Abstract
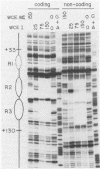
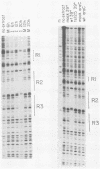
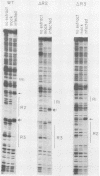
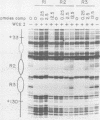
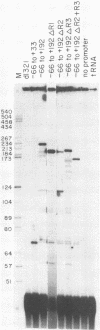
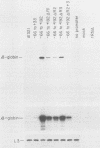
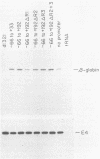
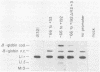
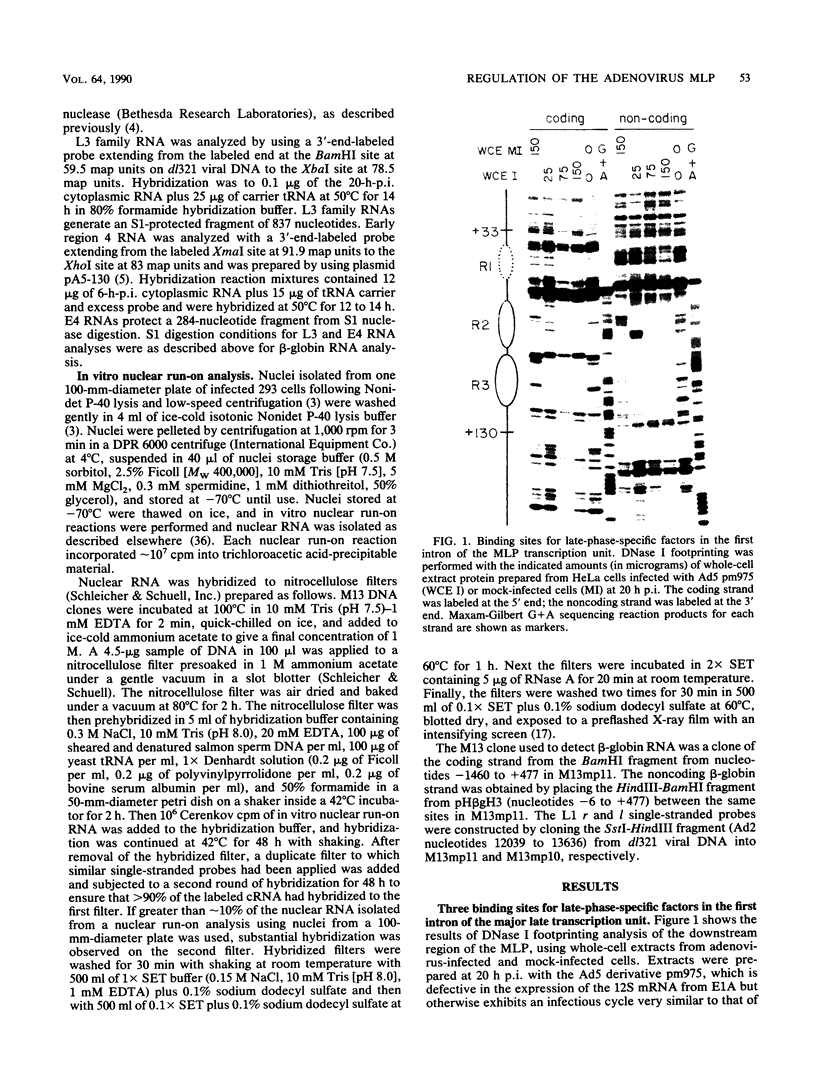
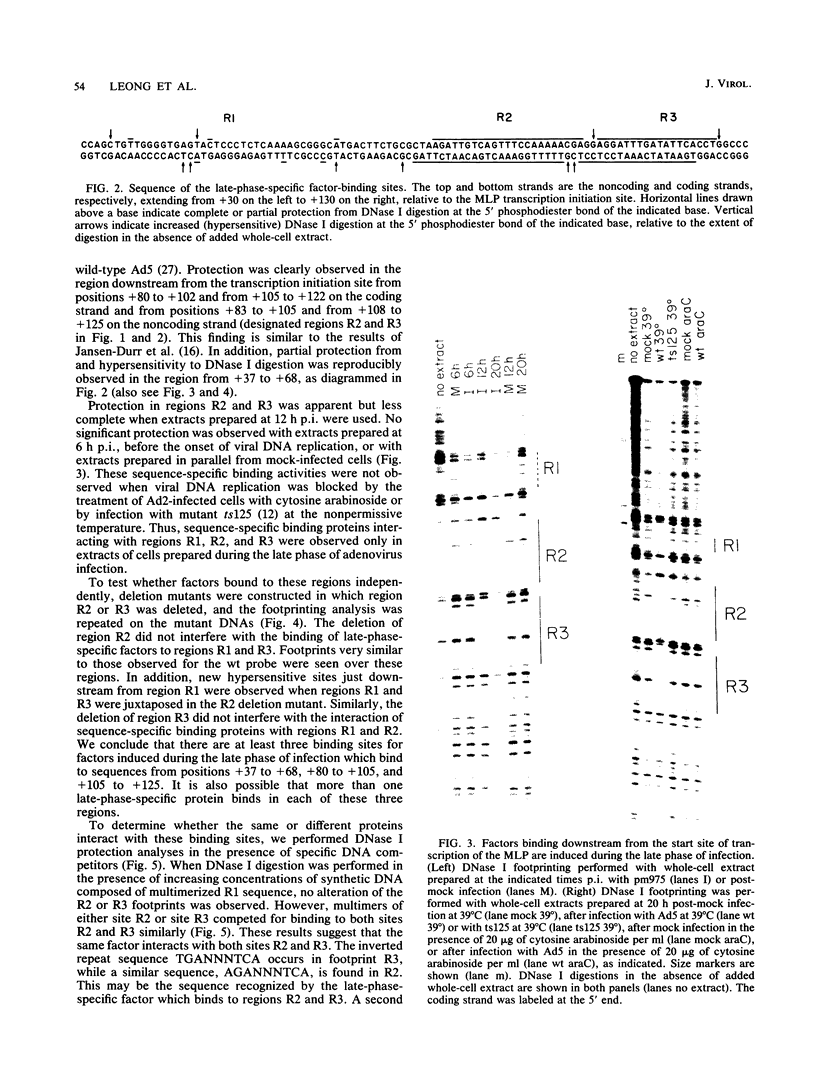
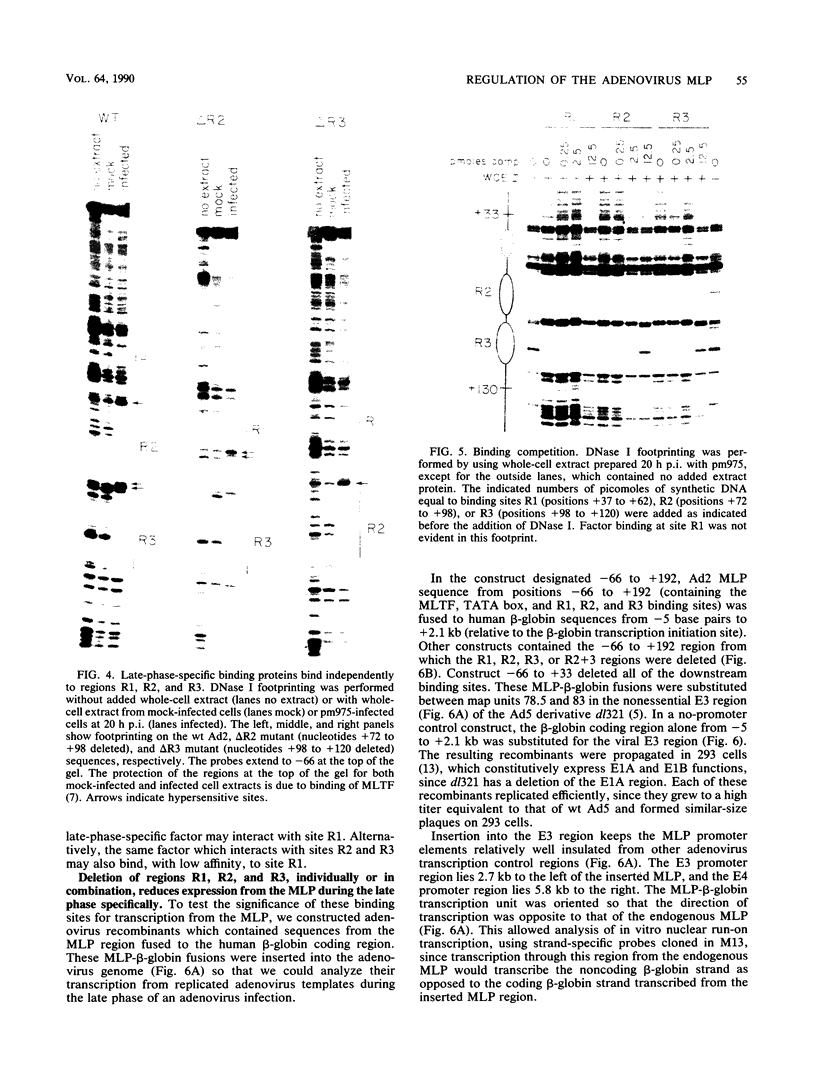
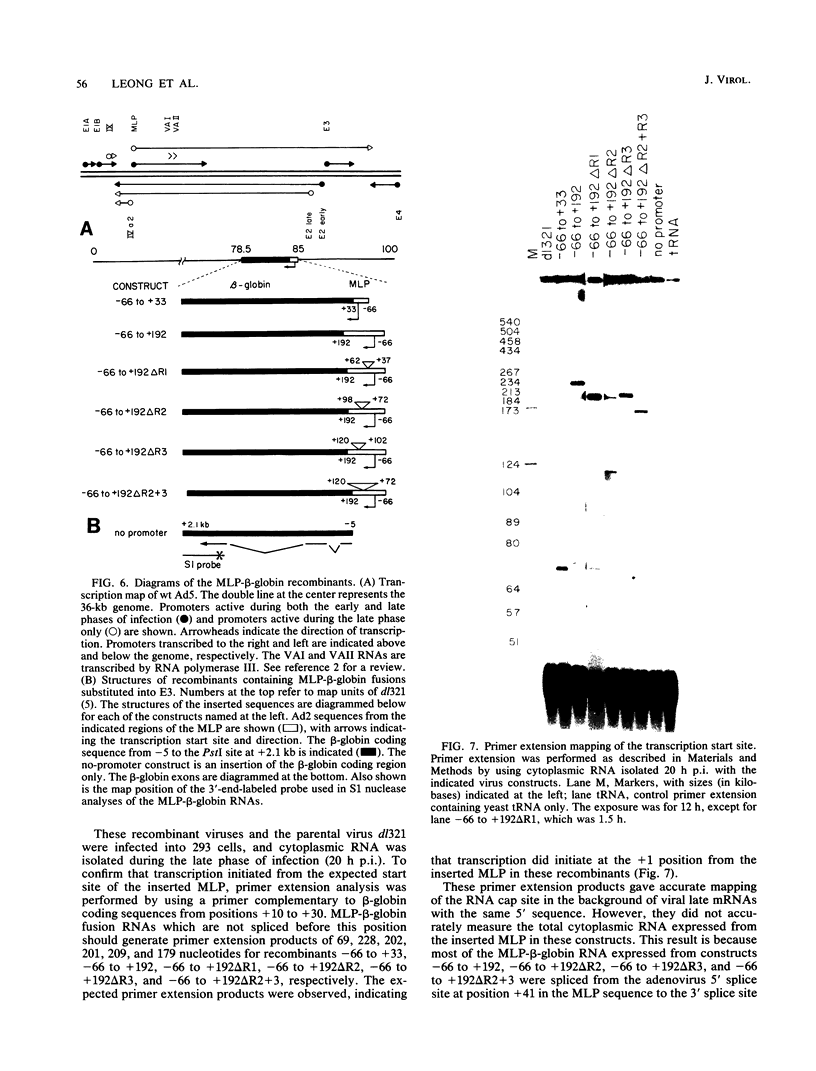
The adenovirus major late promoter (MLP) is active during both the early and late phases of infection. During the early phase the activity of the MLP is similar to those of the other early viral promoters, but during the late phase the rate of transcription from the MLP becomes much greater by comparison. We report here that sequence-specific binding proteins are induced during the late phase which interact with three regions in the first intron of the MLP transcription unit from positions +37 to +68, +80 to +105, and +105 to +125 relative to the transcription initiation site. To measure the significance of these binding sites for transcription during the late phase, we constructed MLP-beta-globin fusions and substituted them for early region 3 in adenovirus recombinants. Deletion of the binding sites caused significant reductions in the rate of transcription, specifically during the late phase of infection. Deletion of all three sites reduced the rate of transcription 25- to 50-fold and the accumulation of cytoplasmic MLP-beta-globin RNA 200-fold. These results indicate that the high rate of transcription from the MLP during the late phase of infection results from the interaction of virus-induced transcription factors with three binding sites in the first intron of the major late transcription unit.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akusjärvi G., Persson H. Controls of RNA splicing and termination in the major late adenovirus transcription unit. Nature. 1981 Jul 30;292(5822):420–426. doi: 10.1038/292420a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J. Adenovirus promoters and E1A transactivation. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:45–79. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.000401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Lee F., Harrison T., Williams J., Sharp P. A. Pre-early adenovirus 5 gene product regulates synthesis of early viral messenger RNAs. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):935–944. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90333-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat G., SivaRaman L., Murthy S., Domer P., Thimmappaya B. In vivo identification of multiple promoter domains of adenovirus EIIA-late promoter. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):2045–2052. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02469.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunet L. J., Babiss L. E., Young C. S., Mills D. R. Mutations in the adenovirus major late promoter: effects on viability and transcription during infection. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1091–1100. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carthew R. W., Chodosh L. A., Sharp P. A. An RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to an upstream element in the adenovirus major late promoter. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Carthew R. W., Sharp P. A. A single polypeptide possesses the binding and transcription activities of the adenovirus major late transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4723–4733. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Lewis J. B., Broker T. R. RNA transcription and splicing at early and intermediate times after adenovirus-2 infection. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):401–414. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Concino M., Goldman R. A., Caruthers M. H., Weinmann R. Point mutations of the adenovirus major late promoter with different transcriptional efficiencies in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8493–8496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensinger M. J., Ginsberg H. S. Selection and preliminary characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of type 5 adenovirus. J Virol. 1972 Sep;10(3):328–339. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.3.328-339.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Smiley J., Russell W. C., Nairn R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):59–74. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hen R., Sassone-Corsi P., Corden J., Gaub M. P., Chambon P. Sequences upstream from the T-A-T-A box are required in vivo and in vitro for efficient transcription from the adenovirus serotype 2 major late promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7132–7136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S. L., Manley J. L. DNA sequence required for initiation of transcription in vitro from the major late promoter of adenovirus 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):820–824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen-Durr P., Boeuf H., Kédinger C. Replication-induced stimulation of the major late promoter of adenovirus is correlated to the binding of a factor to sequences in the first intron. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 11;16(9):3771–3786. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.9.3771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A. The use of intensifying screens or organic scintillators for visualizing radioactive molecules resolved by gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):363–371. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong K., Berk A. J. Adenovirus early region 1A protein increases the number of template molecules transcribed in cell-free extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5844–5848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong K., Brunet L., Berk A. J. Factors responsible for the higher transcriptional activity of extracts of adenovirus-infected cells fractionate with the TATA box transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1765–1774. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis E. D., Manley J. L. Control of adenovirus late promoter expression in two human cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2433–2442. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. B., Mathews M. B. Control of adenovirus early gene expression: a class of immediate early products. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):303–313. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90138-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan J., Shenk T. In vivo identification of sequence elements required for normal function of the adenovirus major late transcriptional control region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 11;14(15):6327–6335. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour S. L., Grodzicker T., Tjian R. Downstream sequences affect transcription initiation from the adenovirus major late promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2684–2694. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto N. G., Moncollin V., Egly J. M., Chambon P. Specific interaction between a transcription factor and the upstream element of the adenovirus-2 major late promoter. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3563–3570. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04118.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncollin V., Miyamoto N. G., Zheng X. M., Egly J. M. Purification of a factor specific for the upstream element of the adenovirus-2 major late promoter. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2577–2584. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04537.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Fisher E. F., Caruthers M. H., Berk A. J. Resolving the functions of overlapping viral genes by site-specific mutagenesis at a mRNA splice site. Nature. 