Abstract
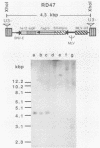
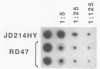
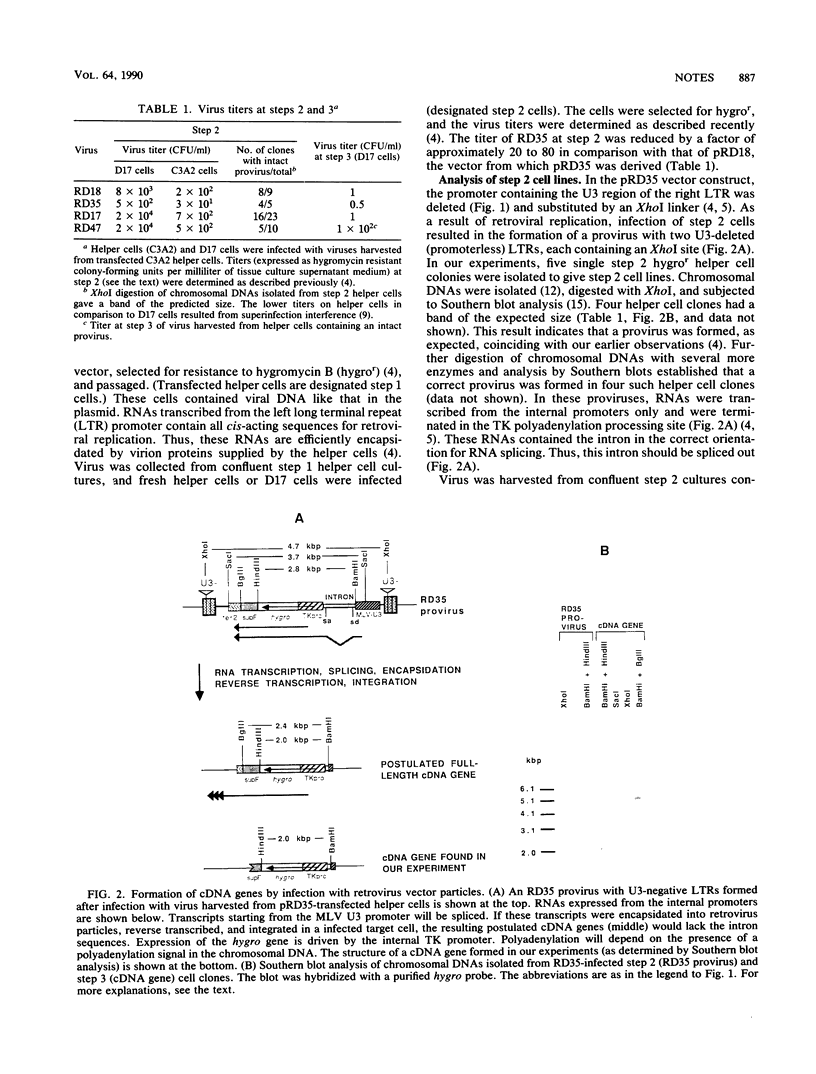
We showed previously that retrovirus vector particles can encapsidate RNAs without retroviral cis-acting sequences, that such RNAs are reverse transcribed in infected target cells, and that the cDNA copies are inserted into the host genome resulting in cDNA genes (R. Dornburg and H. M. Temin, Mol. Cell. Biol. 8:2328-2334, 1988). To provide further evidence that this retrovirus-mediated gene transfer occurred through an RNA intermediate, we constructed retroviral vectors containing an intron from a cellular gene. This intron was lost in a cDNA gene formed after infection with retroviral particles, establishing that an RNA intermediate had existed. Retroviral vectors with additional encapsidation sequences were constructed. The presence of a murine leukemia virus encapsidation sequence in an mRNA transcribed from the hygromycin B phosphotransferase gene increased the efficiency of encapsidation into spleen necrosis virus vector particles and the formation of cDNA genes by approximately 2 orders of magnitude.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam M. A., Miller A. D. Identification of a signal in a murine retrovirus that is sufficient for packaging of nonretroviral RNA into virions. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3802–3806. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3802-3806.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D. Retroviruses and retrotransposons: the role of reverse transcription in shaping the eukaryotic genome. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):481–482. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornburg R., Temin H. M. Retroviral vector system for the study of cDNA gene formation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2328–2334. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty J. P., Temin H. M. A promoterless retroviral vector indicates that there are sequences in U3 required for 3' RNA processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1197–1201. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Embretson J. E., Temin H. M. Lack of competition results in efficient packaging of heterologous murine retroviral RNAs and reticuloendotheliosis virus encapsidation-minus RNAs by the reticuloendotheliosis virus helper cell line. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2675–2683. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2675-2683.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gritz L., Davies J. Plasmid-encoded hygromycin B resistance: the sequence of hygromycin B phosphotransferase gene and its expression in Escherichia coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):179–188. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90223-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kai K., Sato H., Odaka T. Relationship between the cellular resistance to Friend murine leukemia virus infection and the expression of murine leukemia virus-gp70-related glycoprotein on cell surface of BALB/c-Fv-4wr mice. Virology. 1986 Apr 30;150(2):509–512. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90315-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai S., Nishizawa M. New procedure for DNA transfection with polycation and dimethyl sulfoxide. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1172–1174. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn R. M., Efstratiadis A., O'Connell C., Maniatis T. The nucleotide sequence of the human beta-globin gene. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):647–651. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90428-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linial M. Creation of a processed pseudogene by retroviral infection. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):93–102. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90759-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. H. The origin and evolution of retroposons. Int Rev Cytol. 1985;93:187–279. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61375-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Lerner R. A., Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequence of Moloney murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):543–548. doi: 10.1038/293543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M. Origin of retroviruses from cellular moveable genetic elements. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):599–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90420-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M. Reverse transcriptases. Retrons in bacteria. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):254–255. doi: 10.1038/339254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M. Reverse transcription in the eukaryotic genome: retroviruses, pararetroviruses, retrotransposons, and retrotranscripts. Mol Biol Evol. 1985 Nov;2(6):455–468. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanin E. F. Processed pseudogenes: characteristics and evolution. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:253–272. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.001345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. E. Reverse transcriptase rides again. Nature. 1985 Apr 18;314(6012):583–584. doi: 10.1038/314583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe S., Temin H. M. Construction of a helper cell line for avian reticuloendotheliosis virus cloning vectors. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2241–2249. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M., Deininger P. L., Efstratiadis A. Nonviral retroposons: genes, pseudogenes, and transposable elements generated by the reverse flow of genetic information. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:631–661. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]