Abstract
The pathogenic profiles of two heterologous animal rotaviruses, rhesus rotavirus strain MMU 18006 and bovine rotavirus strain WC3, were evaluated in mice with severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID mice) and normal BALB/c mice. Control animals were inoculated with homologous murine strain EDIM 5099 or a tissue culture-adapted murine rotavirus. Heterologous infection with rhesus rotavirus resulted in hepatitis in 84% of SCID and 21% of BALB/c mice, with mortality rates of 27 and 0%, respectively. Surviving SCID animals developed chronic liver disease, while symptoms in BALB/c mice resolved in 2 to 4 weeks after onset. Histopathologic examination revealed a diffuse hepatitis with focal areas of parenchymal necrosis. Rotavirus was detected in liver tissue from 100% of 29 SCID and 85% (11 of 13) BALB/c animals tested by cell culture infectivity, immunofluorescence, or electron microscopy. No extramucosal spread of virus or hepatitis was observed after infection with heterologous bovine strain WC3 or homologous murine rotaviruses. This finding of a novel rotavirus-induced disease manifestation suggests altered tissue tropism in a heterologous host for a group of viruses previously shown to replicate exclusively in the gut mucosa. The implications of our observations suggest that in human vaccine trials utilizing heterologous rotavirus strains, special attention should be paid to children with immunodeficiency disorders, and screening for hepatic function should be included in vaccine protocols.
Full text
PDF
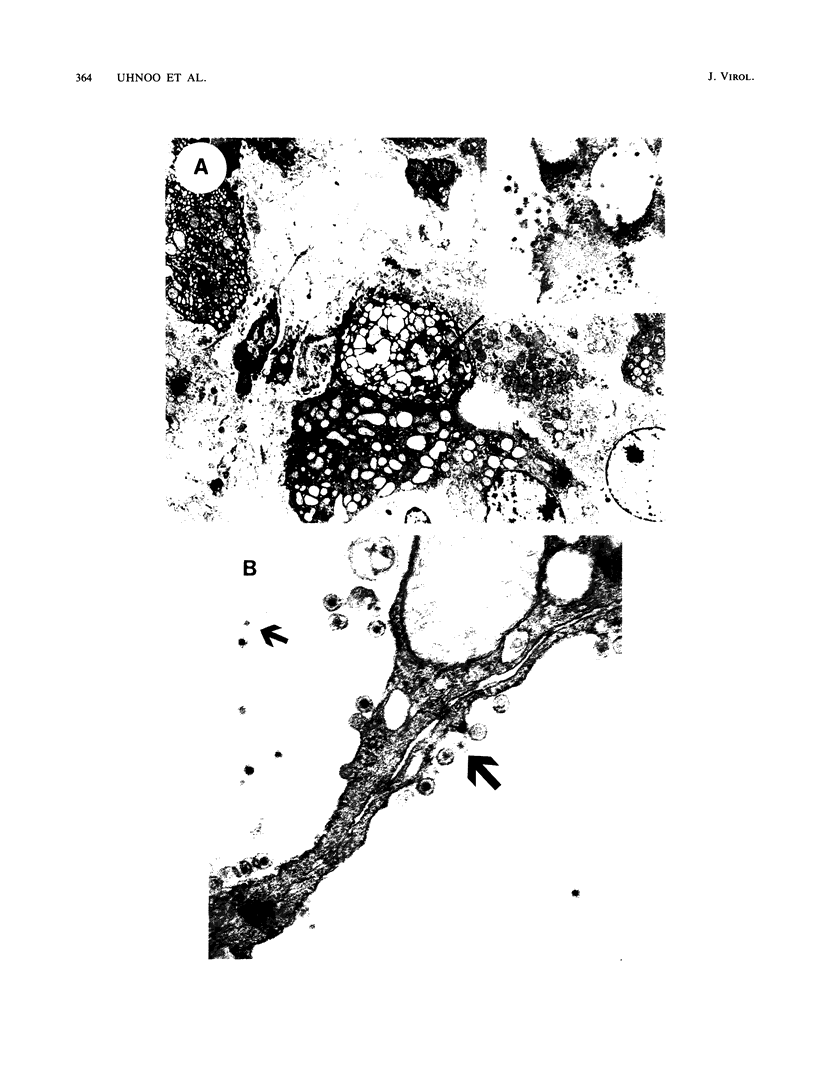






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson E. L., Belshe R. B., Bartram J., Crookshanks-Newman F., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Evaluation of rhesus rotavirus vaccine (MMU 18006) in infants and young children. J Infect Dis. 1986 May;153(5):823–831. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.5.823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell L. M., Clark H. F., O'Brien E. A., Kornstein M. J., Plotkin S. A., Offit P. A. Gastroenteritis caused by human rotaviruses (serotype three) in a suckling mouse model. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1987 Jan;184(1):127–132. doi: 10.3181/00379727-184-rc2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop R. F., Davidson G. P., Holmes I. H., Ruck B. J. Virus particles in epithelial cells of duodenal mucosa from children with acute non-bacterial gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1973 Dec 8;2(7841):1281–1283. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92867-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black R. E., Merson M. H., Rahman A. S., Yunus M., Alim A. R., Huq I., Yolken R. H., Curlin G. T. A two-year study of bacterial, viral, and parasitic agents associated with diarrhea in rural Bangladesh. J Infect Dis. 1980 Nov;142(5):660–664. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.5.660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosma G. C., Custer R. P., Bosma M. J. A severe combined immunodeficiency mutation in the mouse. Nature. 1983 Feb 10;301(5900):527–530. doi: 10.1038/301527a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark H. F., Borian F. E., Bell L. M., Modesto K., Gouvea V., Plotkin S. A. Protective effect of WC3 vaccine against rotavirus diarrhea in infants during a predominantly serotype 1 rotavirus season. J Infect Dis. 1988 Sep;158(3):570–587. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.3.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark H. F., Furukawa T., Bell L. M., Offit P. A., Perrella P. A., Plotkin S. A. Immune response of infants and children to low-passage bovine rotavirus (strain WC3). Am J Dis Child. 1986 Apr;140(4):350–356. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1986.02140180084030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coelho K. I., Bryden A. S., Hall C., Flewett T. H. Pathology of rotavirus infection in suckling mice: A study by conventional histology, immunofluorescence, ultrathin sections, and scanning electron microscopy. Ultrastruct Pathol. 