Abstract
Naturally occurring strains of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) can vary considerably in their in vitro biological properties, and such differences may also be reflected in their in vivo pathogenesis. In an attempt to define genetic determinants of viral pathogenicity, we have molecularly cloned, sequenced, and characterized an attenuated isolate of HIV type 2 (HIV-2/ST) that differs from prototype HIV-2 strains in its inability to fuse with and kill susceptible CD4-bearing target cells. A proviral clone, termed JSP4-27, was identified to be transfection competent and to fully exhibit the noncytopathic and nonfusogenic properties of its parental isolate. Nucleotide sequence analysis of this clone revealed a genomic organization very similar to that of cytopathic HIV-2 strains and an overall nucleotide sequence homology of 88 to 90%. Amino acid sequence comparison confirmed the integrity of all major viral gene products in JSP4-27 but identified two amino acid sequence substitutions in its envelope fusion region. To investigate whether these mutations were responsible for the nonfusogenic phenotype of JSP4-27, we amplified, cloned, and sequenced the envelope fusion regions of four additional HIV-2/ST strains, two of which represented in vitro-generated, fusogenic and cytopathic variants of HIV-2/ST. The analysis showed that all HIV-2/ST strains examined, including the fusogenic variants, contained the same amino acid sequence changes. On the basis of these findings, we conclude that the attenuated phenotype of JSP4-27, and that of its parental virus, is not due to a direct alteration of the envelope fusion domain. Our results also show, for the first time, that individual replication-competent proviral clones can be representative of attenuated strains of HIV.
Full text
PDF
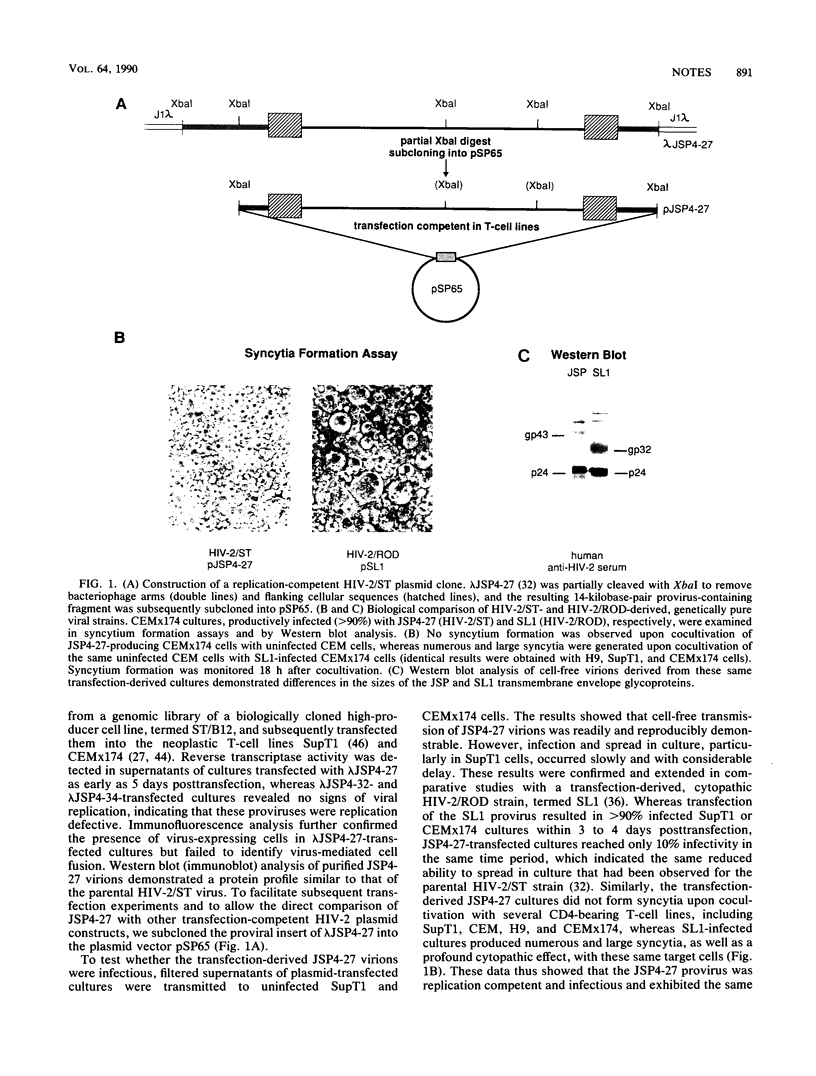



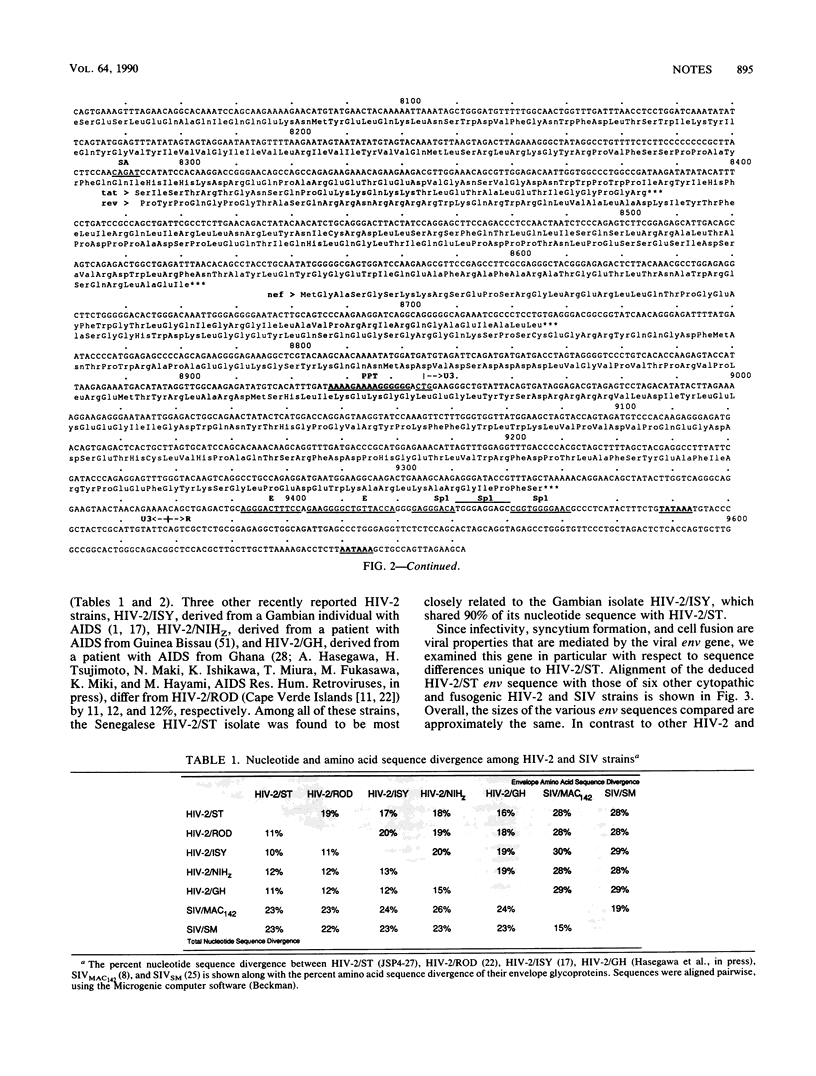
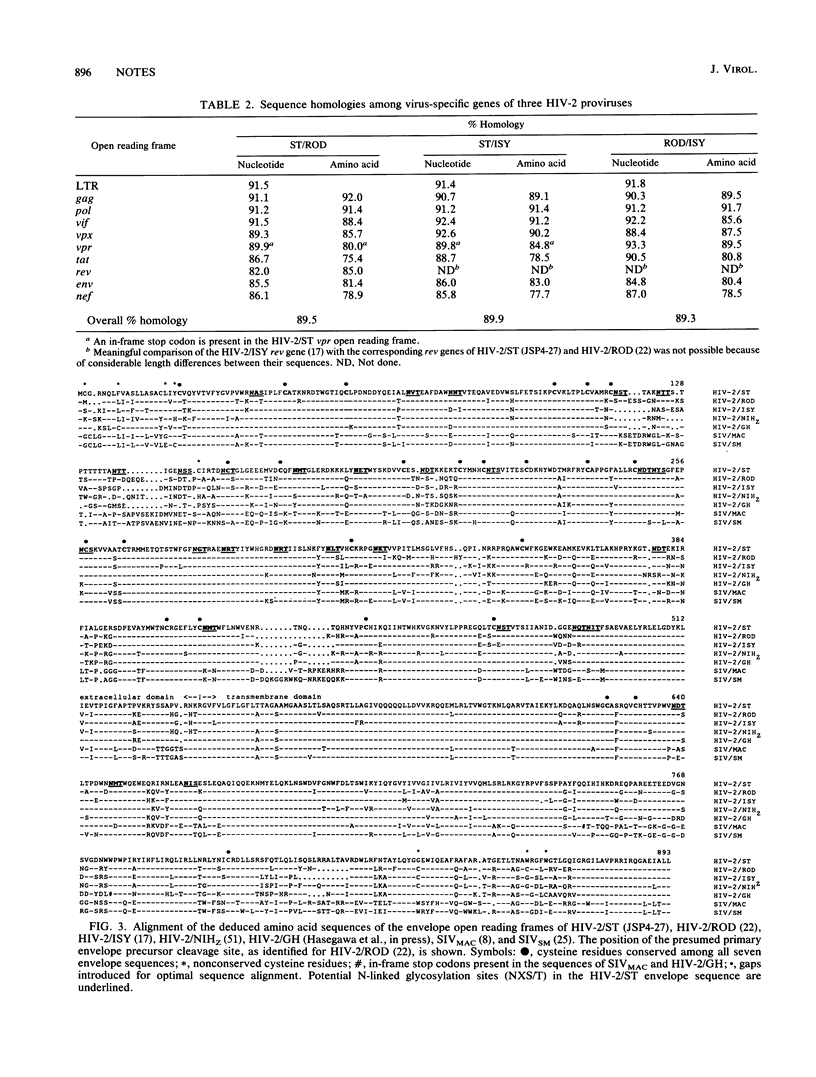





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert J., Bredberg U., Chiodi F., Böttiger B., Fenyö E. M., Norrby E., Biberfeld G. A new human retrovirus isolate of West African origin (SBL-6669) and its relationship to HTLV-IV, LAV-II, and HTLV-IIIB. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1987 Spring;3(1):3–10. doi: 10.1089/aid.1987.3.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asjö B., Morfeldt-Månson L., Albert J., Biberfeld G., Karlsson A., Lidman K., Fenyö E. M. Replicative capacity of human immunodeficiency virus from patients with varying severity of HIV infection. Lancet. 1986 Sep 20;2(8508):660–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barré-Sinoussi F., Chermann J. C., Rey F., Nugeyre M. T., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Dauguet C., Axler-Blin C., Vézinet-Brun F., Rouzioux C. Isolation of a T-lymphotropic retrovirus from a patient at risk for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Science. 1983 May 20;220(4599):868–871. doi: 10.1126/science.6189183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkelman R. L., Heyward W. L., Stehr-Green J. K., Curran J. W. Epidemiology of human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am J Med. 1989 Jun;86(6 Pt 2):761–770. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(89)90470-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosch M. L., Earl P. L., Fargnoli K., Picciafuoco S., Giombini F., Wong-Staal F., Franchini G. Identification of the fusion peptide of primate immunodeficiency viruses. Science. 