Abstract
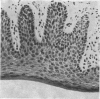
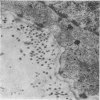
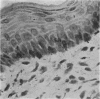
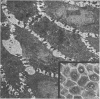
The morphology of the keratinizing epithelia in the mouth is reviwed in the light of recent knowledge. There appears to be a spectrum of degrees of keratinization rather than distinct types, and a degree of keratinization is reflected in the degree of packing and orientation of tonofilaments. The role of keratohyaline and other granules in the process is discussed and it is suggested that modification of the cell membrane is an important part of keratinization. Although the potential of the various areas in the mucosa is genetically determined and appears early in fetal life, the connective tissue exerts an influence on the extent of keratinization of the surface in a manner which is not understood.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cleaton-Jones P. Surface characteristics of cells from different layers of keratinized and non-keratinized oral epithelia. J Periodontal Res. 1975 May;10(2):79–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1975.tb00011.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halprin K. M. Epidermal "turnover time"--a re-examination. Br J Dermatol. 1972 Jan;86(1):14–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1972.tb01886.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton A. I., Blackwood H. J. Cell renewal of oral mucosal epithelium of the rat. J Anat. 1974 Apr;117(Pt 2):313–327. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto K., Lever W. F. An electron microscopic study on pemphigus vulgaris of the mouth and the skin with special reference to the intercellular cement. J Invest Dermatol. 1967 Jun;48(6):540–552. doi: 10.1038/jid.1967.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugoson A., Winberg E., Angström T. Cytologic findings in vaginal and oral smears from pregnant women. Odontol Revy. 1971;22(2):145–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löe H., Karring T. The three-dimensional morphology of the epithelium-connective tissue interface of the gingiva as related to age and sex. Scand J Dent Res. 1971;79(5):315–326. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1971.tb02017.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARQUES-PEREIRA J. P., LEBLOND C. P. MITOSIS AND DIFFERENTIATION IN THE STRATIFIED SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM OF THE RAT ESOPHAGUS. Am J Anat. 1965 Jul;117:73–87. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001170106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matoltsy A. G., Matoltsy M. N. The chemical nature of keratohyalin granules of the epidermis. J Cell Biol. 1970 Dec;47(3):593–603. doi: 10.1083/jcb.47.3.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer J., Alvares O. F., Barrington E. P. Volume and dry weight of cells in the epithelium of rat cheek and palate. Growth. 1970 Mar;34(1):57–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PINKUS H. Examination of the epidermis by the strip method. II. Biometric data on regeneration of the human epidermis. J Invest Dermatol. 1952 Dec;19(6):431–447. doi: 10.1038/jid.1952.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spearman R. I. Alteration of keratinization in mouse ear epidermis in recombinant grafts with tail dermis. Acta Anat (Basel) 1974;89(2):195–202. doi: 10.1159/000144283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock M., Wilgram G. F. Fine-structural observations on the formation and enzymatic activity of keratinosomes in mouse tongue filiform papillae. J Ultrastruct Res. 1970 Feb;30(3):262–274. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(70)80062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilgram G. F., Caulfield J. B. An electron microscopic study of epidermolytic hyperkeratosis. With a special note on the keratinosome as the "fourth" structural factor in the formation of the horny layer. Arch Dermatol. 1966 Aug;94(2):127–143. doi: 10.1001/archderm.94.2.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]