Abstract
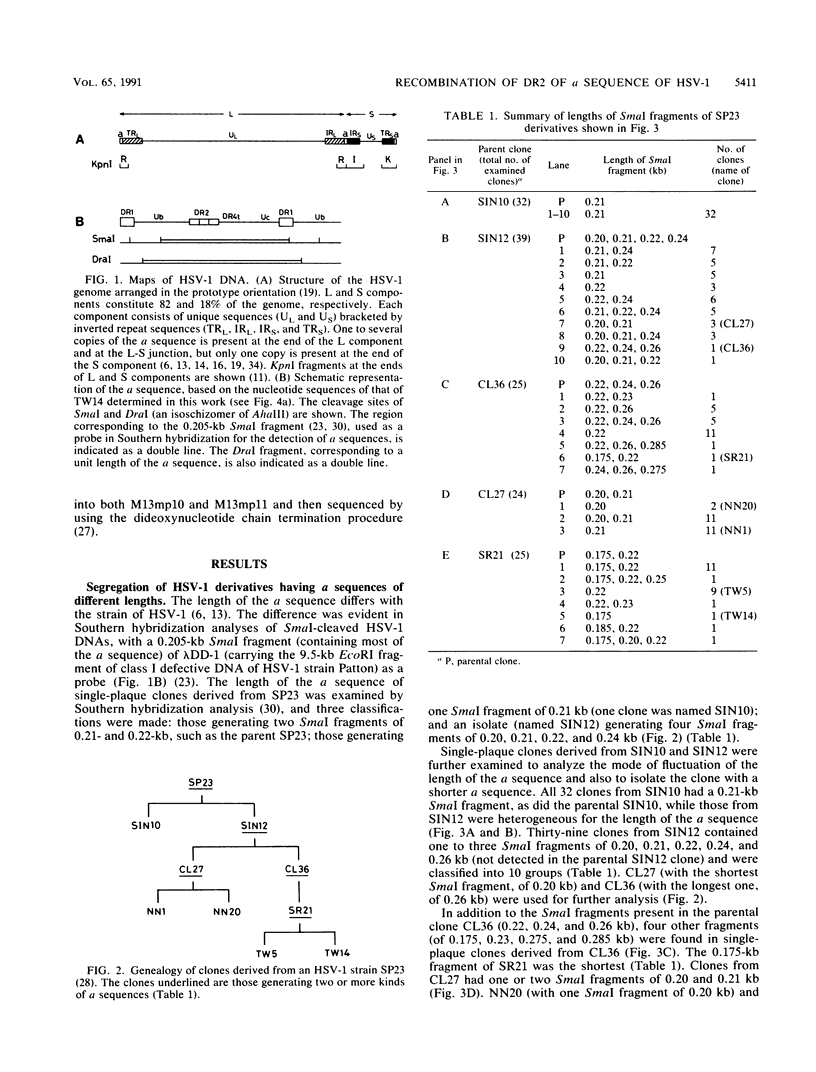
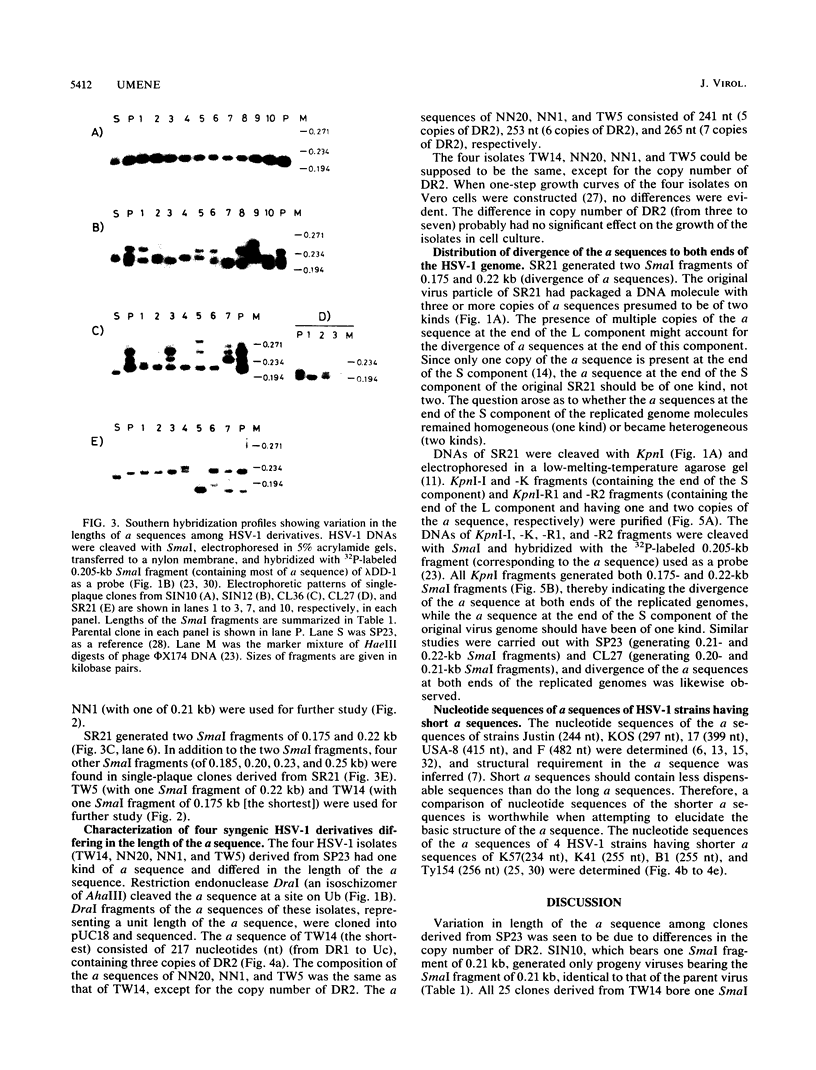
A series of herpes simplex virus type 1 derivatives, having a sequences composed of DR1, Ub, (DR2)3-7, DR4t (a truncated form of DR4), and Uc were isolated and examined. The derivative having a sequences with six copies of DR2 generated progeny viruses having a sequences with the same number (six copies) of DR2. Another derivative, having a sequences with three and seven copies of DR2, generated progeny viruses having a sequences with varied numbers (4, 5, 8, and 10 copies) of DR2, besides the original DR2 arrays (three and seven copies). Therefore, the variation in copy number of DR2 was assumed to be caused mainly by recombination between DR2 arrays rather than by slippage within a DR2 array during DNA replication. The presence of DR2-like sequences in internal direct repeat elements of DR4 and DR3.5 supported the hypothesis of the recombinogenic property of DR2. The equal distribution of divergence of a sequences to both ends of the virus genome favors the double-strand break and gap repair model to explain gene conversion and amplification of the a sequence.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackermann M., Chou J., Sarmiento M., Lerner R. A., Roizman B. Identification by antibody to a synthetic peptide of a protein specified by a diploid gene located in the terminal repeats of the L component of herpes simplex virus genome. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):843–850. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.843-850.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J., Roizman B. Characterization of DNA sequence-common and sequence-specific proteins binding to cis-acting sites for cleavage of the terminal a sequence of the herpes simplex virus 1 genome. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1059–1068. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1059-1068.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J., Roizman B. Isomerization of herpes simplex virus 1 genome: identification of the cis-acting and recombination sites within the domain of the a sequence. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):803–811. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80061-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J., Roizman B. The herpes simplex virus 1 gene for ICP34.5, which maps in inverted repeats, is conserved in several limited-passage isolates but not in strain 17syn+. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1014–1020. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1014-1020.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J., Roizman B. The terminal a sequence of the herpes simplex virus genome contains the promoter of a gene located in the repeat sequences of the L component. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):629–637. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.629-637.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Wilkie N. M. Nucleotide sequences of the joint between the L and S segments of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J Gen Virol. 1981 Aug;55(Pt 2):315–331. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-55-2-315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deiss L. P., Chou J., Frenkel N. Functional domains within the a sequence involved in the cleavage-packaging of herpes simplex virus DNA. J Virol. 1986 Sep;59(3):605–618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.3.605-618.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deiss L. P., Frenkel N. Herpes simplex virus amplicon: cleavage of concatemeric DNA is linked to packaging and involves amplification of the terminally reiterated a sequence. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):933–941. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.933-941.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harland J., Brown S. M. A herpes simplex virus type 2 variant in which a deletion across the L-S junction is replaced by single or multiple reiterations of extraneous DNA. J Gen Virol. 