1989 May 12;244(4905):694–697. doi: 10.1126/science.2541505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasseur R., Cornet B., Burny A., Vandenbranden M., Ruysschaert J. M. Mode of insertion into a lipid membrane of the N-terminal HIV gp41 peptide segment. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1988 Apr;4(2):83–90. doi: 10.1089/aid.1988.4.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti L., Guyader M., Alizon M., Daniel M. D., Desrosiers R. C., Tiollais P., Sonigo P. Sequence of simian immunodeficiency virus from macaque and its relationship to other human and simian retroviruses. Nature. 1987 Aug 6;328(6130):543–547. doi: 10.1038/328543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng-Mayer C., Seto D., Tateno M., Levy J. A. Biologic features of HIV-1 that correlate with virulence in the host. Science. 1988 Apr 1;240(4848):80–82. doi: 10.1126/science.2832945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clapham P. R., Weber J. N., Whitby D., McIntosh K., Dalgleish A. G., Maddon P. J., Deen K. C., Sweet R. W., Weiss R. A. Soluble CD4 blocks the infectivity of diverse strains of HIV and SIV for T cells and monocytes but not for brain and muscle cells. Nature. 1989 Jan 26;337(6205):368–370. doi: 10.1038/337368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clavel F., Guétard D., Brun-Vézinet F., Chamaret S., Rey M. A., Santos-Ferreira M. O., Laurent A. G., Dauguet C., Katlama C., Rouzioux C. Isolation of a new human retrovirus from West African patients with AIDS. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):343–346. doi: 10.1126/science.2425430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clavel F., Mansinho K., Chamaret S., Guetard D., Favier V., Nina J., Santos-Ferreira M. O., Champalimaud J. L., Montagnier L. Human immunodeficiency virus type 2 infection associated with AIDS in West Africa. N Engl J Med. 1987 May 7;316(19):1180–1185. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198705073161903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortes E., Detels R., Aboulafia D., Li X. L., Moudgil T., Alam M., Bonecker C., Gonzaga A., Oyafuso L., Tondo M. HIV-1, HIV-2, and HTLV-I infection in high-risk groups in Brazil. N Engl J Med. 1989 Apr 13;320(15):953–958. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198904133201501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel M. D., Letvin N. L., King N. W., Kannagi M., Sehgal P. K., Hunt R. D., Kanki P. J., Essex M., Desrosiers R. C. Isolation of T-cell tropic HTLV-III-like retrovirus from macaques. Science. 1985 Jun 7;228(4704):1201–1204. doi: 10.1126/science.3159089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedera D., Hu W., Vander Heyden N., Ratner L. Viral protein R of human immunodeficiency virus types 1 and 2 is dispensable for replication and cytopathogenicity in lymphoid cells. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):3205–3208. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.3205-3208.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L. A., Moreau J., Odehouri K., Legg H., Barboza A., Cheng-Mayer C., Levy J. A. Characterization of a noncytopathic HIV-2 strain with unusual effects on CD4 expression. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1522–1525. doi: 10.1126/science.2836951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franchini G., Fargnoli K. A., Giombini F., Jagodzinski L., De Rossi A., Bosch M., Biberfeld G., Fenyo E. M., Albert J., Gallo R. C. Molecular and biological characterization of a replication competent human immunodeficiency type 2 (HIV-2) proviral clone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2433–2437. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franchini G., Rusche J. R., O'Keeffe T. J., Wong-Staal F. The human immunodeficiency virus type 2 (HIV-2) contains a novel gene encoding a 16 kD protein associated with mature virions. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1988 Aug;4(4):243–250. doi: 10.1089/aid.1988.4.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukasawa M., Miura T., Hasegawa A., Morikawa S., Tsujimoto H., Miki K., Kitamura T., Hayami M. Sequence of simian immunodeficiency virus from African green monkey, a new member of the HIV/SIV group. Nature. 1988 Jun 2;333(6172):457–461. doi: 10.1038/333457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallaher W. R. Detection of a fusion peptide sequence in the transmembrane protein of human immunodeficiency virus. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):327–328. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90485-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo R. C., Salahuddin S. Z., Popovic M., Shearer G. M., Kaplan M., Haynes B. F., Palker T. J., Redfield R., Oleske J., Safai B. Frequent detection and isolation of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and at risk for AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):500–503. doi: 10.1126/science.6200936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodenow M., Huet T., Saurin W., Kwok S., Sninsky J., Wain-Hobson S. HIV-1 isolates are rapidly evolving quasispecies: evidence for viral mixtures and preferred nucleotide substitutions. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1989;2(4):344–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyader M., Emerman M., Sonigo P., Clavel F., Montagnier L., Alizon M. Genome organization and transactivation of the human immunodeficiency virus type 2. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):662–669. doi: 10.1038/326662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. E., Sowder R. C., Copeland T. D., Benveniste R. E., Oroszlan S. Isolation and characterization of a novel protein (X-ORF product) from SIV and HIV-2. Science. 1988 Jul 8;241(4862):199–201. doi: 10.1126/science.3388031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch V. M., Olmsted R. A., Murphey-Corb M., Purcell R. H., Johnson P. R. An African primate lentivirus (SIVsm) closely related to HIV-2. Nature. 1989 Jun 1;339(6223):389–392. doi: 10.1038/339389a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horsburgh C. R., Jr, Holmberg S. D. The global distribution of human immunodeficiency virus type 2 (HIV-2) infection. Transfusion. 1988 Mar-Apr;28(2):192–195. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1988.28288179031.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoxie J. A., Haggarty B. S., Bonser S. E., Rackowski J. L., Shan H., Kanki P. J. Biological characterization of a simian immunodeficiency virus-like retrovirus (HTLV-IV): evidence for CD4-associated molecules required for infection. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2557–2568. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2557-2568.