1982 Feb 4;295(5848):380–384. doi: 10.1038/295380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Mechanism of activation of early viral transcription by the adenovirus E1A gene product. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):213–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90304-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R., Wilson M. C. Regulation of adenovirus-2 gene expression at the level of transcriptional termination and RNA processing. Nature. 1981 Mar 12;290(5802):113–118. doi: 10.1038/290113a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Shander M. H., Manley J. L., Gefter M. L., Maniatis T. Structure and in vitro transcription of human globin genes. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1329–1336. doi: 10.1126/science.6158093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a gene-specific transcription factor with the adenovirus major late promoter upstream of the TATA box region. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw A. R., Ziff E. B. Transcripts from the adenovirus-2 major late promoter yield a single early family of 3' coterminal mRNAs and five late families. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):905–916. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90568-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shu L. M., Horwitz M. S., Engler J. A. Expression of enzymatically active adenovirus DNA polymerase from cloned DNA requires sequences upstream of the main open reading frame. Virology. 1987 Dec;161(2):520–526. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90146-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shu L., Pettit S. C., Engler J. A. The precise structure and coding capacity of mRNAs from early region 2B of human adenovirus serotype 2. Virology. 1988 Aug;165(2):348–356. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90579-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman B. W., Lewis J. B., Chow L. T., Mathews M. B., Smart J. E. Identification of the gene and mRNA for the adenovirus terminal protein precursor. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):497–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinheimer S. P., McKnight S. L. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional controls establish the cascade of herpes simplex virus protein synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 20;195(4):819–833. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90487-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu Y. T., Manley J. L. Generation and functional analyses for base-substitution mutants of the adenovirus 2 major late promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9309–9321. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]