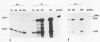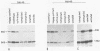Abstract
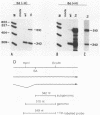
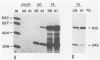
The oncogene v-myb of avian myeloblastosis virus is expressed from an mRNA that arises by splicing of the viral genome. In previous work, we described a mutant strain of avian myeloblastosis virus (tsAMV) that elicits temperature-sensitive transformation and suggested that the mutation affects production of the mRNA for v-myb. We now report that the principal determinant of the biochemical phenotype of tsAMV is a point mutation located in a crucial region of the splice acceptor site for v-myb mRNA. The mutation reduces v-myb mRNA production but could account for the conditional phenotype only in combination with an independent effect of temperature on the splicing of both wild-type and mutant viral RNAs, which we also describe here. Our findings dramatize the manner in which retroviruses normally control the splicing of their RNAs and implicate the sequence of the splice acceptor site in the control.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arrigo S., Beemon K. Regulation of Rous sarcoma virus RNA splicing and stability. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4858–4867. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond U. Heat shock but not other stress inducers leads to the disruption of a sub-set of snRNPs and inhibition of in vitro splicing in HeLa cells. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3509–3518. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03227.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerondakis S., Bishop J. M. Structure of the protein encoded by the chicken proto-oncogene c-myb. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3677–3684. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda T. J., Sheiness D. K., Fanshier L., Bishop J. M., Moscovici C., Moscovici M. G. The genome and the intracellular RNAs of avian myeloblastosis virus. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):279–290. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90292-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. Pre-mRNA splicing. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:671–708. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.003323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz R. A., Kotler M., Skalka A. M. cis-acting intron mutations that affect the efficiency of avian retroviral RNA splicing: implication for mechanisms of control. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2686–2695. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2686-2695.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Gonda T. J., Bishop J. M. Nucleotide sequence of the retroviral leukemia gene v-myb and its cellular progenitor c-myb: the architecture of a transduced oncogene. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):453–463. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90138-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. K., Embretson J. E., Temin H. M. Transforming viruses spontaneously arise from nontransforming reticuloendotheliosis virus strain T-derived viruses as a result of increased accumulation of spliced viral RNA. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1219–1226. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1219-1226.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscovici C., Gazzolo L., Moscovici M. G. Focus assay and defectiveness of avian myeloblastosis virus. Virology. 1975 Nov;68(1):173–181. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90159-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscovici C. Leukemic transformation with avian myeloblastosis virus: present status. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1975;71:79–101. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66193-8_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscovici M. G., Klempnauer K. H., Symonds G., Bishop J. M., Moscovici C. Transformation-defective mutant of avian myeloblastosis virus that is temperature sensitive for production of transforming protein p45v-myb. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3301–3303. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscovici M. G., Moscovici C. Isolation and characterization of a temperature-sensitive mutant of avian myeloblastosis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1421–1425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R., Siliciano P. G., Guthrie C. Recognition of the TACTAAC box during mRNA splicing in yeast involves base pairing to the U2-like snRNA. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):229–239. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90564-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perbal B., Lipsick J. S., Svoboda J., Silva R. F., Baluda M. A. Biologically active proviral clone of myeloblastosis-associated virus type 1: implications for the genesis of avian myeloblastosis virus. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):240–244. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.240-244.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R., Maniatis T. The role of the mammalian branchpoint sequence in pre-mRNA splicing. Genes Dev. 1988 Oct;2(10):1268–1276. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.10.1268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoltzfus C. M. Synthesis and processing of avian sarcoma retrovirus RNA. Adv Virus Res. 1988;35:1–38. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60707-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijayraghavan U., Parker R., Tamm J., Iimura Y., Rossi J., Abelson J., Guthrie C. Mutations in conserved intron sequences affect multiple steps in the yeast splicing pathway, particularly assembly of the spliceosome. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1683–1695. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04412.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber F., de Villiers J., Schaffner W. An SV40 "enhancer trap" incorporates exogenous enhancers or generates enhancers from its own sequences. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):983–992. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yost H. J., Lindquist S. RNA splicing is interrupted by heat shock and is rescued by heat shock protein synthesis. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):185–193. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90382-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Mars M., Cizdziel P. E., Murphy E. C., Jr Activation of thermosensitive RNA splicing and production of a heat-labile P85gag-mos kinase by the introduction of a specific deletion in murine sarcoma virus-124 DNA. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):1907–1916. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.1907-1916.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]