1981 Jan-Mar;2(1):59–80. doi: 10.3109/01913128109031504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cukor G., Blacklow N. R. Human viral gastroenteritis. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Jun;48(2):157–179. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.2.157-179.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Graham D. Y., Mason B. B. Proteolytic enhancement of rotavirus infectivity: molecular mechanisms. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):879–888. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.879-888.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H. B., Vo P. T., Jones R. Cultivation and characterization of three strains of murine rotavirus. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):585–590. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.585-590.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunow J. E., Dunton S. F., Waner J. L. Human rotavirus-like particles in a hepatic abscess. J Pediatr. 1985 Jan;106(1):73–76. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(85)80470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herring A. J., Inglis N. F., Ojeh C. K., Snodgrass D. R., Menzies J. D. Rapid diagnosis of rotavirus infection by direct detection of viral nucleic acid in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):473–477. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.473-477.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hrdy D. B., Rubin D. H., Fields B. N. Molecular basis of reovirus neurovirulence: role of the M2 gene in avirulence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1298–1302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalica A. R., Flores J., Greenberg H. B. Identification of the rotaviral gene that codes for hemagglutination and protease-enhanced plaque formation. Virology. 1983 Feb;125(1):194–205. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalica A. R., Greenberg H. B., Wyatt R. G., Flores J., Sereno M. M., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Genes of human (strain Wa) and bovine (strain UK) rotaviruses that code for neutralization and subgroup antigens. Virology. 1981 Jul 30;112(2):385–390. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90285-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Flores J., Hoshino Y., Glass R. I., Midthun K., Gorziglia M., Chanock R. M. Rotavirus: the major etiologic agent of severe infantile diarrhea may be controllable by a "Jennerian" approach to vaccination. J Infect Dis. 1986 May;153(5):815–822. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.5.815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs A., Chan L., Hotrakitya C., Overturf G., Portnoy B. Serum transaminase elevations in infants with rotavirus gastroenteritis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1986 Nov-Dec;5(6):873–877. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198611000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losonsky G. A., Rennels M. B., Kapikian A. Z., Midthun K., Ferra P. J., Fortier D. N., Hoffman K. M., Baig A., Levine M. M. Safety, infectivity, transmissibility and immunogenicity of rhesus rotavirus vaccine (MMU 18006) in infants. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1986 Jan-Feb;5(1):25–29. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198601000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offit P. A., Blavat G., Greenberg H. B., Clark H. F. Molecular basis of rotavirus virulence: role of gene segment 4. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):46–49. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.46-49.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offit P. A., Blavat G. Identification of the two rotavirus genes determining neutralization specificities. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):376–378. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.376-378.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offit P. A., Clark H. F., Kornstein M. J., Plotkin S. A. A murine model for oral infection with a primate rotavirus (simian SA11). J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):233–236. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.233-236.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters R. L., Collins M. J., O'Beirne A. J., Howton P. A., Hourihan S. L., Thomas S. F. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of antibodies to murine hepatitis virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Oct;10(4):595–597. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.4.595-597.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramig R. F. The effects of host age, virus dose, and virus strain on heterologous rotavirus infection of suckling mice. Microb Pathog. 1988 Mar;4(3):189–202. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riepenhoff-Talty M., Dharakul T., Kowalski E., Michalak S., Ogra P. L. Persistent rotavirus infection in mice with severe combined immunodeficiency. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3345–3348. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3345-3348.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saulsbury F. T., Winkelstein J. A., Yolken R. H. Chronic rotavirus infection in immunodeficiency. J Pediatr. 1980 Jul;97(1):61–65. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw R. D., Vo P. T., Offit P. A., Coulson B. S., Greenberg H. B. Antigenic mapping of the surface proteins of rhesus rotavirus. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):434–451. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90205-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan J. F., Eydelloth R. S., Vonderfecht S. L., Aurelian L. Virus-specific immunity in neonatal and adult mouse rotavirus infection. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):917–927. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.917-927.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuker G., Oshiro L. S., Schmidt N. J. Antigenic comparisons of two new rotaviruses from rhesus monkeys. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Feb;11(2):202–203. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.2.202-203.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabin R., Nusslé D. Entérites à rotavirus chez l'enfant. Helv Paediatr Acta Suppl. 1980 May;(44 Suppl):1–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tallett S., MacKenzie C., Middleton P., Kerzner B., Hamilton R. Clinical, laboratory, and epidemiologic features of a viral gastroenteritis in infants and children. Pediatrics. 1977 Aug;60(2):217–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terrett L. A., Saif L. J., Theil K. W., Kohler E. M. Physicochemical characterization of porcine pararotavirus and detection of virus and viral antibodies using cell culture immunofluorescence. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Feb;25(2):268–272. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.2.268-272.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M. E., Luton P., Mortimer J. Y. Virus diarrhoea associated with pale fatty faeces. J Hyg (Lond) 1981 Oct;87(2):313–319. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400069539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesikari T., Isolauri E., Delem A., D'Hondt E., André F. E., Zissis G. Immunogenicity and safety of live oral attenuated bovine rotavirus vaccine strain RIT 4237 in adults and young children. Lancet. 1983 Oct 8;2(8354):807–811. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90734-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner H. L., Powers M. L., Fields B. N. Absolute linkage of virulence and central nervous system cell tropism of reoviruses to viral hemagglutinin. J Infect Dis. 1980 May;141(5):609–616. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.5.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Zoysa I., Feachem R. G. Interventions for the control of diarrhoeal diseases among young children: rotavirus and cholera immunization. Bull World Health Organ. 1985;63(3):569–583. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]