Abstract
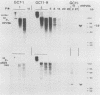
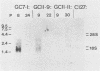
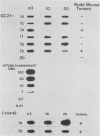
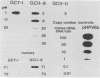
We describe the transformation of C127 mouse fibroblasts with human papillomavirus type 6b (HPV-6b) DNA, which is associated primarily with benign tumors of the human genital tract. The major transformed phenotype of the HPV-6b-transfected cells lines, which had been G418 selected, pooled, and maintained without subsequent selection, was tumorigenicity in nude mice. We found that, unlike that reported for other HPVs or papovaviruses, the transformed phenotype was expressed after a delay, in which the cells had undergone extensive culture passages (about 20 passages or 100 generations). Interestingly, the HPV-6b DNA had become reduced or nondetectable in copy number in the cells by the time the transformed phenotype was expressed and in most of the tumors induced by the cells in nude mice, indicating that high levels of HPV-6b DNA were not required for maintenance of the transformed phenotype. Clonal cell lines gave similar results. When continued G418 selection was used to maintain high-copy-number HPV-6b DNA, the cells were tumorigenic, indicating that high levels of HPV-6b DNA did not suppress tumorigenesis. These studies suggest that HPV-6b DNA initiates transformation of C127 cells but is dispensable for expression or maintenance of the transformed phenotype. Transformation by HPV-6b DNA in vitro may provide insights into the HPV type-specific association with benign versus malignant lesions in vivo and may elucidate some of the oncogenic processes involved in tumor progression.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bedell M. A., Jones K. H., Grossman S. R., Laimins L. A. Identification of human papillomavirus type 18 transforming genes in immortalized and primary cells. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1247–1255. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1247-1255.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedell M. A., Jones K. H., Laimins L. A. The E6-E7 region of human papillomavirus type 18 is sufficient for transformation of NIH 3T3 and rat-1 cells. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3635–3640. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3635-3640.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair D. G., Cooper C. S., Oskarsson M. K., Eader L. A., Vande Woude G. F. New method for detecting cellular transforming genes. Science. 1982 Dec 10;218(4577):1122–1125. doi: 10.1126/science.6293052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesters P. M., McCance D. J. Human papillomavirus types 6 and 16 in cooperation with Ha-ras transform secondary rat embryo fibroblasts. J Gen Virol. 1989 Feb;70(Pt 2):353–365. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-2-353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiPaolo J. A., Woodworth C. D., Popescu N. C., Notario V., Doniger J. Induction of human cervical squamous cell carcinoma by sequential transfection with human papillomavirus 16 DNA and viral Harvey ras. Oncogene. 1989 Apr;4(4):395–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürst M., Croce C. M., Gissmann L., Schwarz E., Huebner K. Papillomavirus sequences integrate near cellular oncogenes in some cervical carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1070–1074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürst M., Dzarlieva-Petrusevska R. T., Boukamp P., Fusenig N. E., Gissmann L. Molecular and cytogenetic analysis of immortalized human primary keratinocytes obtained after transfection with human papillomavirus type 16 DNA. Oncogene. 1987;1(3):251–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasano O., Birnbaum D., Edlund L., Fogh J., Wigler M. New human transforming genes detected by a tumorigenicity assay. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1695–1705. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasher M. S., Roman A. Characterization of human papillomavirus type 6b DNA isolated from an invasive squamous carcinoma of the vulva. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90676-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaur P., McDougall J. K. Characterization of primary human keratinocytes transformed by human papillomavirus type 18. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):1917–1924. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.1917-1924.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. Inhibition of SV40 replication in simian cells by specific pBR322 DNA sequences. Nature. 1981 Sep 3;293(5827):79–81. doi: 10.1038/293079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlashewski G., Schneider J., Banks L., Jones N., Murray A., Crawford L. Human papillomavirus type 16 DNA cooperates with activated ras in transforming primary cells. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1741–1746. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02426.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCance D. J., Kopan R., Fuchs E., Laimins L. A. Human papillomavirus type 16 alters human epithelial cell differentiation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7169–7173. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mincheva A., Gissmann L., zur Hausen H. Chromosomal integration sites of human papillomavirus DNA in three cervical cancer cell lines mapped by in situ hybridization. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1987;176(5):245–256. doi: 10.1007/BF00190531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D., Pecoraro G., Rosenberg I., Defendi V. Transformation of C127 mouse fibroblasts by human papillomavirus 16. Cancer Res. 1988 May 1;48(9):2505–2511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda T., Yajima H., Ito Y. Progression of the phenotype of transformed cells after growth stimulation of cells by a human papillomavirus type 16 gene function. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):313–324. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.313-324.