Abstract
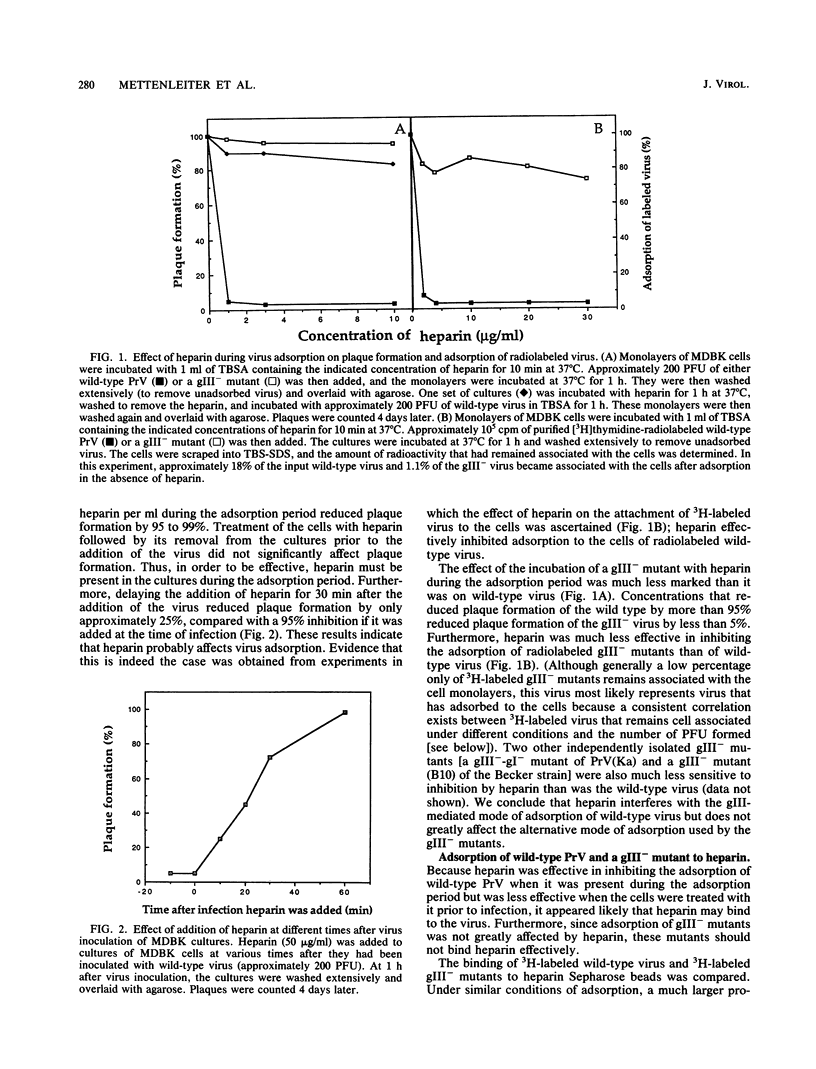
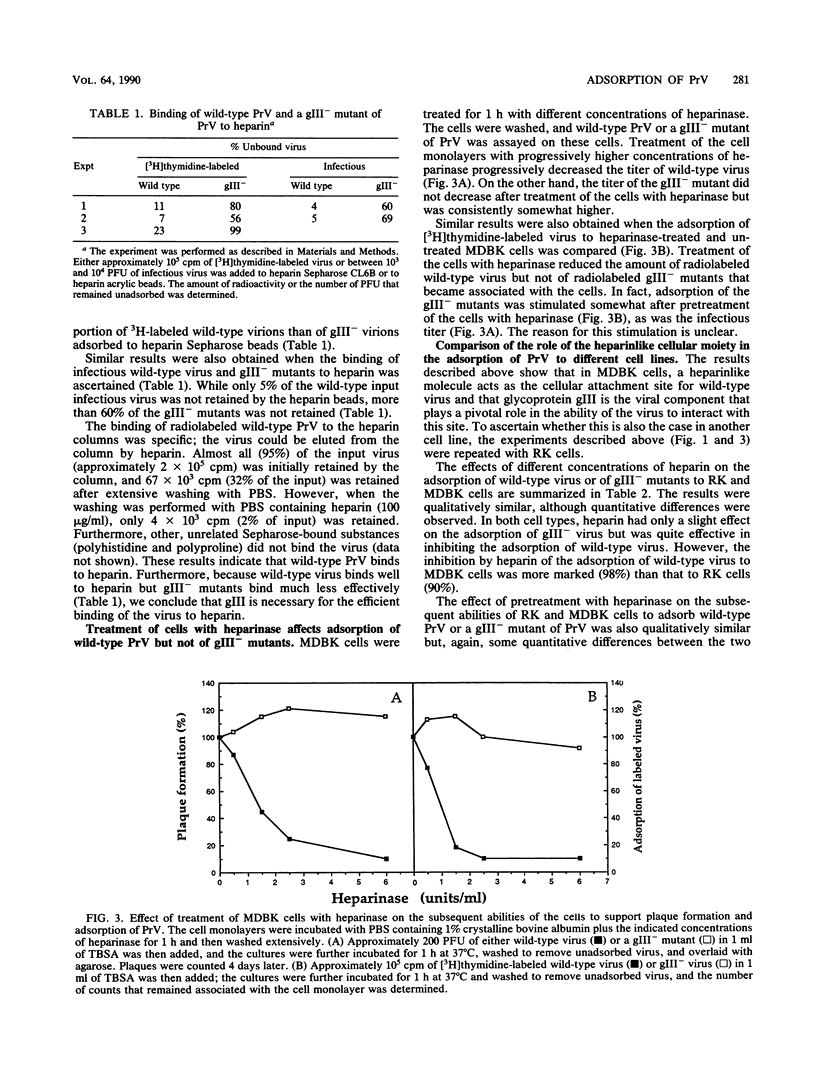
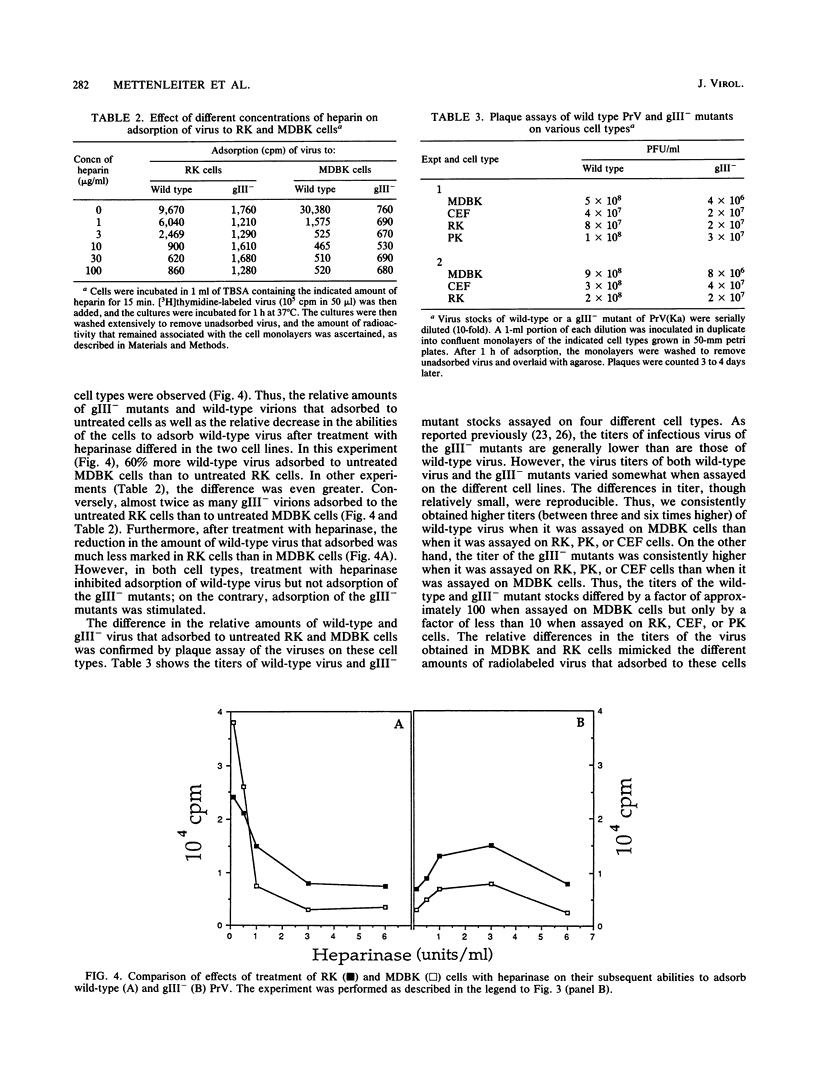
Glycoprotein gIII is one of the major envelope glycoproteins of pseudorabies virus (PrV) (Suid herpesvirus 1). Although it is dispensable for viral growth, it has been shown to play a prominent role in the attachment of the virus to target cells, since gIII- deletion mutants are severely impaired in adsorption (C. Schreurs, T. C. Mettenleiter, F. Zuckermann, N. Sugg, and T. Ben-Porat, J. Virol. 62:2251-2257, 1988). We show here that during the process of adsorption of PrV, the viral glycoprotein gIII interacts with a cellular heparinlike receptor. This conclusion is based on the following findings. (i) Heparin inhibits plaque formation of PrV by preventing the adsorption of wild-type virions to target cells. However, heparin does not interfere with the plaque formation of PrV mutants that lack glycoprotein gIII. (ii) Wild-type virions readily adsorb to matrix-bound heparin, whereas gIII- mutants do not. (iii) Pretreatment of cells with heparinase reduces considerably the ability of wild-type PrV to adsorb to these cells and to form plaques but does not negatively affect gIII- mutants. (iv) Glycoprotein gIII binds to heparin and appears to do so in conjunction with glycoprotein gII. Although heparin significantly reduces the adsorption of wild-type virus to all cell types tested, quantitative differences in the degree of inhibition of virus adsorption by heparin to different cell types were observed. Different cell types also retain their abilities to adsorb wild-type PrV to a different extent after treatment with heparinase and differ somewhat in their relative abilities to adsorb gIII- mutants. Our results show that while the primary pathway of adsorption of wild-type PrV to cells occurs via the interaction of viral glycoprotein gIII with a cellular heparinlike receptor, an alternative mode of adsorption, which is not dependent on either component, exists. Furthermore, the relative abilities of different cell types to adsorb PrV by the gIII-dependent or the alternative mode vary to some extent.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Porat T., Demarchi J. M., Kaplan A. S. Characterization of defective interfering viral particles present in a population of pseudorabies virions. Virology. 1974 Sep;61(1):29–37. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90239-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai W. H., Gu B., Person S. Role of glycoprotein B of herpes simplex virus type 1 in viral entry and cell fusion. