Abstract
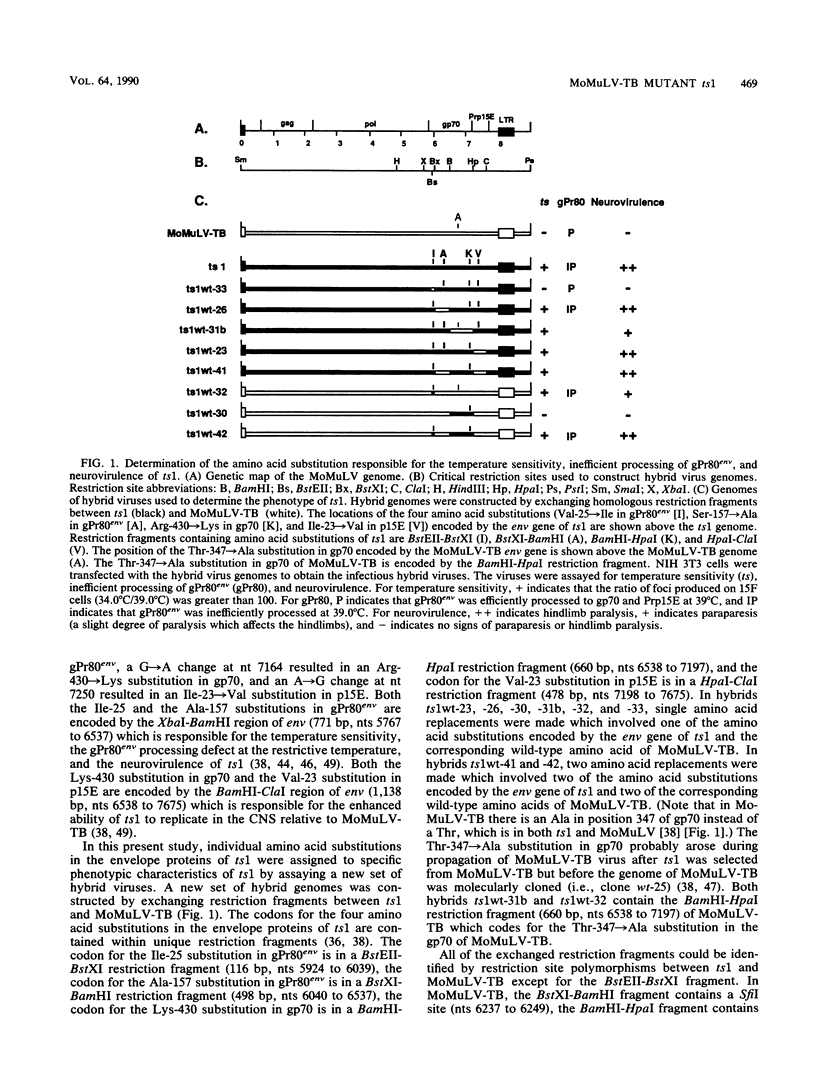
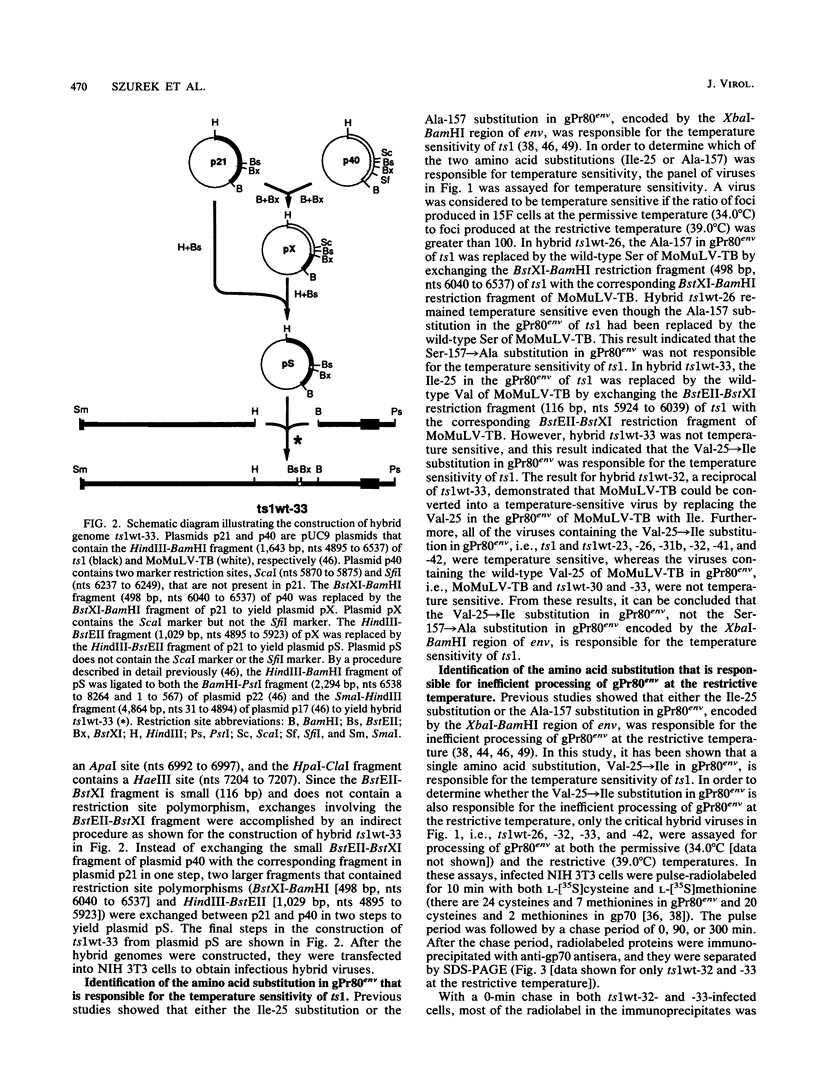
ts1 is a neurovirulent spontaneous temperature-sensitive mutant of Moloney murine leukemia virus TB which causes hindlimb paralysis in mice. Previously, it had been shown that the temperature-sensitive defect resided in the env gene. At the restrictive temperature, the envelope precursor polyprotein, gPr80env, is inefficiently processed intracellularly into two cleavage products, gp70 and Prp15E. This inefficient processing of gPr80env is correlated with neurovirulence. In this study, it was shown that a single amino acid substitution, Val-25----Ile in gPr80env, is responsible for the temperature sensitivity, inefficient processing of gPr80env at the restrictive temperature, and neurovirulence of ts1. At the restrictive temperature, a steady-state level of nonprocessed, endoglycosidase H-sensitive gPr80env remained in the endoplasmic reticulum of cells infected by ts1, but no endoglycosidase H-resistant gPr80env and only trace amounts of gp70 were detected in the infected cells. Since the host cell-encoded processing protease resides in the cis cisternae of the Golgi apparatus, inefficient processing of gPr80env at the restrictive temperature is most likely due to inefficient transport of gPr80env from the endoplasmic reticulum to the cis cisternae of the Golgi apparatus rather than due to misfolded gPr80env being a poor substrate for the processing protease at the restrictive temperature.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albritton L. M., Tseng L., Scadden D., Cunningham J. M. A putative murine ecotropic retrovirus receptor gene encodes a multiple membrane-spanning protein and confers susceptibility to virus infection. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):659–666. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90134-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALL J. K., HUH T. Y., MCCARTER J. A. ON THE STATISTICAL DISTRIBUTION OF EPIDERMAL PAPILLOMATA IN MICE. Br J Cancer. 1964 Mar;18:120–123. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1964.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilello J. A., Pitts O. M., Hoffman P. M. Characterization of a progressive neurodegenerative disease induced by a temperature-sensitive Moloney murine leukemia virus infection. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):234–241. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.234-241.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland C. S., Zimmer K. P., Wagner K. R., Healey G. A., Mellman I., Helenius A. Folding, trimerization, and transport are sequential events in the biogenesis of influenza virus hemagglutinin. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):197–209. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90381-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doms R. W., Ruusala A., Machamer C., Helenius J., Helenius A., Rose J. K. Differential effects of mutations in three domains on folding, quaternary structure, and intracellular transport of vesicular stomatitis virus G protein. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):89–99. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards S. A., Fan H. gag-Related polyproteins of Moloney murine leukemia virus: evidence for independent synthesis of glycosylated and unglycosylated forms. J Virol. 1979 May;30(2):551–563. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.2.551-563.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Famulari N. G., English K. J. Env gene products of AKR dual-tropic viruses: examination of peptide maps and cell surface expression. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):971–976. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.971-976.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitting T., Kabat D. Evidence for a glycoprotein "signal" involved in transport between subcellular organelles. Two membrane glycoproteins encoded by murine leukemia virus reach the cell surface at different rates. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14011–14017. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner M. B. Retroviral spongiform polioencephalomyelopathy. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Jan-Feb;7(1):99–110. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.1.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., McCammon K., Sambrook J. Expression of wild-type and mutant forms of influenza hemagglutinin: the role of folding in intracellular transport. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):939–950. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenberg D. P. Genetic studies of protein stability and mechanisms of folding. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1988;17:481–507. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.17.060188.002405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberger J. S., Stephenson J. R., Aaronson S. A. Temperature-sensitive mutants of murine leukemia virus. V. Impaired leukemogenic activity in vivo. Int J Cancer. 1975 Jun 15;15(6):1009–1015. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910150618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harouse J. M., Kunsch C., Hartle H. T., Laughlin M. A., Hoxie J. A., Wigdahl B., Gonzalez-Scarano F. CD4-independent infection of human neural cells by human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2527–2533. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2527-2533.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland C. A., Wozney J., Hopkins N. Nucleotide sequence of the gp70 gene of murine retrovirus MCF 247. J Virol. 1983 Sep;47(3):413–420. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.3.413-420.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. T., McArthur J. C., Narayan O. The neurobiology of human immunodeficiency virus infections. FASEB J. 1988 Nov;2(14):2970–2981. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.14.2846395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kai K., Furuta T. Isolation of paralysis-inducing murine leukemia viruses from Friend virus passaged in rats. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):970–973. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.970-973.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Kornfeld S. Assembly of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:631–664. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreis T. E., Lodish H. F. Oligomerization is essential for transport of vesicular stomatitis viral glycoprotein to the cell surface. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):929–937. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90075-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machida C. A., Kabat D. Role of partial proteolysis in processing murine leukemia virus membrane envelope glycoproteins to the cell surface. A viral mutant with uncleaved glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14018–14022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarter J. A., Ball J. K., Frei J. V. Lower limb paralysis induced in mice by a temperature-sensitive mutant of Moloney leukemia virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1977 Jul;59(1):179–183. doi: 10.1093/jnci/59.1.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohan S., Pal B. K. Binding characteristics of wild mouse type C virus to mouse spinal cord and spleen cells. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):532–538. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.532-538.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paquette Y., Hanna Z., Savard P., Brousseau R., Robitaille Y., Jolicoeur P. Retrovirus-induced murine motor neuron disease: mapping the determinant of spongiform degeneration within the envelope gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3896–3900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinter A., Fleissner E. Structural studies of retroviruses: characterization of oligomeric complexes of murine and feline leukemia virus envelope and core components formed upon cross-linking. J Virol. 