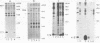Abstract
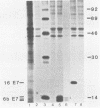
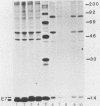
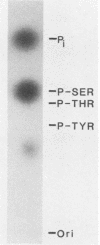
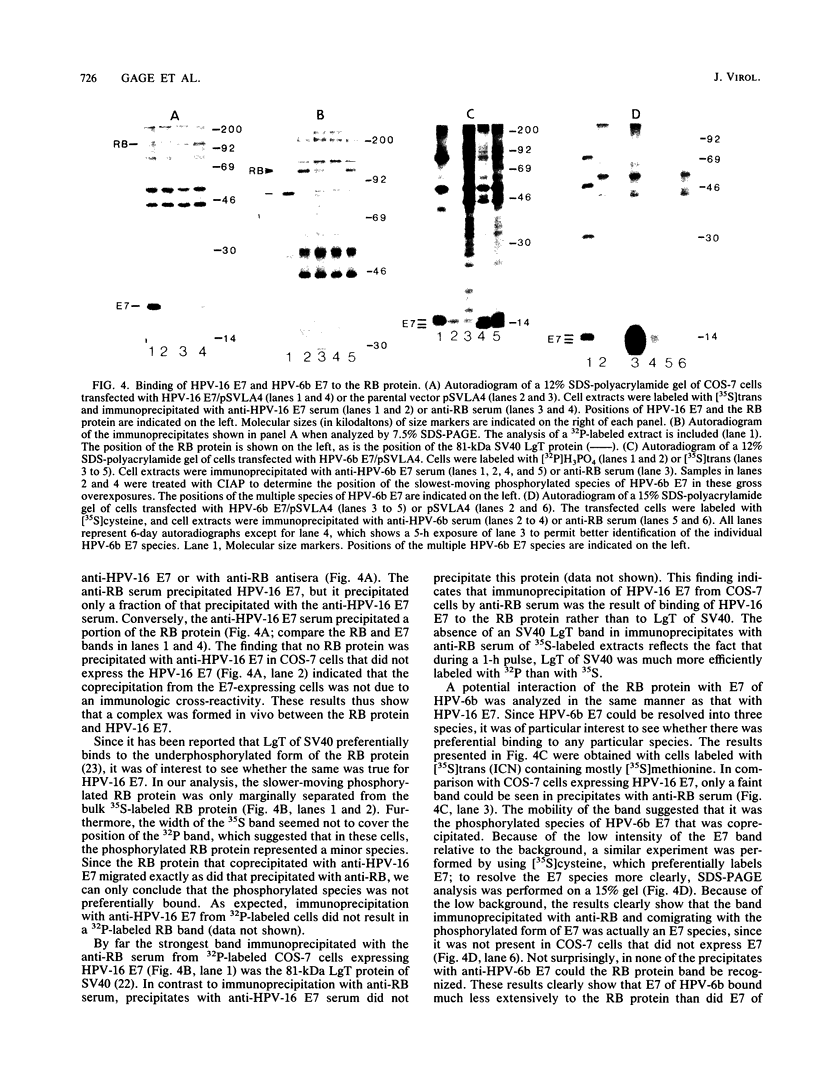
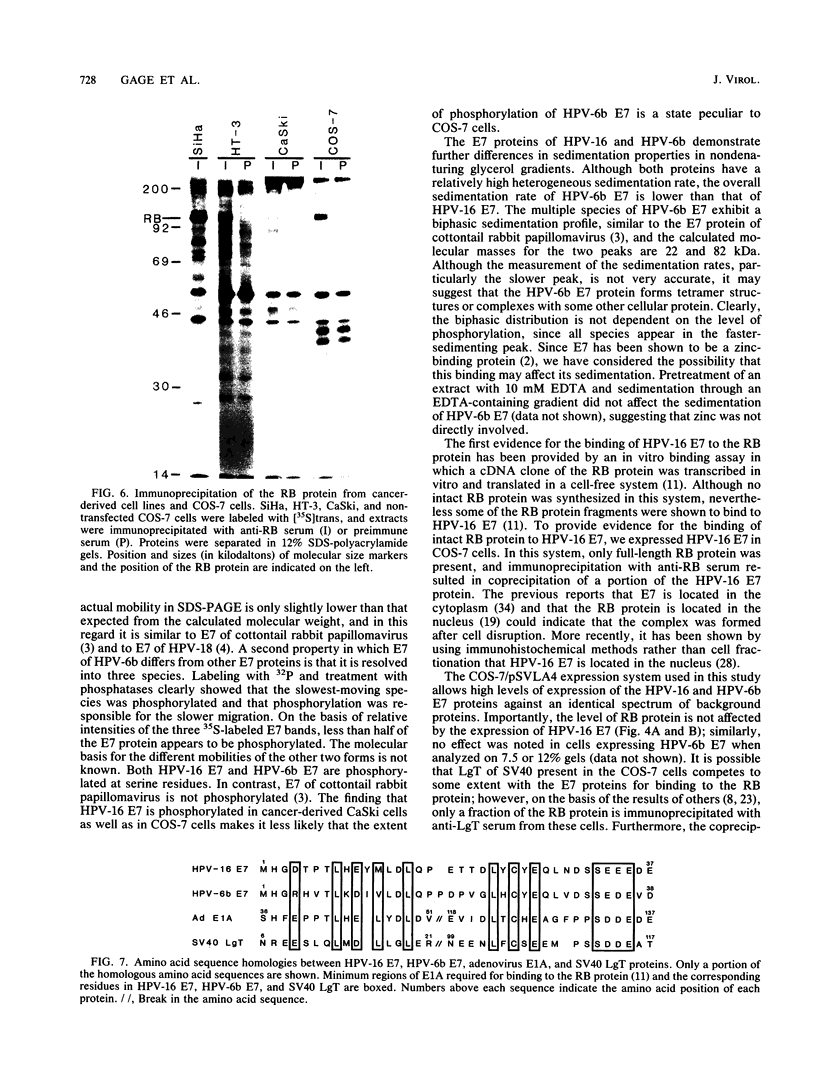
The E7 early viral protein of the oncogenic human papillomavirus type 16 (HPV-16) has been strongly implicated in the maintenance of the malignant phenotype in cervical cancers and cancer-derived cell lines. HPV-16 E7 is a nuclear phosphoprotein that can cooperate with ras to transform baby rat kidney cells, transactivates the adenovirus E2 promoter, and binds to the retinoblastoma (RB) protein. The E7 phosphoprotein of the nononcogenic HPV-6b, which is generally associated with benign genital warts, is similar to the HPV-16 E7 in amino acid sequence but differs dramatically in migration in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels, sedimentation in nondenaturing glycerol gradients, and the ability to bind the RB protein. Our results indicate that the RB protein preferentially binds the phosphorylated form of HPV-6b E7, which comprises a minor fraction of the total E7 expressed in transiently transfected COS-7 cells. These characteristics may help to explain the difference in the oncogenic potential of the oncogenic and nononcogenic types of genital papillomaviruses.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Androphy E. J., Hubbert N. L., Schiller J. T., Lowy D. R. Identification of the HPV-16 E6 protein from transformed mouse cells and human cervical carcinoma cell lines. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):989–992. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04849.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa M. S., Lowy D. R., Schiller J. T. Papillomavirus polypeptides E6 and E7 are zinc-binding proteins. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1404–1407. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1404-1407.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa M. S., Wettstein F. O. Identification and characterization of the CRPV E7 protein expressed in COS-7 cells. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):134–140. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90666-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard H. U., Oltersdorf T., Seedorf K. Expression of the human papillomavirus type 18 E7 gene by a cassette-vector system for the transcription and translation of open reading frames in eukaryotic cells. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):133–138. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04730.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., zur Hausen H. Human papillomaviruses in Buschke-Löwenstein tumors: physical state of the DNA and identification of a tandem duplication in the noncoding region of a human papillomavirus 6 subtype. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):963–966. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.963-966.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M., McCormack M., Zinn K. G., Farrell M. P., Bikel I., Livingston D. M. A recombinant murine retrovirus for simian virus 40 large T cDNA transforms mouse fibroblasts to anchorage-independent growth. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):290–293. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.290-293.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., King C. S. Dephosphorylation or antibody binding to the carboxy terminus stimulates pp60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4467–4477. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Figge J., Shew J. Y., Huang C. M., Lee W. H., Marsilio E., Paucha E., Livingston D. M. SV40 large tumor antigen forms a specific complex with the product of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):275–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90559-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson N., Howley P. M., Münger K., Harlow E. The human papilloma virus-16 E7 oncoprotein is able to bind to the retinoblastoma gene product. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):934–937. doi: 10.1126/science.2537532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürst M., Gissmann L., Ikenberg H., zur Hausen H. A papillomavirus DNA from a cervical carcinoma and its prevalence in cancer biopsy samples from different geographic regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3812–3815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds C., Vousden K. H. A point mutational analysis of human papillomavirus type 16 E7 protein. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2650–2656. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2650-2656.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend S. H., Horowitz J. M., Gerber M. R., Wang X. F., Bogenmann E., Li F. P., Weinberg R. A. Deletions of a DNA sequence in retinoblastomas and mesenchymal tumors: organization of the sequence and its encoded protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9059–9063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz J. M., Yandell D. W., Park S. H., Canning S., Whyte P., Buchkovich K., Harlow E., Weinberg R. A., Dryja T. P. Point mutational inactivation of the retinoblastoma antioncogene. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):937–940. doi: 10.1126/science.2521957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasher M. S., Roman A. Characterization of human papillomavirus type 6b DNA isolated from an invasive squamous carcinoma of the vulva. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90676-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E. Y., To H., Shew J. Y., Bookstein R., Scully P., Lee W. H. Inactivation of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene in human breast cancers. Science. 1988 Jul 8;241(4862):218–221. doi: 10.1126/science.3388033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., Bookstein R., Hong F., Young L. J., Shew J. Y., Lee E. Y. Human retinoblastoma susceptibility gene: cloning, identification, and sequence. Science. 1987 Mar 13;235(4794):1394–1399. doi: 10.1126/science.3823889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., Shew J. Y., Hong F. D., Sery T. W., Donoso L. A., Young L. J., Bookstein R., Lee E. Y. The retinoblastoma susceptibility gene encodes a nuclear phosphoprotein associated with DNA binding activity. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):642–645. doi: 10.1038/329642a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Green M., Green M. R. An adenovirus E1a protein region required for transformation and transcriptional repression. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1043–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90704-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I. The marriage of oncogenes and anti-oncogenes. Trends Genet. 1988 Sep;4(9):245–247. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90029-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston D. M., Bradley M. K. The simian virus 40 large T antigen. A lot packed into a little. Mol Biol Med. 1987 Apr;4(2):63–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludlow J. W., DeCaprio J. A., Huang C. M., Lee W. H., Paucha E., Livingston D. M. SV40 large T antigen binds preferentially to an underphosphorylated member of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene product family. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):57–65. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90983-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps W. C., Yee C. L., Münger K., Howley P. M. The human papillomavirus type 16 E7 gene encodes transactivation and transformation functions similar to those of adenovirus E1A. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):539–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90570-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rando R. F., Groff D. E., Chirikjian J. G., Lancaster W. D. Isolation and characterization of a novel human papillomavirus type 6 DNA from an invasive vulvar carcinoma. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):353–356. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.353-356.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rando R. F., Lancaster W. D., Han P., Lopez C. The noncoding region of HPV-6vc contains two distinct transcriptional enhancing elements. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):545–556. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90215-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Watanabe S., Furuno A., Yoshiike K. Human papillomavirus type 16 E7 protein expressed in Escherichia coli and monkey COS-1 cells: immunofluorescence detection of the nuclear E7 protein. Virology. 1989 May;170(1):311–315. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90386-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider-Gädicke A., Schwarz E. Different human cervical carcinoma cell lines show similar transcription patterns of human papillomavirus type 18 early genes. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2285–2292. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04496.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz E., Dürst M., Demankowski C., Lattermann O., Zech R., Wolfsperger E., Suhai S., zur Hausen H. DNA sequence and genome organization of genital human papillomavirus type 6b. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2341–2348. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01744.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seedorf K., Krämmer G., Dürst M., Suhai S., Röwekamp W. G. Human papillomavirus type 16 DNA sequence. Virology. 1985 Aug;145(1):181–185. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90214-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seedorf K., Oltersdorf T., Krämmer G., Röwekamp W. Identification of early proteins of the human papilloma viruses type 16 (HPV 16) and type 18 (HPV 18) in cervical carcinoma cells. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):139–144. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04731.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smotkin D., Prokoph H., Wettstein F. O. Oncogenic and nononcogenic human genital papillomaviruses generate the E7 mRNA by different mechanisms. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1441–1447. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1441-1447.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smotkin D., Wettstein F. O. The major human papillomavirus protein in cervical cancers is a cytoplasmic phosphoprotein. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1686–1689. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1686-1689.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smotkin D., Wettstein F. O. Transcription of human papillomavirus type 16 early genes in a cervical cancer and a cancer-derived cell line and identification of the E7 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4680–4684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spindler K. R., Rosser D. S., Berk A. J. Analysis of adenovirus transforming proteins from early regions 1A and 1B with antisera to inducible fusion antigens produced in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):132–141. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.132-141.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte P., Buchkovich K. J., Horowitz J. M., Friend S. H., Raybuck M., Weinberg R. A., Harlow E. Association between an oncogene and an anti-oncogene: the adenovirus E1A proteins bind to the retinoblastoma gene product. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):124–129. doi: 10.1038/334124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilczynski S. P., Pearlman L., Walker J. Identification of HPV 16 early genes retained in cervical carcinomas. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):624–627. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90539-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerler B., Roberts R. J., Mathews M. B., Moran E. Different functional domains of the adenovirus E1A gene are involved in regulation of host cell cycle products. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):821–829. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villiers E. M., Gissmann L., zur Hausen H. Molecular cloning of viral DNA from human genital warts. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):932–935. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.932-935.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Knebel Doeberitz M., Oltersdorf T., Schwarz E., Gissmann L. Correlation of modified human papilloma virus early gene expression with altered growth properties in C4-1 cervical carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 1988 Jul 1;48(13):3780–3786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]