Abstract
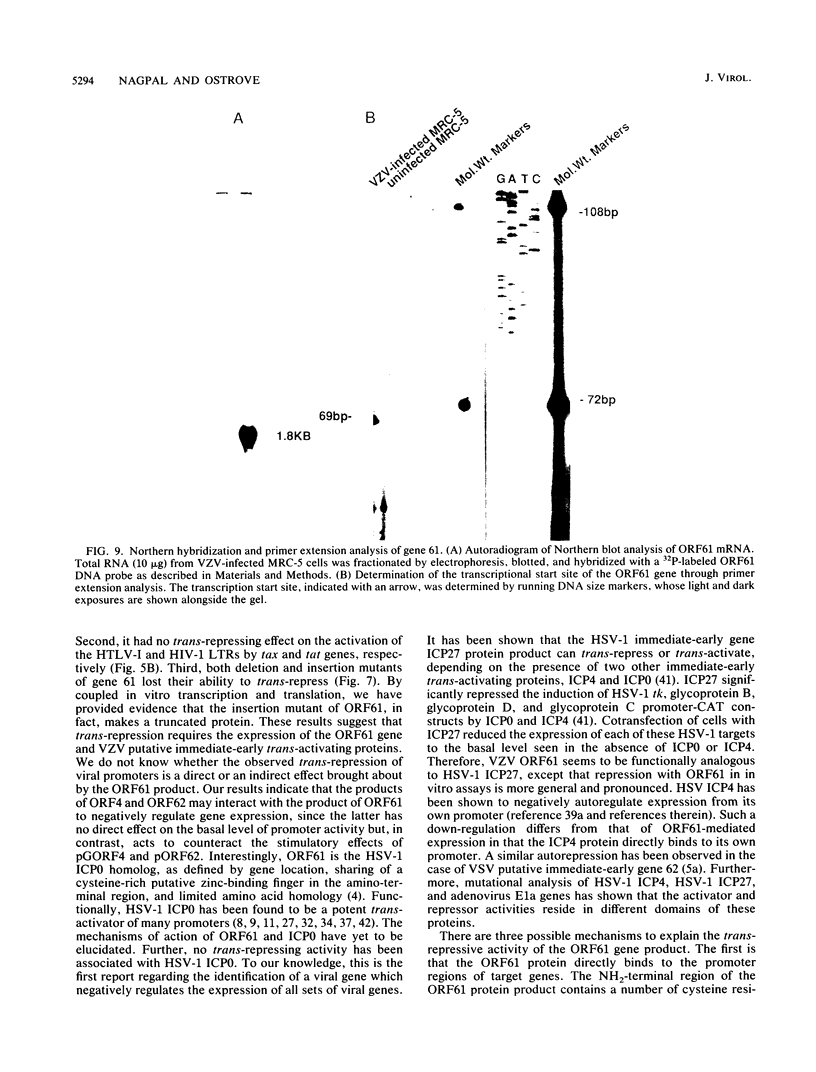
Using a transient expression assay in Vero cells, we have shown that the protein product from gene 61 of varicella-zoster virus (VZV) can repress the function of the VZV encoded trans-activators on putative viral immediate-early, early, and late gene promoters. The repression is exerted at the transcriptional level and requires functional gene 61 protein. This trans-repressor is the herpes simplex type 1 ICP0 (a trans-activator) homolog, as defined by gene location, the sharing of a cysteine-rich putative zinc-binding finger in the amino-terminal region, and limited amino acid homology. Open reading frame 61 (ORF61)-mediated trans-repression appears to be specific for VZV-encoded trans-activators in that it has no effect on simian virus 40 and Rous sarcoma virus promoters. Moreover, it does not inhibit trans-activation of the human T-lymphotropic virus type I and human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeats by tax and tat genes, respectively. We constructed plasmids with mutations in ORF61 and tested them for their ability to inhibit trans-activator (VZV genes 4 and 62)-mediated activation of the viral thymidine kinase promoter-chloramphenicol acetyltransferase construct. Mutants containing interruptions in ORF61 lost their trans-repressing ability, as demonstrated at both the protein and steady-state RNA levels. These results suggest that the ORF61 protein product can mediate down-regulation of VZV gene expression.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berk A. J., Lee F., Harrison T., Williams J., Sharp P. A. Pre-early adenovirus 5 gene product regulates synthesis of early viral messenger RNAs. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):935–944. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90333-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrelli E., Hen R., Chambon P. Adenovirus-2 E1A products repress enhancer-induced stimulation of transcription. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):608–612. doi: 10.1038/312608a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Scott J. E. The complete DNA sequence of varicella-zoster virus. J Gen Virol. 1986 Sep;67(Pt 9):1759–1816. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-9-1759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca N. A., Schaffer P. A. Activation of immediate-early, early, and late promoters by temperature-sensitive and wild-type forms of herpes simplex virus type 1 protein ICP4. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1997–2008. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Disney G. H., McKee T. A., Preston C. M., Everett R. D. The product of varicella-zoster virus gene 62 autoregulates its own promoter. J Gen Virol. 1990 Dec;71(Pt 12):2999–3003. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-12-2999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwarki V. J., Montminy M., Verma I. M. Both the basic region and the 'leucine zipper' domain of the cyclic AMP response element binding (CREB) protein are essential for transcriptional activation. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):225–232. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08099.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. A detailed mutational analysis of Vmw110, a trans-acting transcriptional activator encoded by herpes simplex virus type 1. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):2069–2076. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02472.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. Trans activation of transcription by herpes virus products: requirement for two HSV-1 immediate-early polypeptides for maximum activity. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3135–3141. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02270.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felser J. M., Kinchington P. R., Inchauspe G., Straus S. E., Ostrove J. M. Cell lines containing varicella-zoster virus open reading frame 62 and expressing the "IE" 175 protein complement ICP4 mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2076–2082. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2076-2082.