Abstract
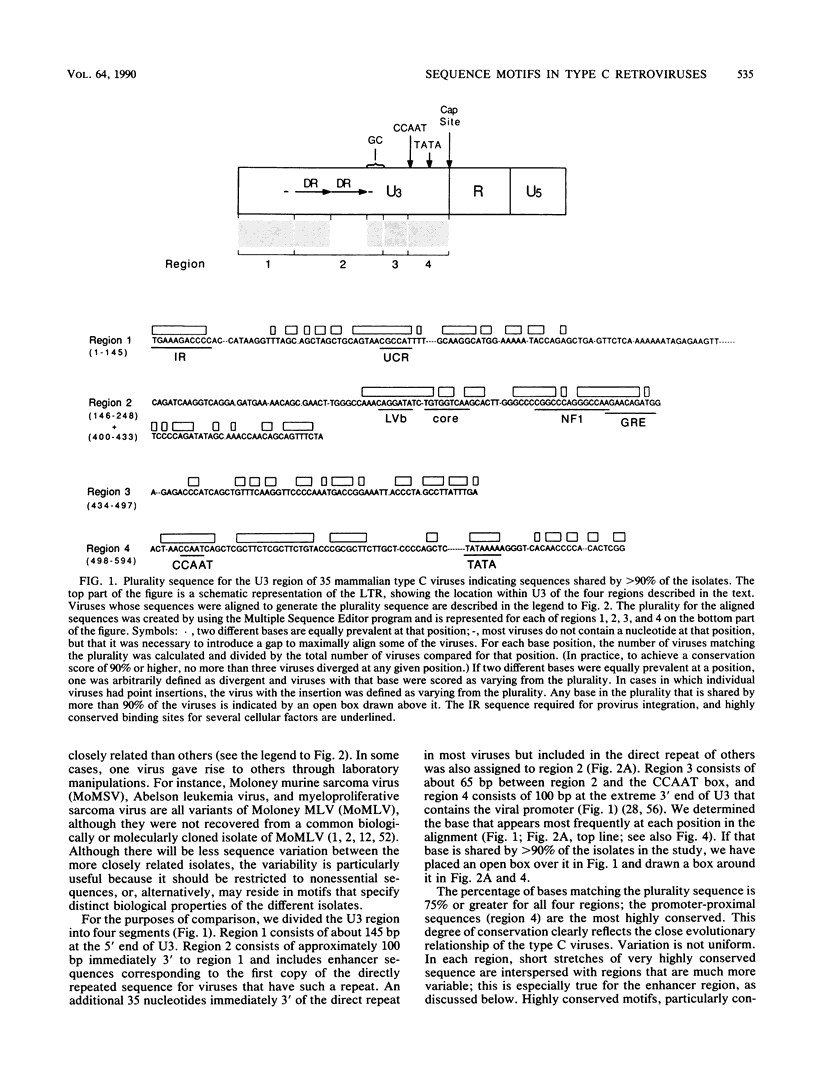
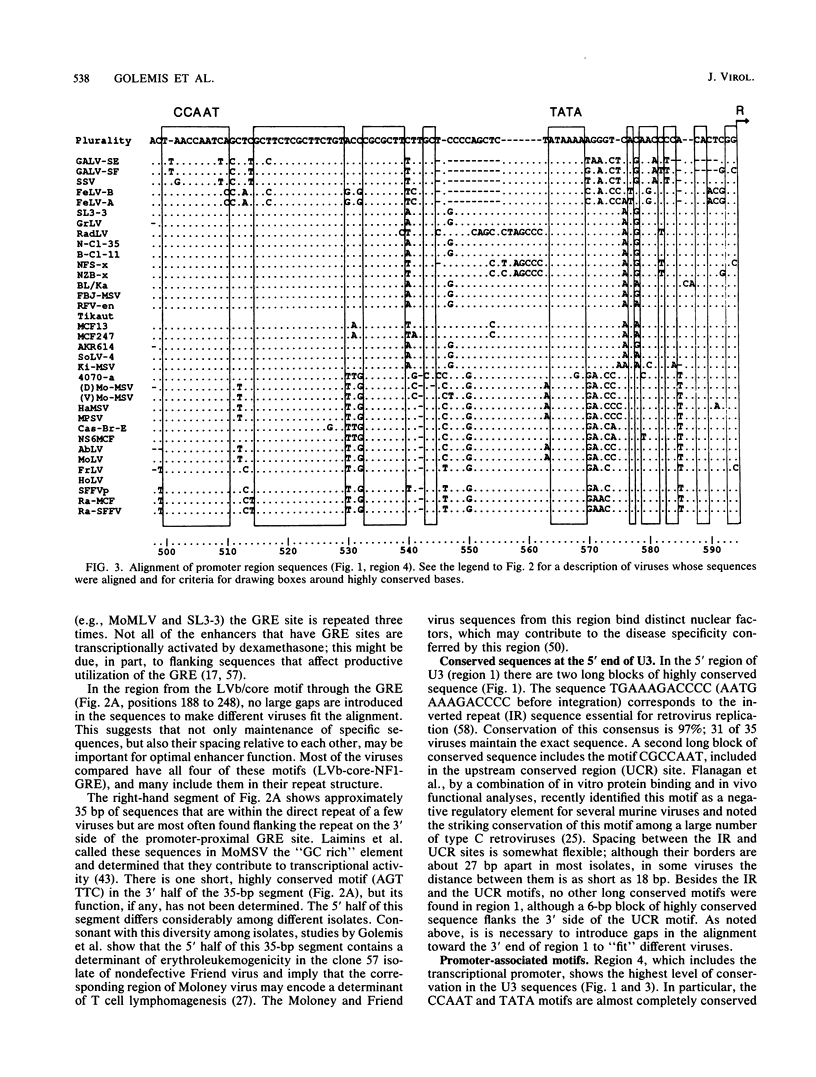
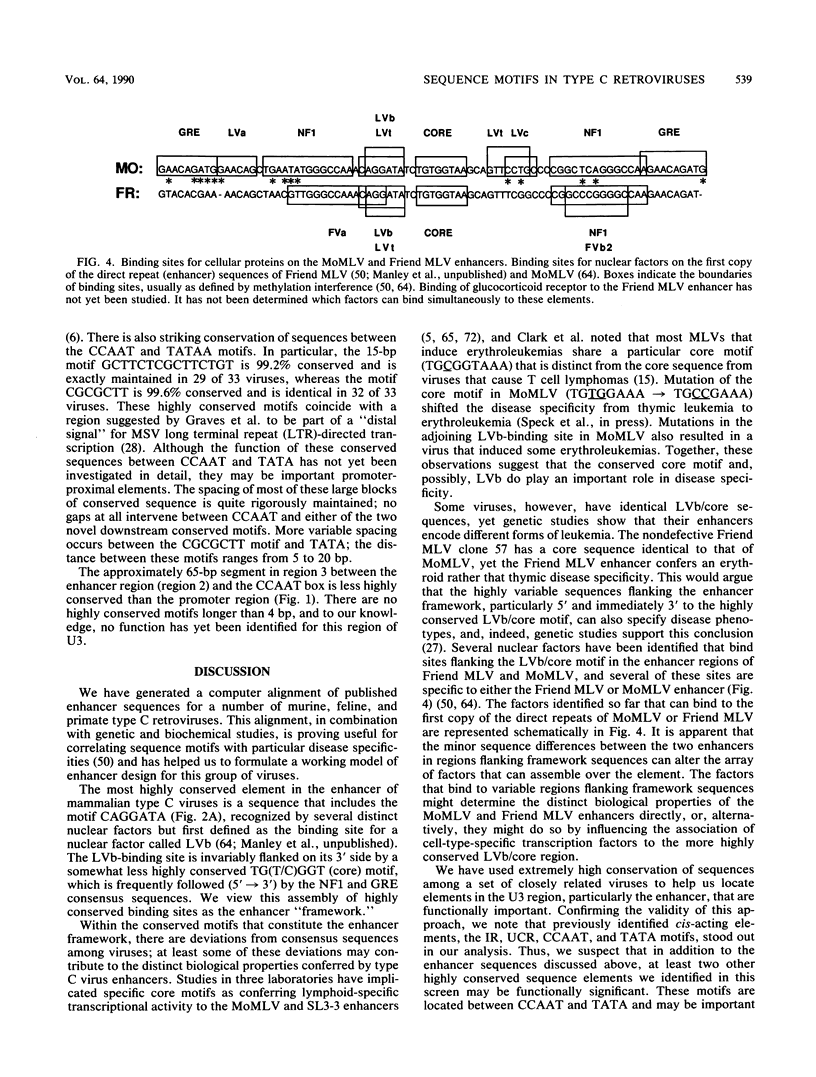
We aligned published sequences for the U3 region of 35 type C mammalian retroviruses. The alignment reveals that certain sequence motifs within the U3 region are strikingly conserved. A number of these motifs correspond to previously identified sites. In particular, we found that the enhancer region of most of the viruses examined contains a binding site for leukemia virus factor b, a viral corelike element, the consensus motif for nuclear factor 1, and the glucocorticoid response element. Most viruses containing more than one copy of enhancer sequences include these binding sites in both copies of the repeat. We consider this set of binding sites to constitute a framework for the enhancers of this set of viruses. Other highly conserved motifs in the U3 region include the retrovirus inverted repeat sequence, a negative regulatory element, and the CCAAT and TATA boxes. In addition, we identified two novel motifs in the promoter region that were exceptionally highly conserved but have not been previously described.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abelson H. T., Rabstein L. S. Influence of prednisolone on Moloney leukemogenic virus in BALB-c mice. Cancer Res. 1970 Aug;30(8):2208–2212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abelson H. T., Rabstein L. S. Lymphosarcoma: virus-induced thymic-independent disease in mice. Cancer Res. 1970 Aug;30(8):2213–2222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumruker T., Sturm R., Herr W. OBP100 binds remarkably degenerate octamer motifs through specific interactions with flanking sequences. Genes Dev. 1988 Nov;2(11):1400–1413. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.11.1400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bestwick R. K., Boswell B. A., Kabat D. Molecular cloning of biologically active Rauscher spleen focus-forming virus and the sequences of its env gene and long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):695–705. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.695-705.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boral A. L., Okenquist S. A., Lenz J. Identification of the SL3-3 virus enhancer core as a T-lymphoma cell-specific element. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):76–84. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.76-84.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celander D., Hsu B. L., Haseltine W. A. Regulatory elements within the murine leukemia virus enhancer regions mediate glucocorticoid responsiveness. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1314–1322. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1314-1322.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ch'ang L. Y., Yang W. K., Myer F. E., Yang D. M. Negative regulatory element associated with potentially functional promoter and enhancer elements in the long terminal repeats of endogenous murine leukemia virus-related proviral sequences. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2746–2757. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2746-2757.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatis P. A., Holland C. A., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Hopkins N. Role for the 3' end of the genome in determining disease specificity of Friend and Moloney murine leukemia viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4408–4411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatis P. A., Holland C. A., Silver J. E., Frederickson T. N., Hopkins N., Hartley J. W. A 3' end fragment encompassing the transcriptional enhancers of nondefective Friend virus confers erythroleukemogenicity on Moloney leukemia virus. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):248–254. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.248-254.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Baroudy B. M., Holmes K. L., Fredrickson T. N., Lander M. R., Morse H. C., 3rd, Hartley J. W. Biologic and molecular genetic characteristics of a unique MCF virus that is highly leukemogenic in ecotropic virus-negative mice. Virology. 1989 Jan;168(1):90–100. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90407-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirigos M. A., Scott D., Turner W., Perk K. Biological, pathological and physical characterization of a possible variant of a murine sarcoma virus (Moloney). Int J Cancer. 1968 Mar 15;3(2):223–227. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910030207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. P., Kaufhold R., Chan A., Mak T. W. Comparison of the transcriptional properties of the Friend and Moloney retrovirus long terminal repeats: importance of tandem duplications and of the core enhancer sequence. Virology. 1985 Jul 30;144(2):481–494. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90288-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. P., Mak T. W. Nucleotide sequences of the murine retrovirus Friend SFFVp long terminal repeats: identification of a structure with extensive dyad symmetry 5' to the TATA box. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 25;10(10):3315–3330. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.10.3315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corcoran L. M., Adams J. M., Dunn A. R., Cory S. Murine T lymphomas in which the cellular myc oncogene has been activated by retroviral insertion. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90306-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFranco D., Yamamoto K. R. Two different factors act separately or together to specify functionally distinct activities at a single transcriptional enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):993–1001. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesGroseillers L., Jolicoeur P. Mapping the viral sequences conferring leukemogenicity and disease specificity in Moloney and amphotropic murine leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):448–456. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.448-456.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesGroseillers L., Rassart E., Jolicoeur P. Thymotropism of murine leukemia virus is conferred by its long terminal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4203–4207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesGroseillers L., Villemur R., Jolicoeur P. The high leukemogenic potential of Gross passage A murine leukemia virus maps in the region of the genome corresponding to the long terminal repeat and to the 3' end of env. J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):24–32. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.24-32.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devare S. G., Reddy E. P., Law J. D., Robbins K. C., Aaronson S. A. Nucleotide sequence of the simian sarcoma virus genome: demonstration that its acquired cellular sequences encode the transforming gene product p28sis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):731–735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhar R., McClements W. L., Enquist L. W., Vande Woude G. F. Nucleotide sequences of integrated Moloney sarcoma provirus long terminal repeats and their host and viral junctions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3937–3941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan J. R., Krieg A. M., Max E. E., Khan A. S. Negative control region at the 5' end of murine leukemia virus long terminal repeats. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):739–746. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman M. Z., Wilson R. N., Weinberg R. A. Multiple protein-binding sites in the 5'-flanking region regulate c-fos expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4305–4316. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golemis E., Li Y., Fredrickson T. N., Hartley J. W., Hopkins N. Distinct segments within the enhancer region collaborate to specify the type of leukemia induced by nondefective Friend and Moloney viruses. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):328–337. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.328-337.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves B. J., Eisenman R. N., McKnight S. L. Delineation of transcriptional control signals within the Moloney murine sarcoma virus long terminal repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1948–1958. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Siegfried Z., Ziff E. B. Mutation of the c-fos gene dyad symmetry element inhibits serum inducibility of transcription in vivo and the nuclear regulatory factor binding in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1217–1225. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland C. A., Thomas C. Y., Chattopadhyay S. K., Koehne C., O'Donnell P. V. Influence of enhancer sequences on thymotropism and leukemogenicity of mink cell focus-forming viruses. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1284–1292. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1284-1292.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishimoto A., Adachi A., Sakai K., Matsuyama M. Long terminal repeat of Friend-MCF virus contains the sequence responsible for erythroid leukemia. Virology. 1985 Feb;141(1):30–42. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90180-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishimoto A., Takimoto M., Adachi A., Kakuyama M., Kato S., Kakimi K., Fukuoka K., Ogiu T., Matsuyama M. Sequences responsible for erythroid and lymphoid leukemia in the long terminal repeats of Friend-mink cell focus-forming and Moloney murine leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):1861–1866. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.1861-1866.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janowski M., Merregaert J., Boniver J., Maisin J. R. Proviral genome of radiation leukemia virus: molecular cloning of biologically active proviral DNA and nucleotide sequence of its long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1985 Jul;55(1):251–255. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.1.251-255.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., Landschulz W. H., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Identification of a rat liver nuclear protein that binds to the enhancer core element of three animal viruses. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):133–146. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolicoeur P., Nicolaiew N., DesGroseillers L., Rassart E. Molecular cloning of infectious viral DNA from ecotropic neurotropic wild mouse retrovirus. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1159–1163. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.1159-1163.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M., Holland C. A., Lung M. L., Chattopadhyay S. K., Lowy D. R., Hopkins N. H. Nucleotide sequence of the 3' end of MCF 247 murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):291–298. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.291-298.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan A. S., Laigret F., Rodi C. P. Expression of mink cell focus-forming murine leukemia virus-related transcripts in AKR mice. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):876–882. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.876-882.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan A. S., Martin M. A. Endogenous murine leukemia proviral long terminal repeats contain a unique 190-base-pair insert. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2699–2703. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. P., Kaplan H. S., Fry K. E. Characterization of an infective molecular clone of the B-tropic, ecotropic BL/Ka(B) murine retrovirus genome. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):217–225. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.217-225.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch W., Zimmermann W., Oliff A., Friedrich R. Molecular analysis of the envelope gene and long terminal repeat of Friend mink cell focus-inducing virus: implications for the functions of these sequences. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):828–840. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.828-840.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg A. M., Khan A. S., Steinberg A. D. Multiple endogenous xenotropic and mink cell focus-forming murine leukemia virus-related transcripts are induced by polyclonal immune activators. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3545–3550. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3545-3550.