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ocadiz R., Sauceda R., Cruz M., Graef A. M., Gariglio P. High correlation between molecular alterations of the c-myc oncogene and carcinoma of the uterine cervix. Cancer Res. 1987 Aug 1;47(15):4173–4177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pecoraro G., Morgan D., Defendi V. Differential effects of human papillomavirus type 6, 16, and 18 DNAs on immortalization and transformation of human cervical epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):563–567. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perucho M., Hanahan D., Wigler M. Genetic and physical linkage of exogenous sequences in transformed cells. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):309–317. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90178-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps W. C., Yee C. L., Münger K., Howley P. M. The human papillomavirus type 16 E7 gene encodes transactivation and transformation functions similar to those of adenovirus E1A. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):539–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90570-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirisi L., Yasumoto S., Feller M., Doniger J., DiPaolo J. A. Transformation of human fibroblasts and keratinocytes with human papillomavirus type 16 DNA. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1061–1066. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1061-1066.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popescu N. C., DiPaolo J. A., Amsbaugh S. C. Integration sites of human papillomavirus 18 DNA sequences on HeLa cell chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1987;44(1):58–62. doi: 10.1159/000132342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scangos G. A., Huttner K. M., Juricek D. K., Ruddle F. H. Deoxyribonucleic acid-mediated gene transfer in mammalian cells: molecular analysis of unstable transformants and their progression to stability. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;1(2):111–120. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.2.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Phelps W. C., Zhang Y. L., Barbosa M. Quantitative keratinocyte assay detects two biological activities of human papillomavirus DNA and identifies viral types associated with cervical carcinoma. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3181–3187. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03185.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz E., Dürst M., Demankowski C., Lattermann O., Zech R., Wolfsperger E., Suhai S., zur Hausen H. DNA sequence and genome organization of genital human papillomavirus type 6b. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2341–2348. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01744.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. T., Campo M. S. Amplification of specific DNA sequences in C127 mouse cells transformed by bovine papillomavirus type 4. Oncogene. 1989 Apr;4(4):409–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. T., Campq M. S. "Hit and run" transformation of mouse C127 cells by bovine papillomavirus type 4: the viral DNA is required for the initiation but not for maintenance of the transformed phenotype. Virology. 1988 May;164(1):39–47. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90617-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoker M. Abortive transformation by polyoma virus. Nature. 1968 Apr 20;218(5138):234–238. doi: 10.1038/218234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storey A., Pim D., Murray A., Osborn K., Banks L., Crawford L. Comparison of the in vitro transforming activities of human papillomavirus types. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1815–1820. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03013.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsunokawa Y., Takebe N., Kasamatsu T., Terada M., Sugimura T. Transforming activity of human papillomavirus type 16 DNA sequence in a cervical cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2200–2203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vousden K. H., Doniger J., DiPaolo J. A., Lowy D. R. The E7 open reading frame of human papillomavirus type 16 encodes a transforming gene. Oncogene Res. 1988 Sep;3(2):167–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe S., Kanda T., Yoshiike K. Human papillomavirus type 16 transformation of primary human embryonic fibroblasts requires expression of open reading frames E6 and E7. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):965–969. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.965-969.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R., Urlaub G., Chasin L. DNA-mediated transfer of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1373–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodworth C. D., Bowden P. E., Doniger J., Pirisi L., Barnes W., Lancaster W. D., DiPaolo J. A. Characterization of normal human exocervical epithelial cells immortalized in vitro by papillomavirus types 16 and 18 DNA. Cancer Res. 1988 Aug 15;48(16):4620–4628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodworth C. D., Doniger J., DiPaolo J. A. Immortalization of human foreskin keratinocytes by various human papillomavirus DNAs corresponds to their association with cervical carcinoma. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):159–164. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.159-164.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasumoto S., Burkhardt A. L., Doniger J., DiPaolo J. A. Human papillomavirus type 16 DNA-induced malignant transformation of NIH 3T3 cells. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):572–577. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.572-577.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasumoto S., Doniger J., DiPaolo J. A. Differential early viral gene expression in two stages of human papillomavirus type 16 DNA-induced malignant transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2165–2172. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villiers E. M., Gissmann L., zur Hausen H. Molecular cloning of viral DNA from human genital warts. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):932–935. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.932-935.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]