Abstract
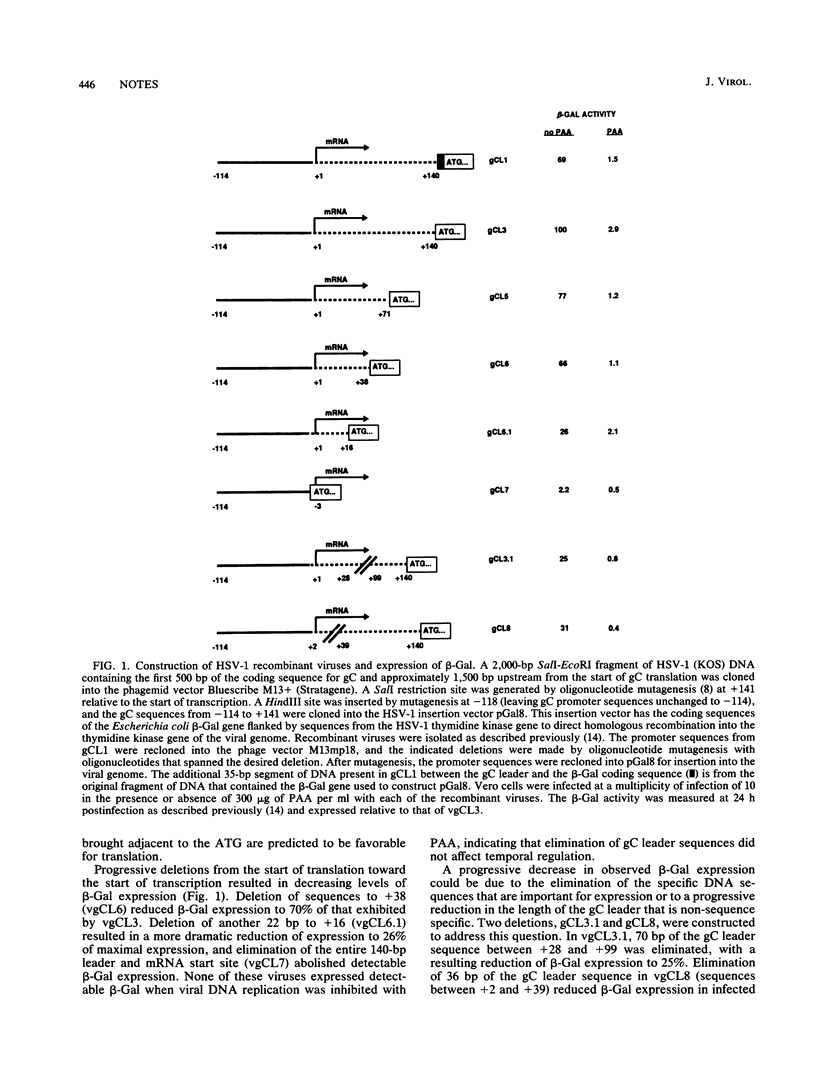
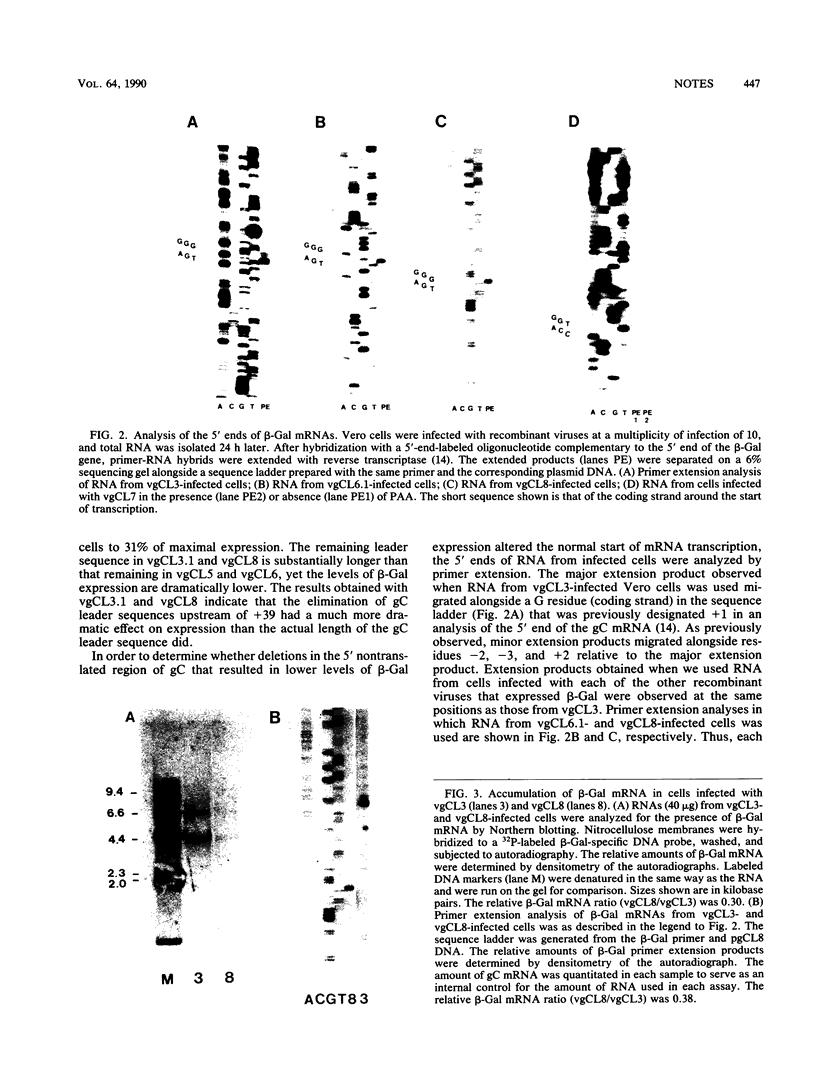
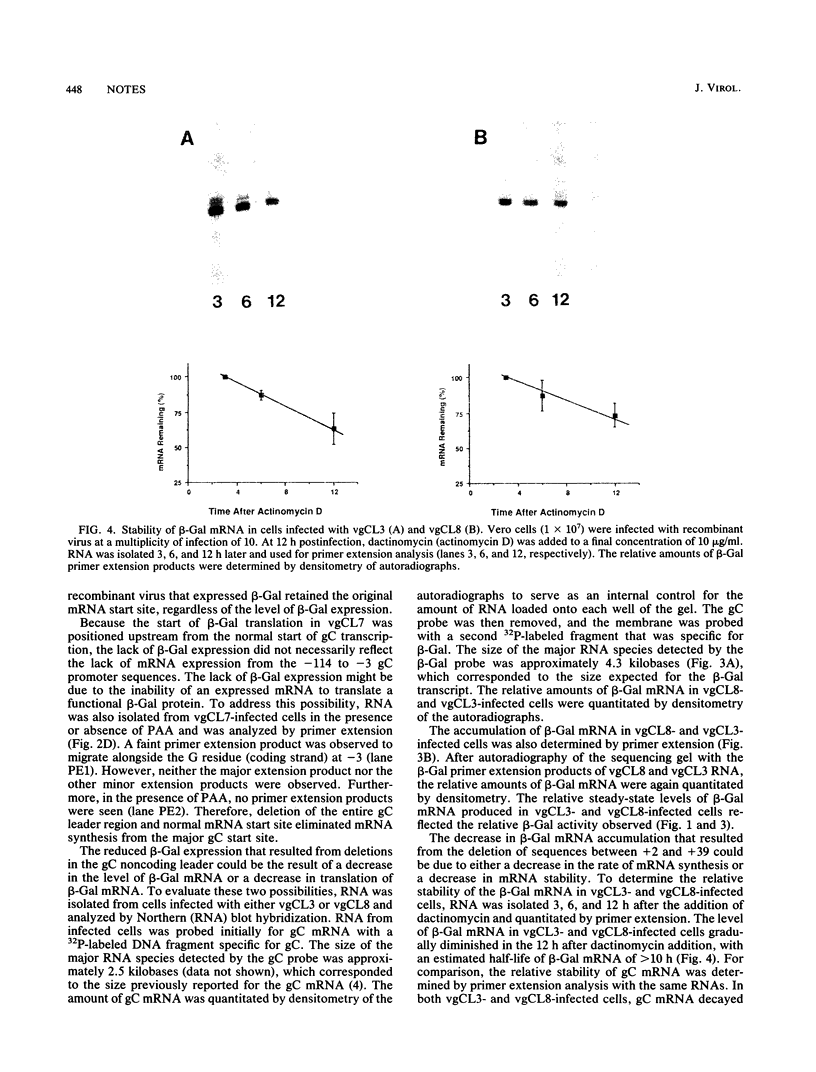
The role of the 5' noncoding region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein C (gC) gene in viral gene expression was investigated with recombinant herpesviruses that contained the bacterial beta-galactosidase gene under the control of the gC promoter-regulatory region. Each of these viruses had the same DNA sequences from the start of gC transcription upstream to -114 but had variable segments of the downstream 140-base-pair sequence that is between the start of gC transcription and translation. Analysis of beta-galactosidase expression and mRNA synthesis from these viruses demonstrated the importance of DNA sequences from the start of gC transcription downstream to +38 for optimal expression from the gC promoter.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blair E. D., Blair C. C., Wagner E. K. Herpes simplex virus virion stimulatory protein mRNA leader contains sequence elements which increase both virus-induced transcription and mRNA stability. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2499–2508. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2499-2508.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen D. M., Weinheimer S. P., McKnight S. L. A genetic approach to promoter recognition during trans induction of viral gene expression. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):53–59. doi: 10.1126/science.3018926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis D., Smiley J. R. Transactivation of a late herpes simplex virus promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):544–551. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frink R. J., Eisenberg R., Cohen G., Wagner E. K. Detailed analysis of the portion of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome encoding glycoprotein C. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):634–647. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.634-647.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homa F. L., Glorioso J. C., Levine M. A specific 15-bp TATA box promoter element is required for expression of a herpes simplex virus type 1 late gene. Genes Dev. 1988 Jan;2(1):40–53. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.1.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homa F. L., Otal T. M., Glorioso J. C., Levine M. Transcriptional control signals of a herpes simplex virus type 1 late (gamma 2) gene lie within bases -34 to +124 relative to the 5' terminus of the mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3652–3666. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavromara-Nazos P., Silver S., Hubenthal-Voss J., McKnight J. L., Roizman B. Regulation of herpes simplex virus 1 genes: alpha gene sequence requirements for transient induction of indicator genes regulated by beta or late (gamma 2) promoters. Virology. 1986 Mar;149(2):152–164. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90117-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael N., Spector D., Mavromara-Nazos P., Kristie T. M., Roizman B. The DNA-binding properties of the major regulatory protein alpha 4 of herpes simplex viruses. Science. 1988 Mar 25;239(4847):1531–1534. doi: 10.1126/science.2832940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira M., Homa F. L., Glorioso J. C., Levine M. Regulation of the herpes simplex virus type 1 late (gamma 2) glycoprotein C gene: sequences between base pairs -34 to +29 control transient expression and responsiveness to transactivation by the products of the immediate early (alpha) 4 and 0 genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 10;15(7):3097–3111. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.7.3097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver S., Roizman B. gamma 2-Thymidine kinase chimeras are identically transcribed but regulated a gamma 2 genes in herpes simplex virus genomes and as beta genes in cell genomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):518–528. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinheimer S. P., McKnight S. L. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional controls establish the cascade of herpes simplex virus protein synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 20;195(4):819–833. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90487-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir J. P., Narayanan P. R. The use of beta-galactosidase as a marker gene to define the regulatory sequences of the herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein C gene in recombinant herpesviruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 11;16(21):10267–10282. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.21.10267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]