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriegler M., Botchan M. Enhanced transformation by a simian virus 40 recombinant virus containing a Harvey murine sarcoma virus long terminal repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;3(3):325–339. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.3.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Gruss P., Pozzatti R., Khoury G. Characterization of enhancer elements in the long terminal repeat of Moloney murine sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):183–189. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.183-189.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leegwater P. A., van der Vliet P. C., Rupp R. A., Nowock J., Sippel A. E. Functional homology between the sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins nuclear factor I from HeLa cells and the TGGCA protein from chicken liver. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):381–386. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04223.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenz J., Celander D., Crowther R. L., Patarca R., Perkins D. W., Haseltine W. A. Determination of the leukaemogenicity of a murine retrovirus by sequences within the long terminal repeat. 1984 Mar 29-Apr 4Nature. 308(5958):467–470. doi: 10.1038/308467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson B., Khoury G., Vande Woude G., Gruss P. Activation of SV40 genome by 72-base pair tandem repeats of Moloney sarcoma virus. Nature. 1982 Feb 18;295(5850):568–572. doi: 10.1038/295568a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Golemis E., Hartley J. W., Hopkins N. Disease specificity of nondefective Friend and Moloney murine leukemia viruses is controlled by a small number of nucleotides. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):693–700. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.693-700.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liou R. S., Boone L. R., Kiggans J. O., Yang D. M., Wang T. W., Tennant R. W., Yang W. K. Molecular cloning and analysis of the endogenous retrovirus chemically induced from RFM/Un mouse cell cultures. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):288–292. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.288-292.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lung M. L., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Hopkins N. H. Large RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotides encoding p15E and the U3 region of the long terminal repeat distinguish two biological classes of mink cell focus-forming type C viruses of inbred mice. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):275–290. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.275-290.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley N. R., O'Connell M. A., Sharp P. A., Hopkins N. Nuclear factors that bind to the enhancer region of nondefective Friend murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4210–4223. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4210-4223.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miksicek R., Heber A., Schmid W., Danesch U., Posseckert G., Beato M., Schütz G. Glucocorticoid responsiveness of the transcriptional enhancer of Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):283–290. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90745-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moloney J. B. A virus-induced rhabdomyosarcoma of mice. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1966 Sep;22:139–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata K., Guggenheimer R. A., Enomoto T., Lichy J. H., Hurwitz J. Adenovirus DNA replication in vitro: identification of a host factor that stimulates synthesis of the preterminal protein-dCMP complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6438–6442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton J. D., Connor J., Avery R. J. Genesis of Kirsten murine sarcoma virus: sequence analysis reveals recombination points and potential leukaemogenic determinant on parental leukaemia virus genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 11;12(17):6839–6852. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.17.6839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill R. R., Buckler C. E., Theodore T. S., Martin M. A., Repaske R. Envelope and long terminal repeat sequences of a cloned infectious NZB xenotropic murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):100–106. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.100-106.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrowski M. C., Berard D., Hager G. L. Specific transcriptional initiation in vitro on murine type C retrovirus promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4485–4489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overhauser J., Fan H. Generation of glucocorticoid-responsive Moloney murine leukemia virus by insertion of regulatory sequences from murine mammary tumor virus into the long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):133–144. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.133-144.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panganiban A. T., Temin H. M. The terminal nucleotides of retrovirus DNA are required for integration but not virus production. Nature. 1983 Nov 10;306(5939):155–160. doi: 10.1038/306155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer K., Prezant T., Guarente L. Yeast HAP1 activator binds to two upstream activation sites of different sequence. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90751-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prywes R., Roeder R. G. Inducible binding of a factor to the c-fos enhancer. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):777–784. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90520-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy E. P., Smith M. J., Srinivasan A. Nucleotide sequence of Abelson murine leukemia virus genome: structural similarity of its transforming gene product to other onc gene products with tyrosine-specific kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3623–3627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Lerner R. A., Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequence of Moloney murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):543–548. doi: 10.1038/293543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorge J., Wright D., Erdman V. D., Cutting A. E. Amphotropic retrovirus vector system for human cell gene transfer. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1730–1737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck N. A., Baltimore D. Six distinct nuclear factors interact with the 75-base-pair repeat of the Moloney murine leukemia virus enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1101–1110. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck N. A., Renjifo B., Hopkins N. Point mutations in the Moloney murine leukemia virus enhancer identify a lymphoid-specific viral core motif and 1,3-phorbol myristate acetate-inducible element. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):543–550. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.543-550.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacey A., Arbuthnott C., Kollek R., Coggins L., Ostertag W. Comparison of myeloproliferative sarcoma virus with Moloney murine sarcoma virus variants by nucleotide sequencing and heteroduplex analysis. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):725–732. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.725-732.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M. A., Warnock M., Wheeler A., Wilkie N., Mullins J. I., Onions D. E., Neil J. C. Nucleotide sequences of a feline leukemia virus subgroup A envelope gene and long terminal repeat and evidence for the recombinational origin of subgroup B viruses. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):825–834. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.825-834.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stocking C., Kollek R., Bergholz U., Ostertag W. Point mutations in the U3 region of the long terminal repeat of Moloney murine leukemia virus determine disease specificity of the myeloproliferative sarcoma virus. Virology. 1986 Aug;153(1):145–149. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90015-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoye J. P., Coffin J. M. The four classes of endogenous murine leukemia virus: structural relationships and potential for recombination. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2659–2669. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2659-2669.