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2596–2604. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2596-2604.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller A. O., Spear P. G. Anti-glycoprotein D antibodies that permit adsorption but block infection by herpes simplex virus 1 prevent virion-cell fusion at the cell surface. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5454–5458. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller A. O., Spear P. G. Specificities of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies that inhibit adsorption of herpes simplex virus to cells and lack of inhibition by potent neutralizing antibodies. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):475–482. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.475-482.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampl H., Ben-Porat T., Ehrlicher L., Habermehl K. O., Kaplan A. S. Characterization of the envelope proteins of pseudorabies virus. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):583–590. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.583-590.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highlander S. L., Sutherland S. L., Gage P. J., Johnson D. C., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies specific for herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D inhibit virus penetration. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3356–3364. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3356-3364.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Ligas M. W. Herpes simplex viruses lacking glycoprotein D are unable to inhibit virus penetration: quantitative evidence for virus-specific cell surface receptors. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4605–4612. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4605-4612.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN A. S., BEN-PORAT T. The action of 5-fluorouracil on the nucleic acid metabolism of pseudorabies virus-infected and noninfected rabbit kidney cells. Virology. 1961 Jan;13:78–92. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90034-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langeland N., Holmsen H., Lillehaug J. R., Haarr L. Evidence that neomycin inhibits binding of herpes simplex virus type 1 to the cellular receptor. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3388–3393. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3388-3393.