1979 Apr;30(1):157–165. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.1.157-165.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinter A., Honnen W. J., Tung J. S., O'Donnell P. V., Hämmerling U. Structural domains of endogenous murine leukemia virus gp70s containing specific antigenic determinants defined by monoclonal antibodies. Virology. 1982 Jan 30;116(2):499–516. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90143-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polonoff E., Machida C. A., Kabat D. Glycosylation and intracellular transport of membrane glycoproteins encoded by murine leukemia viruses. Inhibition by amino acid analogues and by tunicamycin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14023–14028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad G., Stoica G., Wong P. K. The role of the thymus in the pathogenesis of hind-limb paralysis induced by ts1, a mutant of Moloney murine leukemia virus-TB. Virology. 1989 Apr;169(2):332–340. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90158-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy E. P., Sandberg-Wollheim M., Mettus R. V., Ray P. E., DeFreitas E., Koprowski H. Amplification and molecular cloning of HTLV-I sequences from DNA of multiple sclerosis patients. Science. 1989 Jan 27;243(4890):529–533. doi: 10.1126/science.2536193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Doms R. W. Regulation of protein export from the endoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:257–288. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.001353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rude R., Gallick G. E., Wong P. K. A fast replica plating technique for the isolation of post-integration mutants of the Moloney strain of murine leukaemia virus. J Gen Virol. 1980 Aug;49(2):367–374. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-49-2-367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruta M., Murray M. J., Webb M. C., Kabat D. A murine leukemia virus mutant with a temperature-sensitive defect in membrane glycoprotein synthesis. Cell. 1979 Jan;16(1):77–88. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90189-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarin P. S., Rodgers-Johnson P., Sun D. K., Thornton A. H., Morgan O. S., Gibbs W. N., Mora C., McKhann G., 2nd, Gajdusek D. C., Gibbs C. J., Jr Comparison of a human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I strain from cerebrospinal fluid of a Jamaican patient with tropical spastic paraparesis with a prototype human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):2021–2025. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. L., Viñuela E., Maizel J. V., Jr Molecular weight estimation of polypeptide chains by electrophoresis in SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 7;28(5):815–820. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90391-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe A. H., Jaenisch R., Ruprecht R. M. Retroviruses and mouse embryos: a rapid model for neurovirulence and transplacental antiviral therapy. Science. 1987 Jun 26;236(4809):1671–1674. doi: 10.1126/science.3037694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Lerner R. A., Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequence of Moloney murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):543–548. doi: 10.1038/293543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens E. B., Compans R. W. Assembly of animal viruses at cellular membranes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:489–516. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.002421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szurek P. F., Yuen P. H., Jerzy R., Wong P. K. Identification of point mutations in the envelope gene of Moloney murine leukemia virus TB temperature-sensitive paralytogenic mutant ts1: molecular determinants for neurovirulence. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):357–360. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.357-360.