Abstract
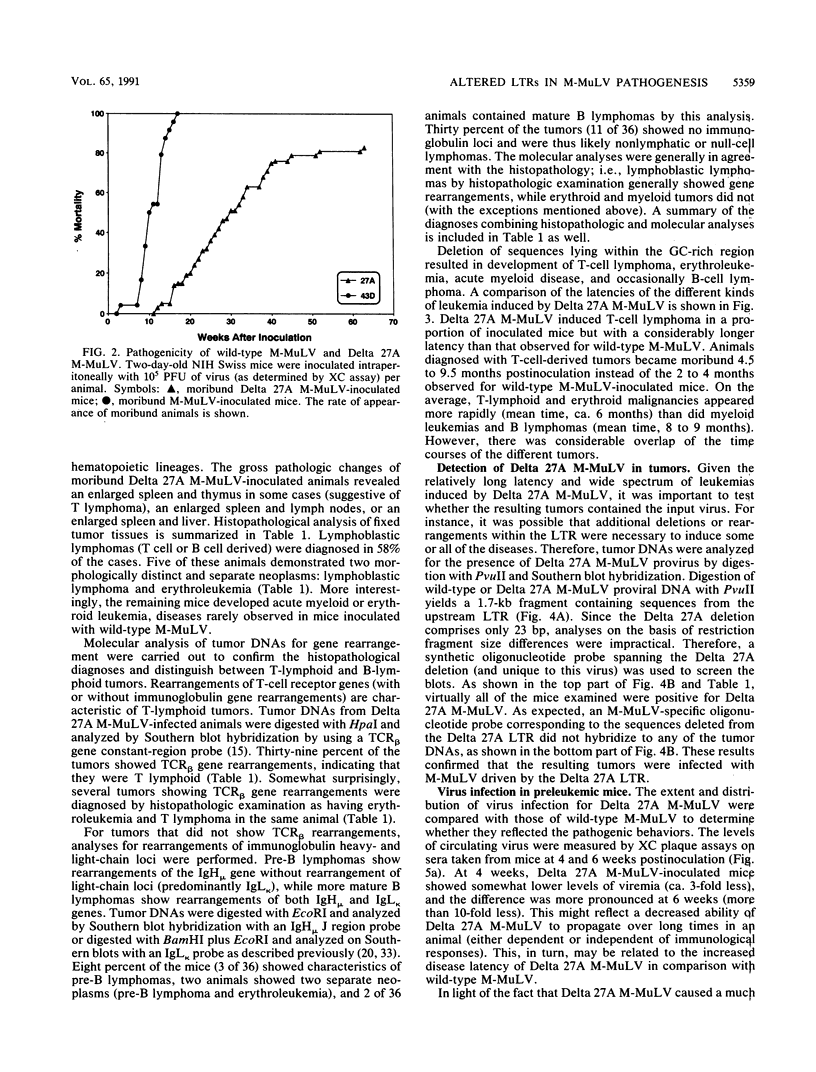
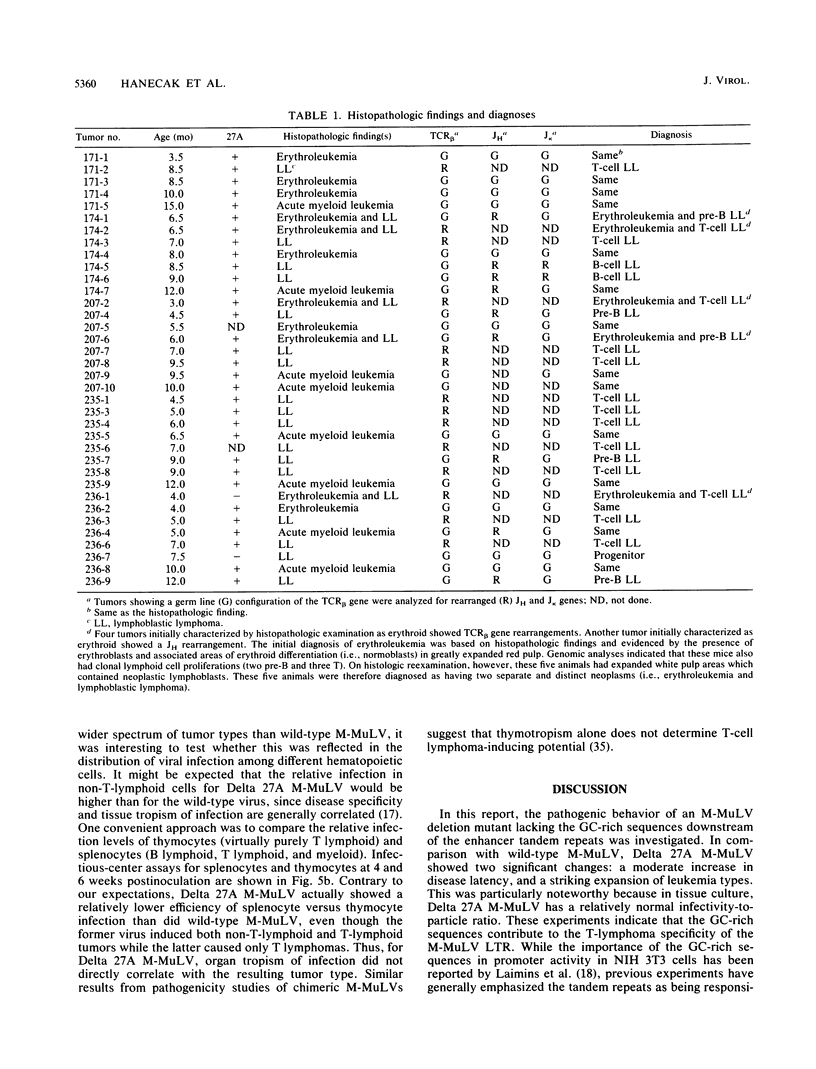
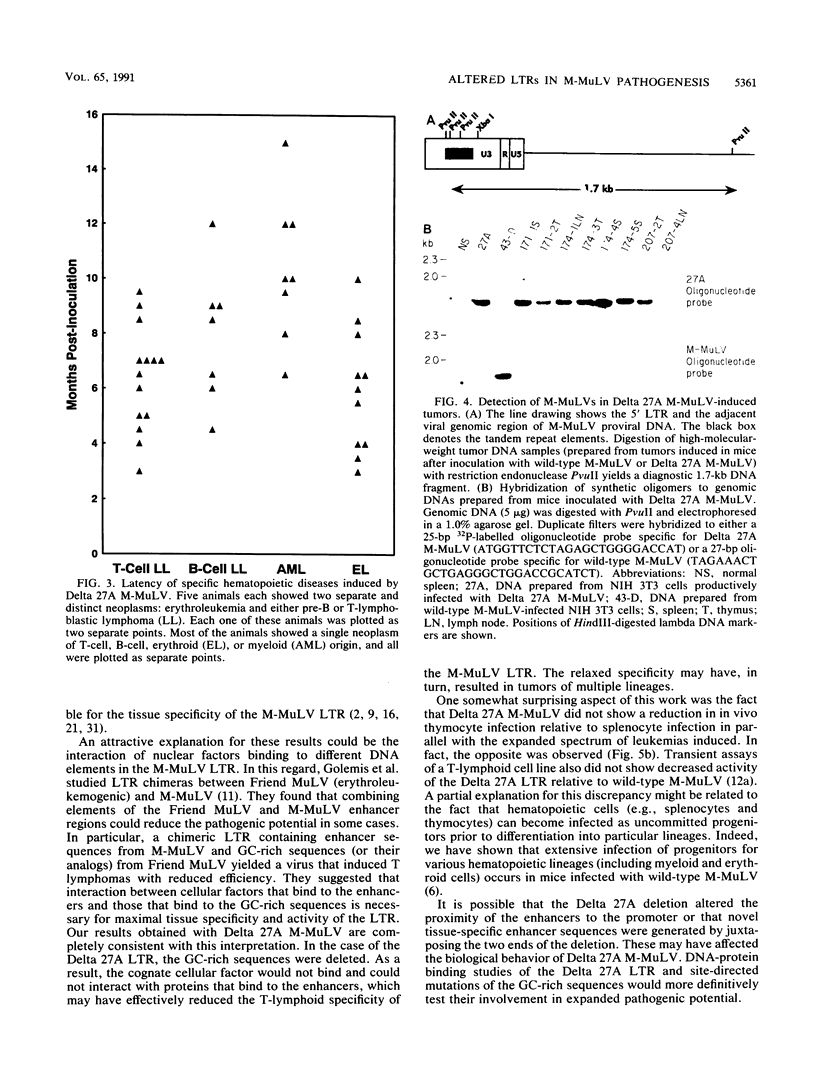
Moloney murine leukemia virus (M-MuLV) is a replication-competent retrovirus which induces T-lymphoblastic lymphoma 2 to 4 months after inoculation. Enhancer sequences in the U3 region of the M-MuLV long terminal repeat, primarily the 75-bp tandem repeats, strongly influence the disease specificity and latency of M-MuLV. We investigated the role of GC-rich sequences downstream of the tandem repeats in the disease specificity of M-MuLV. A recombinant M-MuLV lacking 23 bases of a GC-rich sequence (-174 to -151), Delta 27A M-MuLV, was tested for pathogenesis in neonatal NIH Swiss mice. Delta 27A M-MuLV induced disease with a longer latency than did M-MuLV (7 versus 3 months) in greater than 85% of inoculated mice. More interestingly, this virus showed an expanded repertoire of hematopoietic diseases. Molecular analyses and histopathologic examinations indicated that while 39% of mice inoculated with Delta 27A M-MuLV developed T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma typical of wild-type M-MuLV, the majority developed acute myeloid leukemia, erythroleukemia, or B-cell lymphoma. Viral DNA corresponding to Delta 27A M-MuLV was detectable in most of the tumors analyzed. These findings indicate that the GC-rich region significantly influences the disease specificity and latency of M-MuLV.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brightman B. K., Chandy K. G., Spencer R. H., Gupta S., Pattengale P. K., Fan H. Characterization of lymphoid tumors induced by a recombinant murine retrovirus carrying the avian v-myc oncogene. Identification of novel (B-lymphoid) tumors in the thymus. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 15;141(8):2844–2854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatis P. A., Holland C. A., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Hopkins N. Role for the 3' end of the genome in determining disease specificity of Friend and Moloney murine leukemia viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4408–4411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corcoran L. M., Adams J. M., Dunn A. R., Cory S. Murine T lymphomas in which the cellular myc oncogene has been activated by retroviral insertion. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90306-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuypers H. T., Selten G., Quint W., Zijlstra M., Maandag E. R., Boelens W., van Wezenbeek P., Melief C., Berns A. Murine leukemia virus-induced T-cell lymphomagenesis: integration of proviruses in a distinct chromosomal region. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):141–150. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90309-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B. R., Brightman B. K., Chandy K. G., Fan H. Characterization of a preleukemic state induced by Moloney murine leukemia virus: evidence for two infection events during leukemogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4875–4879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B. R., Chandy K. G., Brightman B. K., Gupta S., Fan H. Effects of nonleukemogenic and wild-type Moloney murine leukemia virus on lymphoid cells in vivo: identification of a preleukemic shift in thymocyte subpopulations. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):423–430. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.423-430.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B., Linney E., Fan H. Suppression of leukaemia virus pathogenicity by polyoma virus enhancers. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):550–553. doi: 10.1038/314550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesGroseillers L., Jolicoeur P. The tandem direct repeats within the long terminal repeat of murine leukemia viruses are the primary determinant of their leukemogenic potential. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):945–952. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.945-952.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesGroseillers L., Rassart E., Jolicoeur P. Thymotropism of murine leukemia virus is conferred by its long terminal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4203–4207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golemis E., Li Y., Fredrickson T. N., Hartley J. W., Hopkins N. Distinct segments within the enhancer region collaborate to specify the type of leukemia induced by nondefective Friend and Moloney viruses. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):328–337. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.328-337.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves B. J., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Homologous recognition of a promoter domain common to the MSV LTR and the HSV tk gene. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):565–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90266-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanecak R., Mittal S., Davis B. R., Fan H. Generation of infectious Moloney murine leukemia viruses with deletions in the U3 portion of the long terminal repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4634–4640. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanecak R., Pattengale P. K., Fan H. Addition of substitution of simian virus 40 enhancer sequences into the Moloney murine leukemia virus (M-MuLV) long terminal repeat yields infectious M-MuLV with altered biological properties. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2427–2436. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2427-2436.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick S. M., Nielsen E. A., Kavaler J., Cohen D. I., Davis M. M. Sequence relationships between putative T-cell receptor polypeptides and immunoglobulins. Nature. 