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langeland N., Moore L. J., Holmsen H., Haarr L. Interaction of polylysine with the cellular receptor for herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jun;69(Pt 6):1137–1145. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-6-1137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ligas M. W., Johnson D. C. A herpes simplex virus mutant in which glycoprotein D sequences are replaced by beta-galactosidase sequences binds to but is unable to penetrate into cells. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1486–1494. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1486-1494.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettenleiter T. C. Glycoprotein gIII deletion mutants of pseudorabies virus are impaired in virus entry. Virology. 1989 Aug;171(2):623–625. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90635-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettenleiter T. C., Schreurs C., Zuckermann F., Ben-Porat T., Kaplan A. S. Role of glycoprotein gIII of pseudorabies virus in virulence. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2712–2717. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2712-2717.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettenleiter T. C., Schreurs C., Zuckermann F., Ben-Porat T. Role of pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gI in virus release from infected cells. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2764–2769. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2764-2769.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettenleiter T. C., Zsak L., Kaplan A. S., Ben-Porat T., Lomniczi B. Role of a structural glycoprotein of pseudorabies in virus virulence. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):4030–4032. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.4030-4032.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohanty J. G., Rosenthal K. S. 2-deoxy-D-glucose inhibition of herpes simplex virus type-1 receptor expression. Antiviral Res. 1986 May;6(3):137–149. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(86)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan C., Rose H. M., Mednis B. Electron microscopy of herpes simplex virus. I. Entry. J Virol. 1968 May;2(5):507–516. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.5.507-516.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahmias A. J., Kibrick S. Inhibitory effect of heparin on herpes simplex virus. J Bacteriol. 1964 May;87(5):1060–1066. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.5.1060-1066.