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa K., Tsujimoto H., Nakai M., Mingle J. A., Osei-Kwasi M., Aggrey S. E., Nettey V. B., Afoakwa S. N., Fukasawa M., Kodama T. Isolation and characterization of HIV-2 from an AIDS patient in Ghana. AIDS. 1988 Oct;2(5):383–388. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198810000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanki P. J., M'Boup S., Ricard D., Barin F., Denis F., Boye C., Sangare L., Travers K., Albaum M., Marlink R. Human T-lymphotropic virus type 4 and the human immunodeficiency virus in West Africa. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):827–831. doi: 10.1126/science.3033826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappes J. C., Morrow C. D., Lee S. W., Jameson B. A., Kent S. B., Hood L. E., Shaw G. M., Hahn B. H. Identification of a novel retroviral gene unique to human immunodeficiency virus type 2 and simian immunodeficiency virus SIVMAC. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3501–3505. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3501-3505.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig S., Hirsch V. M., Olmsted R. A., Powell D., Maury W., Rabson A., Fauci A. S., Purcell R. H., Johnson P. R. Selective infection of human CD4+ cells by simian immunodeficiency virus: productive infection associated with envelope glycoprotein-induced fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2443–2447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong L. I., Lee S. W., Kappes J. C., Parkin J. S., Decker D., Hoxie J. A., Hahn B. H., Shaw G. M. West African HIV-2-related human retrovirus with attenuated cytopathicity. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1525–1529. doi: 10.1126/science.3375832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski M., Potz J., Basiripour L., Dorfman T., Goh W. C., Terwilliger E., Dayton A., Rosen C., Haseltine W., Sodroski J. Functional regions of the envelope glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Science. 1987 Sep 11;237(4820):1351–1355. doi: 10.1126/science.3629244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühnel H., von Briesen H., Dietrich U., Adamski M., Mix D., Biesert L., Kreutz R., Immelmann A., Henco K., Meichsner C. Molecular cloning of two west African human immunodeficiency virus type 2 isolates that replicate well in macrophages: a Gambian isolate, from a patient with neurologic acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, and a highly divergent Ghanian isolate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2383–2387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasky L. A., Nakamura G., Smith D. H., Fennie C., Shimasaki C., Patzer E., Berman P., Gregory T., Capon D. J. Delineation of a region of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 glycoprotein critical for interaction with the CD4 receptor. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90524-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifson J. D., Reyes G. R., McGrath M. S., Stein B. S., Engleman E. G. AIDS retrovirus induced cytopathology: giant cell formation and involvement of CD4 antigen. Science. 1986 May 30;232(4754):1123–1127. doi: 10.1126/science.3010463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCune J. M., Rabin L. B., Feinberg M. B., Lieberman M., Kosek J. C., Reyes G. R., Weissman I. L. Endoproteolytic cleavage of gp160 is required for the activation of human immunodeficiency virus. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):55–67. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90487-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovic M., Sarngadharan M. G., Read E., Gallo R. C. Detection, isolation, and continuous production of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and pre-AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):497–500. doi: 10.1126/science.6200935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poss M. L., Mullins J. I., Hoover E. A. Posttranslational modifications distinguish the envelope glycoprotein of the immunodeficiency disease-inducing feline leukemia virus retrovirus. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):189–195. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.189-195.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saag M. S., Hahn B. H., Gibbons J., Li Y., Parks E. S., Parks W. P., Shaw G. M. Extensive variation of human immunodeficiency virus type-1 in vivo. Nature. 1988 Aug 4;334(6181):440–444. doi: 10.1038/334440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salter R. D., Howell D. N., Cresswell P. Genes regulating HLA class I antigen expression in T-B lymphoblast hybrids. Immunogenetics. 1985;21(3):235–246. doi: 10.1007/BF00375376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. D., Shatsky M., Cohen P. S., Warnke R., Link M. P., Glader B. E. Monoclonal antibody and enzymatic profiles of human malignant T-lymphoid cells and derived cell lines. Cancer Res. 1984 Dec;44(12 Pt 1):5657–5660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tersmette M., Gruters R. A., de Wolf F., de Goede R. E., Lange J. M., Schellekens P. T., Goudsmit J., Huisman H. G., Miedema F. Evidence for a role of virulent human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) variants in the pathogenesis of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: studies on sequential HIV isolates. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2118–2125. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2118-2125.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willey R. L., Smith D. H., Lasky L. A., Theodore T. S., Earl P. L., Moss B., Capon D. J., Martin M. A. In vitro mutagenesis identifies a region within the envelope gene of the human immunodeficiency virus that is critical for infectivity. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):139–147. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.139-147.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoffe B., Lewis D. E., Petrie B. L., Noonan C. A., Melnick J. L., Hollinger F. B. Fusion as a mediator of cytolysis in mixtures of uninfected CD4+ lymphocytes and cells infected by human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1429–1433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu X. F., Ito S., Essex M., Lee T. H. A naturally immunogenic virion-associated protein specific for HIV-2 and SIV. Nature. 1988 Sep 15;335(6187):262–265. doi: 10.1038/335262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagury J. F., Franchini G., Reitz M., Collalti E., Starcich B., Hall L., Fargnoli K., Jagodzinski L., Guo H. G., Laure F. Genetic variability between isolates of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 2 is comparable to the variability among HIV type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5941–5945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