1984 Mar 8;308(5955):153–158. doi: 10.1038/308153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishimoto A., Takimoto M., Adachi A., Kakuyama M., Kato S., Kakimi K., Fukuoka K., Ogiu T., Matsuyama M. Sequences responsible for erythroid and lymphoid leukemia in the long terminal repeats of Friend-mink cell focus-forming and Moloney murine leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):1861–1866. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.1861-1866.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenisch R. Moloney leukemia virus gene expression and gene amplification in preleukemic and leukemic BALB/Mo mice. Virology. 1979 Feb;93(1):80–90. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90277-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Gruss P., Pozzatti R., Khoury G. Characterization of enhancer elements in the long terminal repeat of Moloney murine sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):183–189. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.183-189.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenz J., Celander D., Crowther R. L., Patarca R., Perkins D. W., Haseltine W. A. Determination of the leukaemogenicity of a murine retrovirus by sequences within the long terminal repeat. 1984 Mar 29-Apr 4Nature. 308(5958):467–470. doi: 10.1038/308467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S., Rosenberg N., Alt F., Baltimore D. Continuing kappa-gene rearrangement in a cell line transformed by Abelson murine leukemia virus. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):807–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90285-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Golemis E., Hartley J. W., Hopkins N. Disease specificity of nondefective Friend and Moloney murine leukemia viruses is controlled by a small number of nucleotides. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):693–700. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.693-700.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linney E., Davis B., Overhauser J., Chao E., Fan H. Non-function of a Moloney murine leukaemia virus regulatory sequence in F9 embryonal carcinoma cells. 1984 Mar 29-Apr 4Nature. 308(5958):470–472. doi: 10.1038/308470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overhauser J., Fan H. Generation of glucocorticoid-responsive Moloney murine leukemia virus by insertion of regulatory sequences from murine mammary tumor virus into the long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):133–144. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.133-144.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Pugh W. E., Hartley J. W. Plaque assay techniques for murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):1136–1139. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90362-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selten G., Cuypers H. T., Berns A. Proviral activation of the putative oncogene Pim-1 in MuLV induced T-cell lymphomas. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1793–1798. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03852.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selten G., Cuypers H. T., Zijlstra M., Melief C., Berns A. Involvement of c-myc in MuLV-induced T cell lymphomas in mice: frequency and mechanisms of activation. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3215–3222. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02281.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short M. K., Okenquist S. A., Lenz J. Correlation of leukemogenic potential of murine retroviruses with transcriptional tissue preference of the viral long terminal repeats. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1067–1072. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1067-1072.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck N. A., Baltimore D. Six distinct nuclear factors interact with the 75-base-pair repeat of the Moloney murine leukemia virus enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1101–1110. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck N. A., Renjifo B., Golemis E., Fredrickson T. N., Hartley J. W., Hopkins N. Mutation of the core or adjacent LVb elements of the Moloney murine leukemia virus enhancer alters disease specificity. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):233–242. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen D. Proviruses are adjacent to c-myc in some murine leukemia virus-induced lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2097–2101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiesen H. J., Bösze Z., Henry L., Charnay P. A DNA element responsible for the different tissue specificities of Friend and Moloney retroviral enhancers. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):614–618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.614-618.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsichlis P. N., Lohse M. A., Szpirer C., Szpirer J., Levan G. Cellular DNA regions involved in the induction of rat thymic lymphomas (Mlvi-1, Mlvi-2, Mlvi-3, and c-myc) represent independent loci as determined by their chromosomal map location in the rat. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):938–942. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.938-942.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver D., Costantini F., Imanishi-Kari T., Baltimore D. A transgenic immunoglobulin mu gene prevents rearrangement of endogenous genes. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):117–127. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80107-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuen P. H., Szurek P. F. The reduced virulence of the thymotropic Moloney murine leukemia virus derivative MoMuLV-TB is mapped to 11 mutations within the U3 region of the long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):471–480. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.471-480.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]