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble A. G., Lee G. T., Sprague R., Parish M. L., Spear P. G. Anti-gD monoclonal antibodies inhibit cell fusion induced by herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1983 Aug;129(1):218–224. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90409-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Para M. F., Baucke R. B., Spear P. G. Immunoglobulin G(Fc)-binding receptors on virions of herpes simplex virus type 1 and transfer of these receptors to the cell surface by infection. J Virol. 1980 May;34(2):512–520. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.2.512-520.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins A. K., Watson R. J., Whealy M. E., Hays W. W., Enquist L. W. Characterization of a pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gene with homology to herpes simplex virus type 1 and type 2 glycoprotein C. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):339–347. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.339-347.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreurs C., Mettenleiter T. C., Zuckermann F., Sugg N., Ben-Porat T. Glycoprotein gIII of pseudorabies virus is multifunctional. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2251–2257. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2251-2257.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEMOTO K. K., FABISCH P. INHIBITION OF HERPES VIRUS BY NATURAL AND SYNTHETIC ACID POLYSACCHARIDES. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 May;116:140–144. doi: 10.3181/00379727-116-29183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whealy M. E., Robbins A. K., Enquist L. W. Pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gIII is required for efficient virus growth in tissue culture. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2512–2515. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2512-2515.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WuDunn D., Spear P. G. Initial interaction of herpes simplex virus with cells is binding to heparan sulfate. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):52–58. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.52-58.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckermann F., Zsak L., Reilly L., Sugg N., Ben-Porat T. Early interactions of pseudorabies virus with host cells: functions of glycoprotein gIII. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3323–3329. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3323-3329.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]