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theodore T. S., Khan A. S. Nucleotide sequence analysis of long terminal repeats of leukemogenic and non-leukemogenic MCF MuLVs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5898–5898. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiesen H. J., Bösze Z., Henry L., Charnay P. A DNA element responsible for the different tissue specificities of Friend and Moloney retroviral enhancers. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):614–618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.614-618.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornell A., Hallberg B., Grundström T. Differential protein binding in lymphocytes to a sequence in the enhancer of the mouse retrovirus SL3-3. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1625–1637. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trainor C. D., Scott M. L., Josephs S. F., Fry K. E., Reitz M. S., Jr Nucleotide sequence of the large terminal repeat of two different strains of gibbon ape leukemia virus. Virology. 1984 Aug;137(1):201–205. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90025-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Identification of a protein-binding site that mediates transcriptional response of the c-fos gene to serum factors. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):567–574. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90882-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Transient accumulation of c-fos RNA following serum stimulation requires a conserved 5' element and c-fos 3' sequences. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):889–902. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90285-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Beveren C., Rands E., Chattopadhyay S. K., Lowy D. R., Verma I. M. Long terminal repeat of murine retroviral DNAs: sequence analysis, host-proviral junctions, and preintegration site. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):542–556. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.542-556.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Beveren C., van Straaten F., Curran T., Müller R., Verma I. M. Analysis of FBJ-MuSV provirus and c-fos (mouse) gene reveals that viral and cellular fos gene products have different carboxy termini. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1241–1255. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90306-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Beveren C., van Straaten F., Galleshaw J. A., Verma I. M. Nucleotide sequence of the genome of a murine sarcoma virus. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):97–108. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90364-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villemur R., Rassart E., DesGroseillers L., Jolicoeur P. Molecular cloning of viral DNA from leukemogenic Gross passage A murine leukemia virus and nucleotide sequence of its long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):539–546. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.539-546.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voytek P., Kozak C. A. Nucleotide sequence and mode of transmission of the wild mouse ecotropic virus, HoMuLV. Virology. 1989 Nov;173(1):58–67. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90221-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiher H., König M., Gruss P. Multiple point mutations affecting the simian virus 40 enhancer. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):626–631. doi: 10.1126/science.6297005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R. Steroid receptor regulated transcription of specific genes and gene networks. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:209–252. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.001233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries E., van Driel W., Tromp M., van Boom J., van der Vliet P. C. Adenovirus DNA replication in vitro: site-directed mutagenesis of the nuclear factor I binding site of the Ad2 origin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 11;13(13):4935–4952. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.13.4935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