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelman I. H., Silverstein S. Identification of immediate early genes from herpes simplex virus that transactivate the virus thymidine kinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5265–5269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gendelman H. E., Phelps W., Feigenbaum L., Ostrove J. M., Adachi A., Howley P. M., Khoury G., Ginsberg H. S., Martin M. A. Trans-activation of the human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat sequence by DNA viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9759–9763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerster T., Roeder R. G. A herpesvirus trans-activating protein interacts with transcription factor OTF-1 and other cellular proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6347–6351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen U., Tenen D. G., Livingston D. M., Sharp P. A. T antigen repression of SV40 early transcription from two promoters. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):603–613. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90402-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
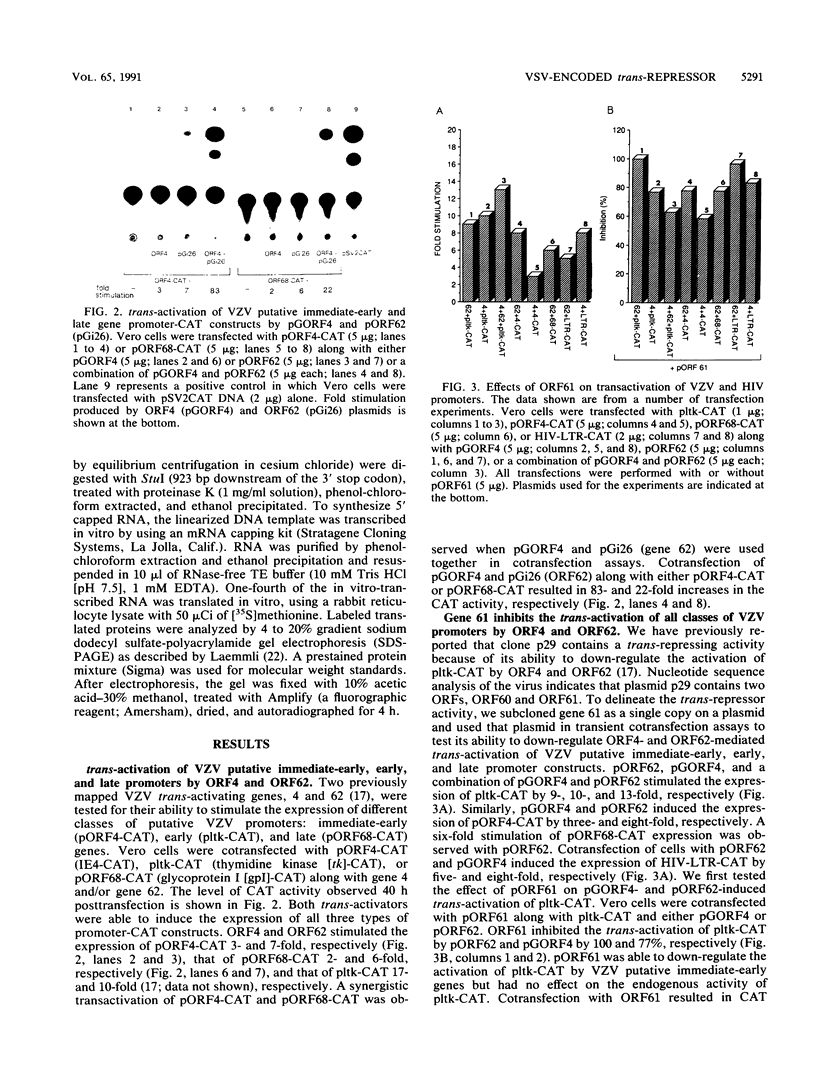
- Inchauspe G., Nagpal S., Ostrove J. M. Mapping of two varicella-zoster virus-encoded genes that activate the expression of viral early and late genes. Virology. 1989 Dec;173(2):700–709. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90583-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inchauspe G., Ostrove J. M. Differential regulation by varicella-zoster virus (VZV) and herpes simplex virus type-1 trans-activating genes. Virology. 1989 Dec;173(2):710–714. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90584-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeang K. T., Widen S. G., Semmes O. J., 4th, Wilson S. H. HTLV-I trans-activator protein, tax, is a trans-repressor of the human beta-polymerase gene. Science. 1990 Mar 2;247(4946):1082–1084. doi: 10.1126/science.2309119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. C., Rigby P. W., Ziff E. B. Trans-acting protein factors and the regulation of eukaryotic transcription: lessons from studies on DNA tumor viruses. Genes Dev. 1988 Mar;2(3):267–281. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.3.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff T., Elkaim R., Goding C. R., Jalinot P., Sassone-Corsi P., Perricaudet M., Kédinger C., Chambon P. Individual products of the adenovirus 12S and 13S EIa mRNAs stimulate viral EIIa and EIII expression at the transcriptional level. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4381–4385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Green M. R. Transcription activation by the adenovirus E1a protein. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):39–44. doi: 10.1038/338039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F., Green M. R. A specific member of the ATF transcription factor family can mediate transcription activation by the adenovirus E1a protein. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1217–1224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90686-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavromara-Nazos P., Silver S., Hubenthal-Voss J., McKnight J. L., Roizman B. Regulation of herpes simplex virus 1 genes: alpha gene sequence requirements for transient induction of indicator genes regulated by beta or late (gamma 2) promoters. Virology. 1986 Mar;149(2):152–164. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90117-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight J. L., Kristie T. M., Roizman B. Binding of the virion protein mediating alpha gene induction in herpes simplex virus 1-infected cells to its cis site requires cellular proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7061–7065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Rio D. C., Robbins A. K., Tjian R. SV40 gene expression is modulated by the cooperative binding of T antigen to DNA. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):373–384. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nerenberg M., Hinrichs S. H., Reynolds R. K., Khoury G., Jay G. The tat gene of human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 induces mesenchymal tumors in transgenic mice. Science. 1987 Sep 11;237(4820):1324–1329. doi: 10.1126/science.2888190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Goding C. R. Herpes simplex virus regulatory elements and the immunoglobulin octamer domain bind a common factor and are both targets for virion transactivation. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):435–445. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Evidence for a direct role for both the 175,000- and 110,000-molecular-weight immediate-early proteins of herpes simplex virus in the transactivation of delayed-early promoters. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):751–760. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.751-760.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Three trans-acting regulatory proteins of herpes simplex virus modulate immediate-early gene expression in a pathway involving positive and negative feedback regulation. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):723–733. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.723-733.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrove J. M., Leonard J., Weck K. E., Rabson A. B., Gendelman H. E. Activation of the human immunodeficiency virus by herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3726–3732. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3726-3732.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrove J. M., Reinhold W., Fan C. M., Zorn S., Hay J., Straus S. E. Transcription mapping of the varicella-zoster virus genome. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):600–606. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.600-606.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M., Frame M. C., Campbell M. E. A complex formed between cell components and an HSV structural polypeptide binds to a viral immediate early gene regulatory DNA sequence. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):425–434. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan M. P., Knipe D. M. Stimulation of expression of a herpes simplex virus DNA-binding protein by two viral functions. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):957–963. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I., Stark G. R., Alwine J. C. Autoregulation of simian virus 40 gene A by T antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3083–3087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi R. P., Jones R. L., Cepko C. L., Sharp P. A., Roberts B. E. Expression of early adenovirus genes requires a viral encoded acidic polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6121–6125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M. S., Boundy A., O'Hare P., Pizzorno M. C., Ciufo D. M., Hayward G. S. Direct correlation between a negative autoregulatory response element at the cap site of the herpes simplex virus type 1 IE175 (alpha 4) promoter and a specific binding site for the IE175 (ICP4) protein. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4307–4320. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4307-4320.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekulovich R. E., Leary K., Sandri-Goldin R. M. The herpes simplex virus type 1 alpha protein ICP27 can act as a trans-repressor or a trans-activator in combination with ICP4 and ICP0. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4510–4522. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4510-4522.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira M., Homa F. L., Glorioso J. C., Levine M. Regulation of the herpes simplex virus type 1 late (gamma 2) glycoprotein C gene: sequences between base pairs -34 to +29 control transient expression and responsiveness to transactivation by the products of the immediate early (alpha) 4 and 0 genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 10;15(7):3097–3111. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.7.3097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J. G., Rosen C. A., Haseltine W. A. Trans-acting transcriptional activation of the long terminal repeat of human T lymphotropic viruses in infected cells. Science. 1984 Jul 27;225(4660):381–385. doi: 10.1126/science.6330891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus S. E., Aulakh H. S., Ruyechan W. T., Hay J., Casey T. A., Vande Woude G. F., Owens J., Smith H. A. Structure of varicella-zoster virus DNA. J Virol. 1981 Nov;40(2):516–525. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.2.516-525.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R. T antigen binding and the control of SV40 gene expression. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(1 Pt 1):1–2. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90026-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velcich A., Ziff E. Adenovirus E1a proteins repress transcription from the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90219-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]