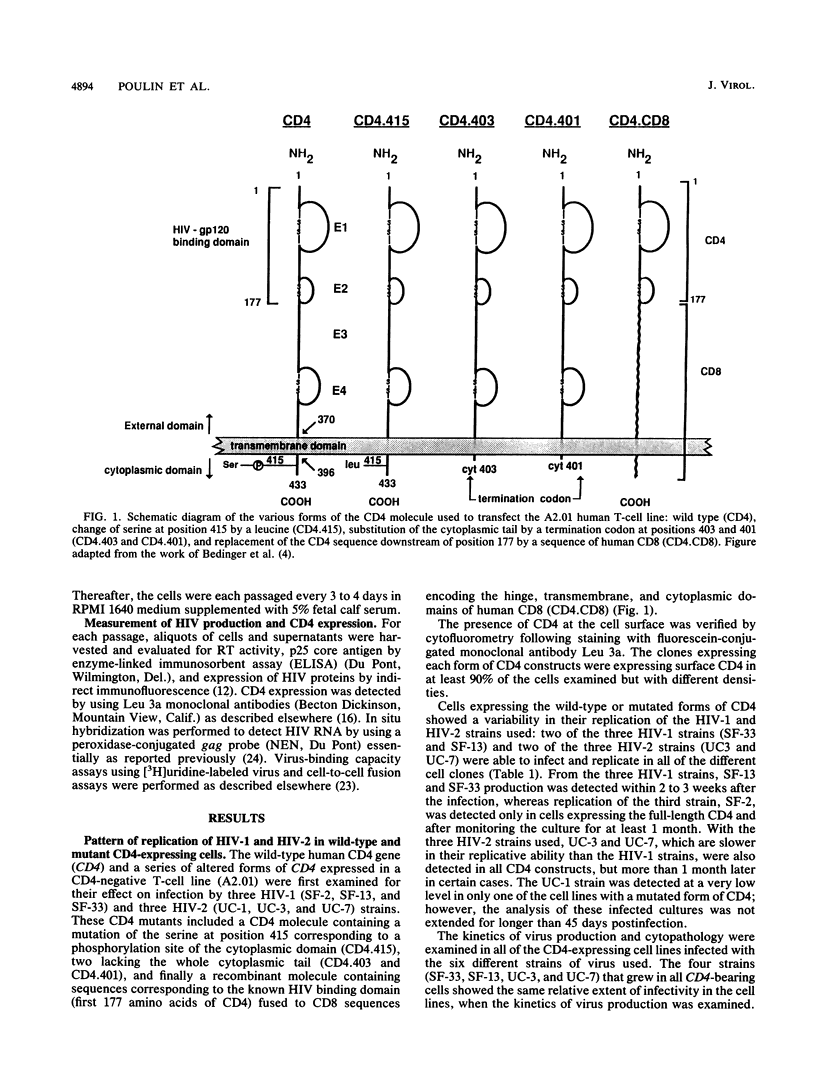
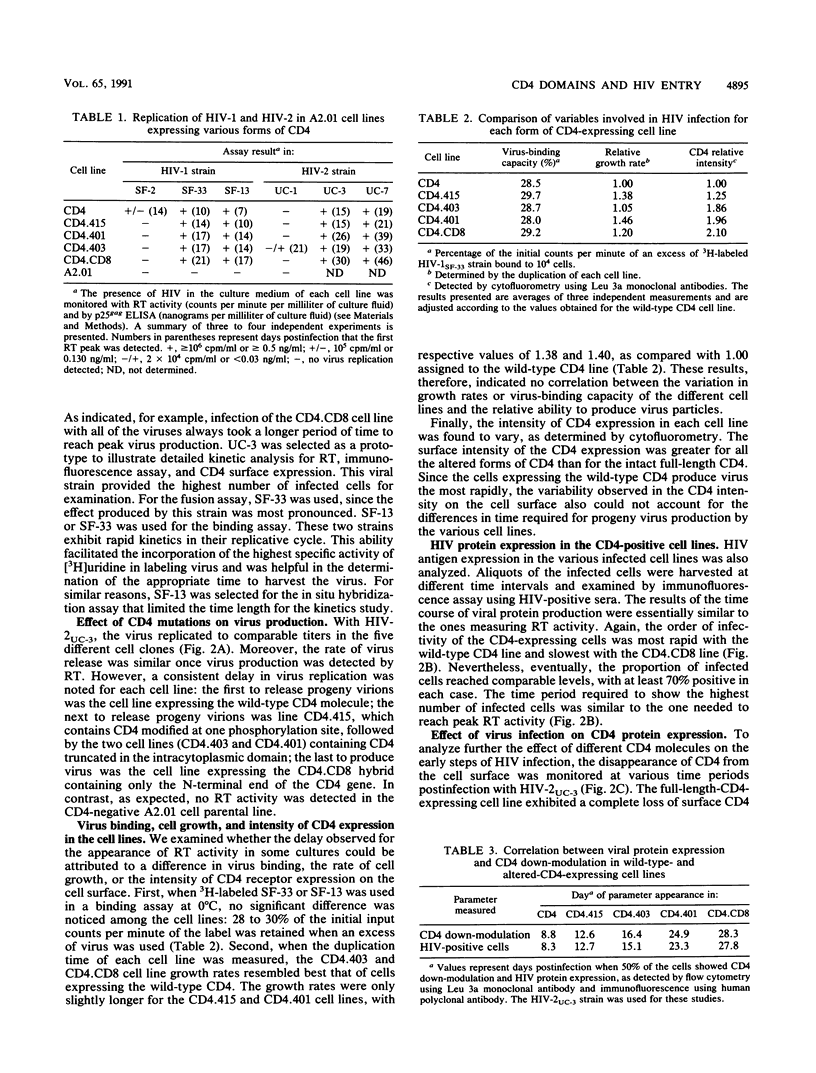


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashkenazi A., Presta L. G., Marsters S. A., Camerato T. R., Rosenthal K. A., Fendly B. M., Capon D. J. Mapping the CD4 binding site for human immunodeficiency virus by alanine-scanning mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7150–7154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashorn P. A., Berger E. A., Moss B. Human immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoprotein/CD4-mediated fusion of nonprimate cells with human cells. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2149–2156. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2149-2156.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedinger P., Moriarty A., von Borstel R. C., 2nd, Donovan N. J., Steimer K. S., Littman D. R. Internalization of the human immunodeficiency virus does not require the cytoplasmic domain of CD4. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):162–165. doi: 10.1038/334162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky M. H., Warton M., Myers R. M., Littman D. R. Analysis of the site in CD4 that binds to the HIV envelope glycoprotein. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 15;144(8):3078–3086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton L. K., Hussey R. E., Steinbrich R., Ramachandran H., Husain Y., Reinherz E. L. Substitution of murine for human CD4 residues identifies amino acids critical for HIV-gp120 binding. Nature. 1988 Sep 22;335(6188):363–366. doi: 10.1038/335363a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L. A., Levy J. A. Characteristics of HIV infection and pathogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Dec 27;989(3):237–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallaher W. R. Detection of a fusion peptide sequence in the transmembrane protein of human immunodeficiency virus. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):327–328. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90485-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Scarano F., Waxham M. N., Ross A. M., Hoxie J. A. Sequence similarities between human immunodeficiency virus gp41 and paramyxovirus fusion proteins. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1987 Fall;3(3):245–252. doi: 10.1089/aid.1987.3.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman A. D., Banapour B., Levy J. A. Characterization of the AIDS-associated retrovirus reverse transcriptase and optimal conditions for its detection in virions. Virology. 1985 Dec;147(2):326–335. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90135-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameson B. A., Rao P. E., Kong L. I., Hahn B. H., Shaw G. M., Hood L. E., Kent S. B. Location and chemical synthesis of a binding site for HIV-1 on the CD4 protein. Science. 1988 Jun 3;240(4857):1335–1339. doi: 10.1126/science.2453925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminsky L. S., McHugh T., Stites D., Volberding P., Henle G., Henle W., Levy J. A. High prevalence of antibodies to acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS)-associated retrovirus (ARV) in AIDS and related conditions but not in other disease states. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5535–5539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S., Ikeuchi K., Groopman J., Baltimore D. Factors affecting cellular tropism of human immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5600–5604. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5600-5604.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski M., Potz J., Basiripour L., Dorfman T., Goh W. C., Terwilliger E., Dayton A., Rosen C., Haseltine W., Sodroski J. Functional regions of the envelope glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Science. 1987 Sep 11;237(4820):1351–1355. doi: 10.1126/science.3629244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A., Shimabukuro J. Recovery of AIDS-associated retroviruses from patients with AIDS or AIDS-related conditions and from clinically healthy individuals. J Infect Dis. 1985 Oct;152(4):734–738. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.4.734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A., Tobler L. H., McHugh T. M., Casavant C. H., Stites D. P. Long-term cultivation of T-cell subsets from patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1985 Jun;35(3):328–336. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(85)90093-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifson J. D., Feinberg M. B., Reyes G. R., Rabin L., Banapour B., Chakrabarti S., Moss B., Wong-Staal F., Steimer K. S., Engleman E. G. Induction of CD4-dependent cell fusion by the HTLV-III/LAV envelope glycoprotein. Nature. 1986 Oct 23;323(6090):725–728. doi: 10.1038/323725a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure M. O., Marsh M., Weiss R. A. Human immunodeficiency virus infection of CD4-bearing cells occurs by a pH-independent mechanism. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):513–518. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02839.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson A., Seed B. Genetic analysis of monoclonal antibody and HIV binding sites on the human lymphocyte antigen CD4. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):65–72. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90180-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattentau Q. J., Weiss R. A. The CD4 antigen: physiological ligand and HIV receptor. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):631–633. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90397-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinangil F., Loyter A., Volsky D. J. Quantitative measurement of fusion between human immunodeficiency virus and cultured cells using membrane fluorescence dequenching. FEBS Lett. 1988 Oct 24;239(1):88–92. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80551-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein B. S., Gowda S. D., Lifson J. D., Penhallow R. C., Bensch K. G., Engleman E. G. pH-independent HIV entry into CD4-positive T cells via virus envelope fusion to the plasma membrane. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):659–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90542-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tateno M., Gonzalez-Scarano F., Levy J. A. Human immunodeficiency virus can infect CD4-negative human fibroblastoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4287–4290. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams I. G., Gabriel G., Kelly G., Loveday C., Tedder R. S., Weller I. V. Response of serum p24 antigen and antibody to p24 antigen in patients with AIDS and AIDS-related complex treated with zidovudine. AIDS. 1990 Sep;4(9):909–912. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199009000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]