1989 Aug;70(Pt 8):2121–2137. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-8-2121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessberger R., Berg P. Repair of deletions and double-strand gaps by homologous recombination in a mammalian in vitro system. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):445–457. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locker H., Frenkel N. BamI, KpnI, and SalI restriction enzyme maps of the DNAs of herpes simplex virus strains Justin and F: occurrence of heterogeneities in defined regions of the viral DNA. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):429–441. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.429-441.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dalrymple M. A., Davison A. J., Dolan A., Frame M. C., McNab D., Perry L. J., Scott J. E., Taylor P. The complete DNA sequence of the long unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jul;69(Pt 7):1531–1574. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-7-1531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocarski E. S., Deiss L. P., Frenkel N. Nucleotide sequence and structural features of a novel US-a junction present in a defective herpes simplex virus genome. J Virol. 1985 Jul;55(1):140–146. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.1.140-146.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocarski E. S., Post L. E., Roizman B. Molecular engineering of the herpes simplex virus genome: insertion of a second L-S junction into the genome causes additional genome inversions. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):243–255. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90172-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocarski E. S., Roizman B. Site-specific inversion sequence of the herpes simplex virus genome: domain and structural features. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7047–7051. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocarski E. S., Roizman B. Structure and role of the herpes simplex virus DNA termini in inversion, circularization and generation of virion DNA. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):89–97. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90408-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasseri M., Mocarski E. S. The cleavage recognition signal is contained within sequences surrounding an a-a junction in herpes simplex virus DNA. Virology. 1988 Nov;167(1):25–30. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90050-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pogue-Geile K. L., Lee G. T., Spear P. G. Novel rearrangements of herpes simplex virus DNA sequences resulting from duplication of a sequence within the unique region of the L component. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):456–461. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.456-461.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roizman B. The structure and isomerization of herpes simplex virus genomes. Cell. 1979 Mar;16(3):481–494. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smiley J. R., Duncan J., Howes M. Sequence requirements for DNA rearrangements induced by the terminal repeat of herpes simplex virus type 1 KOS DNA. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):5036–5050. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.5036-5050.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostak J. W., Orr-Weaver T. L., Rothstein R. J., Stahl F. W. The double-strand-break repair model for recombination. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90331-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Kobayashi I. Evidence for the double-strand break repair model of bacteriophage lambda recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2790–2794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umene K., Enquist L. W. Isolation of novel herpes simplex virus type 1 derivatives with tandem duplications of DNA sequences encoding immediate-early mRNA-5 and an origin of replication. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):607–615. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.607-615.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umene K. Intermolecular recombination of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome analysed using two strains differing in restriction enzyme cleavage sites. J Gen Virol. 1985 Dec;66(Pt 12):2659–2670. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-12-2659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umene K. Restriction endonucleases recognizing DNA sequences of four base pairs facilitate differentiation of herpes simplex virus type 1 strains. Arch Virol. 1987;97(3-4):197–214. doi: 10.1007/BF01314421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umene K. Short, duplicated sequence indicative of the recombinogenicity of the junction between a unique and an inverted repeat sequence in the S component of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):1877–1883. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.1877-1883.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umene K. Transition from a heterozygous to a homozygous state of a pair of loci in the inverted repeat sequences of the L component of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1187–1192. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1187-1192.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umene K. Variability of the region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome yielding defective DNA: SmaI fragment polymorphism. Intervirology. 1985;23(3):131–139. doi: 10.1159/000149596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umene K., Watson R. J., Enquist L. W. Tandem repeated DNA in an intergenic region of herpes simplex virus type 1 (Patton). Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):33–39. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90102-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umene K., Yoshida M. Reiterated sequences of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) genome can serve as physical markers for the differentiation of HSV-1 strains. Arch Virol. 1989;106(3-4):281–299. doi: 10.1007/BF01313958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmuza S. L., Smiley J. R. Signals for site-specific cleavage of HSV DNA: maturation involves two separate cleavage events at sites distal to the recognition sequences. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):793–802. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80060-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmuza S. L., Smiley J. R. Unstable heterozygosity in a diploid region of herpes simplex virus DNA. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):356–362. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.356-362.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlazny D. A., Kwong A., Frenkel N. Site-specific cleavage/packaging of herpes simplex virus DNA and the selective maturation of nucleocapsids containing full-length viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1423–1427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner M. J., Summers W. C. Structure of the joint region and the termini of the DNA of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1978 Aug;27(2):374–387. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.2.374-387.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber P. C., Challberg M. D., Nelson N. J., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. Inversion events in the HSV-1 genome are directly mediated by the viral DNA replication machinery and lack sequence specificity. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):369–381. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90200-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber P. C., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. Recombinogenic properties of herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA sequences resident in simian virus 40 minichromosomes. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):300–306. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.300-306.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]