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimble R. B., Maley F. Optimizing hydrolysis of N-linked high-mannose oligosaccharides by endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase H. Anal Biochem. 1984 Sep;141(2):515–522. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90080-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte O. N., Wirth D. F. Structure of the murine leukemia virus envelope glycoprotein precursor. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):735–743. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.735-743.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. K., Knupp C., Yuen P. H., Soong M. M., Zachary J. F., Tompkins W. A. ts1, a Paralytogenic mutant of Moloney murine leukemia virus TB, has an enhanced ability to replicate in the central nervous system and primary nerve cell culture. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):760–767. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.760-767.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. K., Prasad G., Hansen J., Yuen P. H. ts1, a mutant of Moloney murine leukemia virus-TB, causes both immunodeficiency and neurologic disorders in BALB/c mice. Virology. 1989 Jun;170(2):450–459. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90436-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. K., Russ L. J., McCarter J. A. Rapid, selective procedure for isolation of spontaneous temperature-sensitive mutants of Moloney leukemia virus. Virology. 1973 Feb;51(2):424–431. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90441-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. K., Soong M. M., MacLeod R., Gallick G. E., Yuen P. H. A group of temperature-sensitive mutants of Moloney leukemia virus which is defective in cleavage of env precursor polypeptide in infected cells also induces hind-limb paralysis in newborn CFW/D mice. Virology. 1983 Mar;125(2):513–518. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90225-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. K., Soong M. M., Yuen P. H. Replication of murine leukemia virus in heterologous cells: interaction between ecotropic and xenotropic viruses. Virology. 1981 Mar;109(2):366–378. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90507-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuen P. H., Malehorn D., Knupp C., Wong P. K. A 1.6-kilobase-pair fragment in the genome of the ts1 mutant of Moloney murine leukemia virus TB that is associated with temperature sensitivity, nonprocessing of Pr80env, and paralytogenesis. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):364–373. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.364-373.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuen P. H., Malehorn D., Nau C., Soong M. M., Wong P. K. Molecular cloning of two paralytogenic, temperature-sensitive mutants, ts1 and ts7, and the parental wild-type Moloney murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):178–185. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.178-185.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuen P. H., Szurek P. F. The reduced virulence of the thymotropic Moloney murine leukemia virus derivative MoMuLV-TB is mapped to 11 mutations within the U3 region of the long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):471–480. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.471-480.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuen P. H., Tzeng E., Knupp C., Wong P. K. The neurovirulent determinants of ts1, a paralytogenic mutant of Moloney murine leukemia virus TB, are localized in at least two functionally distinct regions of the genome. J Virol. 1986 Jul;59(1):59–65. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.1.59-65.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachary J. F., Knupp C. J., Wong P. K. Noninflammatory spongiform polioencephalomyelopathy caused by a neurotropic temperature-sensitive mutant of Moloney murine leukemia virus TB. Am J Pathol. 1986 Sep;124(3):457–468. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




