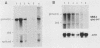Abstract
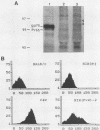
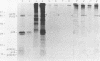
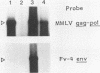
A nucleotide sequence of the mouse Fv-4 env gene was completed. Structural comparison revealed a close relationship of Fv-4 to the ecotropic Cas-Br-E murine leukemia virus isolated from a wild mouse in southern California. Various portions of the env gene of Moloney murine leukemia virus were replaced by the corresponding Fv-4 env sequence to construct recombinant murine leukemia virus clones. Infectivity of these recombinants was checked by the S+L- cell focus induction assay and the XC cell syncytium formation assay. Recombinants bearing the following Fv-4 env sequence retained ecotropic infectivity; the AccI-BamHI and BamHI-BalI regions coding for the N- and C-terminal halves of Fv-4 gp70SU, respectively; and the BalI-NcoI region encoding the cleavage site between gp70SU and p15(E)TM of the Fv-4 env. However, when the Fv-4 sequence was substituted for the p15(E)TM-coding NcoI-EcoRV region or the AccI-EcoRV region covering almost the entire env gene, infectivity was undetectable in our assays. The recombinant clone containing the Fv-4 AccI-EcoRV region, i.e., almost the entire Fv-4 env sequence, was introduced with pSV2neo into NIH 3T3 cells, and a G418r cell line named NIH(Fv4)-2 was isolated. The NIH(Fv4)-2 cell released viral particles that contained reverse transcriptase, Fv-4 env molecules as well as the other viral proteins, and viral genomic RNA. However, proviral DNA synthesis was not detected upon inoculation of this virus in NIH 3T3 cells. The loss of infectivity of the recombinant virus bearing the Fv-4 AccI-EcoRV region appeared to be caused by failure in an early step of replication.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson P., Goldfarb M. P., Weinberg R. A. A defined subgenomic fragment of in vitro synthesized Moloney sarcoma virus DNA can induce cell transformation upon transfection. Cell. 1979 Jan;16(1):63–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90188-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ando T., Toyoshima K. Genetic control of chick helper factor in cells which lack natural group-specific antigen of avian leukosis. Virology. 1976 Sep;73(2):521–527. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90413-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astrin S. M. Endogenous viral genes of the White Leghorn chicken: common site of residence and sites associated with specific phenotypes of viral gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5941–5945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astrin S. M., Robinson H. L., Crittenden L. B., Buss E. G., Wyban J., Hayward W. S. Ten genetic loci in the chicken that contain structural genes for endogenous avian leukosis viruses. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 2):1105–1109. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astrin S. M., Robinson H. L. Gs, an allele of chickens for endogenous avian leukosis viral antigens, segregates with ev 3, a genetic locus that contains structural genes for virus. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):420–425. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.420-425.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacheler L., Fan H. Isolation of recombinant DNA clones carrying complete integrated proviruses of Moloney murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):181–190. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.181-190.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassin R. H., Ruscetti S., Ali I., Haapala D. K., Rein A. Normal DBA/2 mouse cells synthesize a glycoprotein which interferes with MCF virus infection. Virology. 1982 Nov;123(1):139–151. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90301-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassin R. H., Tuttle N., Fischinger P. J. Isolation of murine sarcoma virus-transformed mouse cells which are negative for leukemia virus from agar suspension cultures. Int J Cancer. 1970 Jul 15;6(1):95–107. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910060114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassin R. H., Tuttle N., Fischinger P. J. Rapid cell culture assay technic for murine leukaemia viruses. Nature. 1971 Feb 19;229(5286):564–566. doi: 10.1038/229564b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Lee F., Harrison T., Williams J., Sharp P. A. Pre-early adenovirus 5 gene product regulates synthesis of early viral messenger RNAs. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):935–944. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90333-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berns A. J., Lai M. H., Bosselman R. A., McKennett M. A., Bacheler L. T., Fan H., Maandag E. C., van der Putten H. V., Verma I. M. Molecular cloning of unintegrated and a portion of integrated moloney murine leukemia viral DNA in bacteriophage lambda. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):254–263. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.254-263.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dandekar S., Rossitto P., Pickett S., Mockli G., Bradshaw H., Cardiff R., Gardner M. Molecular characterization of the Akvr-1 restriction gene: a defective endogenous retrovirus-borne gene identical to Fv-4r. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):308–314. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.308-314.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freed E. O., Risser R. The role of envelope glycoprotein processing in murine leukemia virus infection. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2852–2856. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2852-2856.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner M. B., Rasheed S., Pal B. K., Estes J. D., O'Brien S. J. Akvr-1, a dominant murine leukemia virus restriction gene, is polymorphic in leukemia-prone wild mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):531–535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner M. B. Retroviral spongiform polioencephalomyelopathy. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Jan-Feb;7(1):99–110. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.1.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner M. B. Type C viruses of wild mice: characterization and natural history of amphotropic, ecotropic, and xenotropic MuLv. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;79:215–259. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66853-1_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanafusa H., Miyamoto T., Hanafusa T. A cell-associated factor essential for formation of an infectious form of Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):314–321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Hidaka S., Sakaki Y. Sequence analysis of a KpnI family member near the 3' end of human beta-globin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 11;13(21):7813–7827. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.21.7813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W. Nucleotide sequence of AKV murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):471–478. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.471-478.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda H., Laigret F., Martin M. A., Repaske R. Characterization of a molecularly cloned retroviral sequence associated with Fv-4 resistance. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):768–777. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.768-777.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda H., Odaka T. A cell membrane "gp70" associated with Fv-4 gene: immunological characterization, and tissue and strain distribution. Virology. 1984 Feb;133(1):65–76. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90426-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda H., Odaka T. Cellular expression of murine leukemia virus gp70-related antigen on thymocytes of uninfected mice correlates with Fv-4 gene-controlled resistance to Friend leukemia virus infection. Virology. 1983 Jul 15;128(1):127–139. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90324-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jainchill J. L., Aaronson S. A., Todaro G. J. Murine sarcoma and leukemia viruses: assay using clonal lines of contact-inhibited mouse cells. J Virol. 1969 Nov;4(5):549–553. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.5.549-553.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kai K., Ikeda H., Yuasa Y., Suzuki S., Odaka T. Mouse strain resistant to N-, B-, and NB-tropic murine leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1976 Nov;20(2):436–440. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.2.436-440.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kai K., Sato H., Odaka T. Relationship between the cellular resistance to Friend murine leukemia virus infection and the expression of murine leukemia virus-gp70-related glycoprotein on cell surface of BALB/c-Fv-4wr mice. Virology. 1986 Apr 30;150(2):509–512. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90315-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch W., Hunsmann G., Friedrich R. Nucleotide sequence of the envelope gene of Friend murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):1–9. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.1-9.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak C. A., Gromet N. J., Ikeda H., Buckler C. E. A unique sequence related to the ecotropic murine leukemia virus is associated with the Fv-4 resistance gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):834–837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak C. A., O'Neill R. R. Diverse wild mouse origins of xenotropic, mink cell focus-forming, and two types of ecotropic proviral genes. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3082–3088. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3082-3088.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak C. A., Villar C. J., Voytek P. Genetic aspects of oncogenesis by murine leukemia viruses in wild mice. Crit Rev Oncog. 1989;1(2):127–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leis J., Baltimore D., Bishop J. M., Coffin J., Fleissner E., Goff S. P., Oroszlan S., Robinson H., Skalka A. M., Temin H. M. Standardized and simplified nomenclature for proteins common to all retroviruses. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1808–1809. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1808-1809.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCune J. M., Rabin L. B., Feinberg M. B., Lieberman M., Kosek J. C., Reyes G. R., Weissman I. L. Endoproteolytic cleavage of gp160 is required for the activation of human immunodeficiency virus. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):55–67. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90487-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A. J., Caravatti M., Robert B., Cohen A., Daubas P., Weydert A., Gros F., Buckingham M. E. Mouse actin messenger RNAs. Construction and characterization of a recombinant plasmid molecule containing a complementary DNA transcript of mouse alpha-actin mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):1008–1014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman S. B., Wunsch C. D. A general method applicable to the search for similarities in the amino acid sequence of two proteins. J Mol Biol. 1970 Mar;48(3):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill R. R., Buckler C. E., Theodore T. S., Martin M. A., Repaske R. Envelope and long terminal repeat sequences of a cloned infectious NZB xenotropic murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):100–106. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.100-106.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odaka T., Ikeda H., Akatsuka T. Restricted expression of endogenous N-tropic XC-positive leukemia virus in hybrids between G and AKR mice: an effect of the Fv-4r gene. Int J Cancer. 1980 Jun 15;25(6):757–762. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910250611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odaka T., Ikeda H. Genetic resistance to Friend leukemia virus in mice: masking of Fv-2 phenotype by an epistatic gene, Fv-4. Jpn J Exp Med. 1977 Dec;47(6):515–521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odaka T., Ikeda H., Moriwaki K., Matsuzawa A., Mizuno M., Kondo K. Genetic resistance in Japanese wild mice (Mus musculus molossinus) to an NB-tropic Friend murine leukemia virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1978 Nov;61(5):1301–1306. doi: 10.1093/jnci/61.5.1301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odaka T., Ikeda H., Yoshikura H., Moriwaki K., Suzuki S. Fv-4: gene controlling resistance to NB-tropic Friend murine leukemia virus. Distribution in wild mice, introduction into genetic background of BALB/c mice, and mapping of chromosomes. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1981 Nov;67(5):1123–1127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeples P. T., Gerwin B. I., Papageorge A. G., Smith S. G. Murine sarcoma virus defectiveness. Viral polymerase expression murine and nonmurine host cells transformed by S+L-type murine sarcoma virus. Virology. 1975 Oct;67(2):344–355. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90436-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rassart E., Nelbach L., Jolicoeur P. Cas-Br-E murine leukemia virus: sequencing of the paralytogenic region of its genome and derivation of specific probes to study its origin and the structure of its recombinant genomes in leukemic tissues. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):910–919. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.910-919.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson H. L., Astrin S. M., Senior A. M., Salazar F. H. Host Susceptibility to endogenous viruses: defective, glycoprotein-expressing proviruses interfere with infections. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):745–751. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.745-751.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson H. L., Lamoreux W. F. Expression of endogenous ALV antigens and susceptibility to subgroup E ALV in three strains of chickens (endogenous avian C-type virus). Virology. 1976 Jan;69(1):50–62. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90193-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Pugh W. E., Hartley J. W. Plaque assay techniques for murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):1136–1139. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90362-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy-Burman P., Dougherty M., Pal B. K., Charman H. P., Klement V., Gardner M. B. Assay for type C virus in mouse sera based on particulate reverse transcriptase activity. J Virol. 1976 Sep;19(3):1107–1110. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.3.1107-1110.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruscetti S., Davis L., Feild J., Oliff A. Friend murine leukemia virus-induced leukemia is associated with the formation of mink cell focus-inducing viruses and is blocked in mice expressing endogenous mink cell focus-inducing xenotropic viral envelope genes. J Exp Med. 1981 Sep 1;154(3):907–920. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.3.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVOBODA J., CHYLE P., SIMKOVIC D., HILGERT I. Demonstration of the absence of infectious Rous virus in rat tumour XC, whose structurally intact cells produce Rous sarcoma when transferred to chicks. Folia Biol (Praha) 1963 Apr;9:77–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Lerner R. A., Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequence of Moloney murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):543–548. doi: 10.1038/293543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sithanandam G., Rapp U. R. A single point mutation in the envelope gene is responsible for replication and XC fusion deficiency of the endogenous ecotropic C3H/He murine leukemia virus and for its repair in culture. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):932–943. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.932-943.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoye J. P., Coffin J. M. The four classes of endogenous murine leukemia virus: structural relationships and potential for recombination. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2659–2669. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2659-2669.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki S. FV-4: a new gene affecting the splenomegaly induction by Friend leukemia virus. Jpn J Exp Med. 1975 Dec;45(6):473–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki S., Matsubara S. Isolation of Friend leukemia virus resistant line from non-inbred mouse colony. Jpn J Exp Med. 1975 Dec;45(6):467–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang W. K., Kiggans J. O., Yang D. M., Ou C. Y., Tennant R. W., Brown A., Bassin R. H. Synthesis and circularization of N- and B-tropic retroviral DNA Fv-1 permissive and restrictive mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2994–2998. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikura H., Naito Y., Moriwaki K. Unstable resistance of G mouse fibroblasts to ecotropic murine leukemia virus infection. J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):1078–1086. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.1078-1086.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikura H., Odaka T. Resistance of G mice to murine leukemia virus infection: apparent disparity in in vivo and in vitro resistances. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1978 Aug;61(2):461–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikura H., Yoshida M. Intracellular restriction of ecotropic murine leukemia virus in rat NRK cells and its abolishment by adaptation. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):612–618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.612-618.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Larco J. E., Todaro G. J. Epithelioid and fibroblastic rat kidney cell clones: epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptors and the effect of mouse sarcoma virus transformation. J Cell Physiol. 1978 Mar;94(3):335–342. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040940311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]