Abstract
An avian leukosis virus-based packaging cell line was constructed from the genome of the Rous-associated virus type 1. The gag, pol, and env genes were separated on two different plasmids; the packaging signal and the 3' long terminal repeat were removed. On a plasmid expressing the gag and pol genes, the env gene was replaced by the hygromycin resistance gene. The phleomycin resistance gene was inserted in the place of the gag-pol genes on a plasmid expressing the env gene. The plasmid containing the gag, pol, and Hygror genes was transfected into QT6 cells. Clones that produced high levels of p27gag were transfected with the plasmid containing the Phleor and env genes. Clones that produced high levels of env protein (as measured by an interference assay) were tested for their ability to package NeoR-expressing replication-defective vectors (TXN3'). One of the clones (Isolde) was able to transfer the Neo+ phenotype to recipient cells at a titer of 10(5) resistance focus-forming units per ml. Titers of supernatants of cells infected with Rous-associated virus type 1 prior to transfection by Neor vectors were similar. Tests for recombination events that might result in intact helper virus showed no evidence for the generation of replication-competent virus. The use of selectable genes inserted next to the viral genes to generate high-producer packaging cell lines is discussed.
Full text
PDF
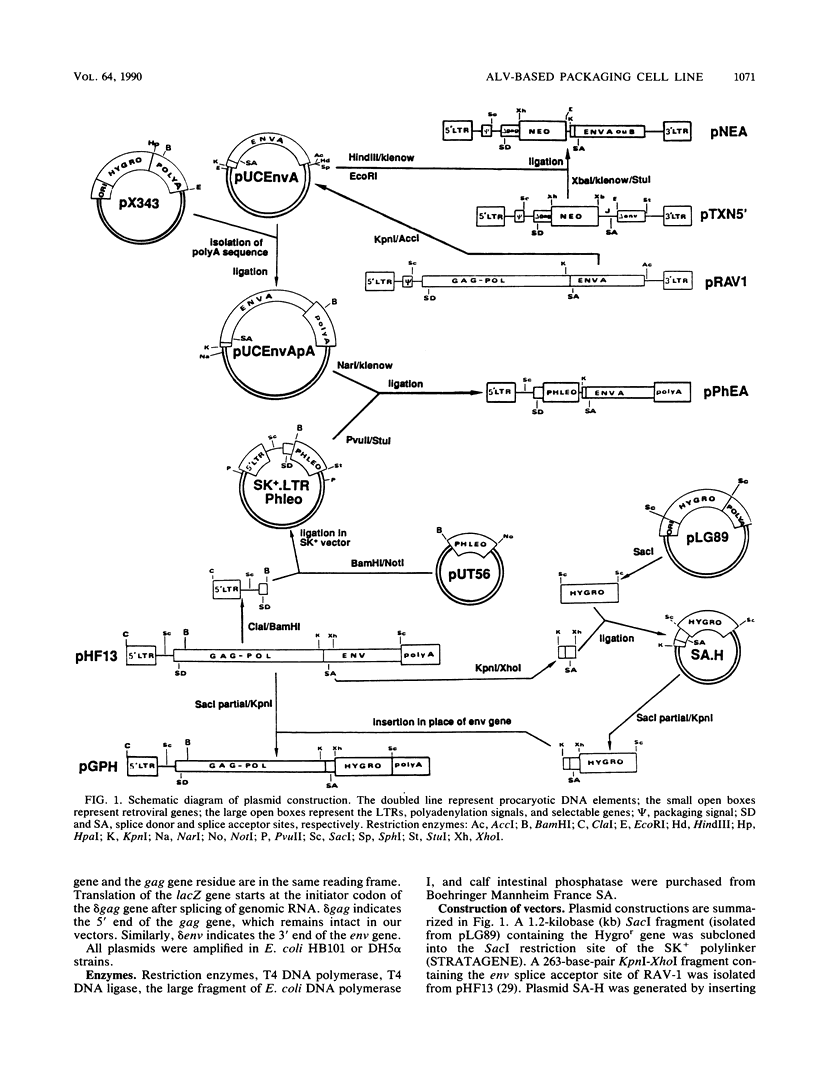

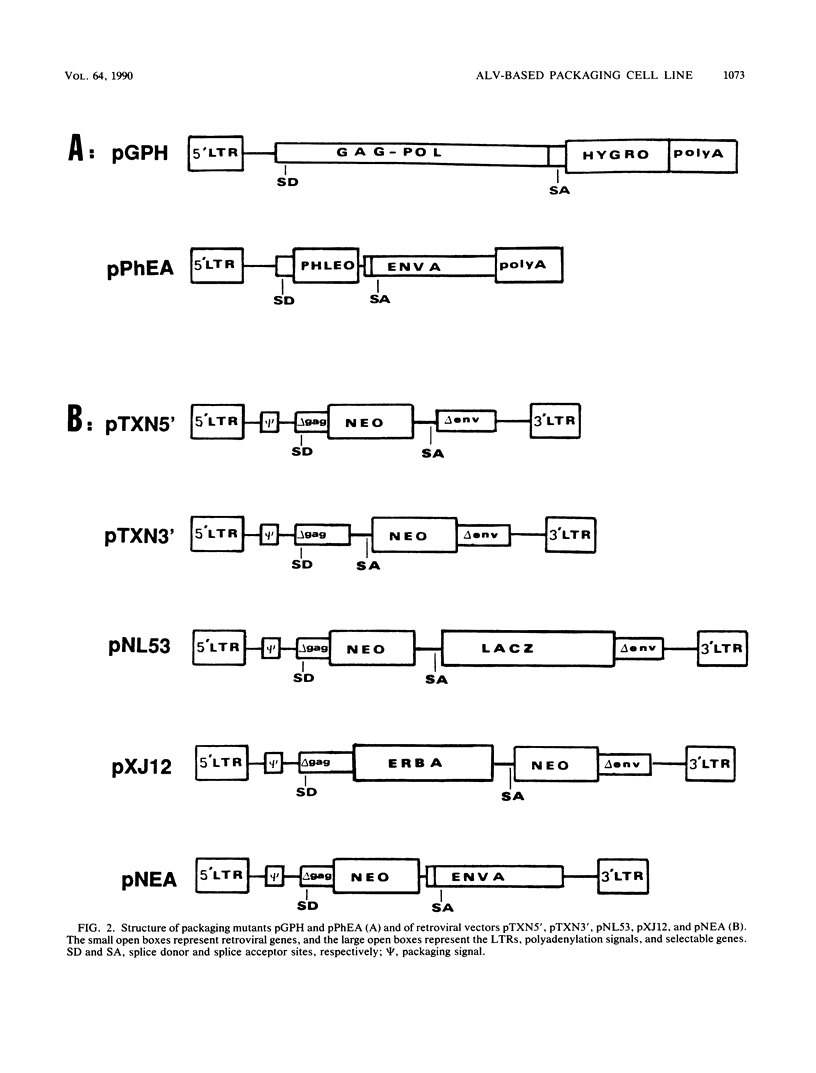
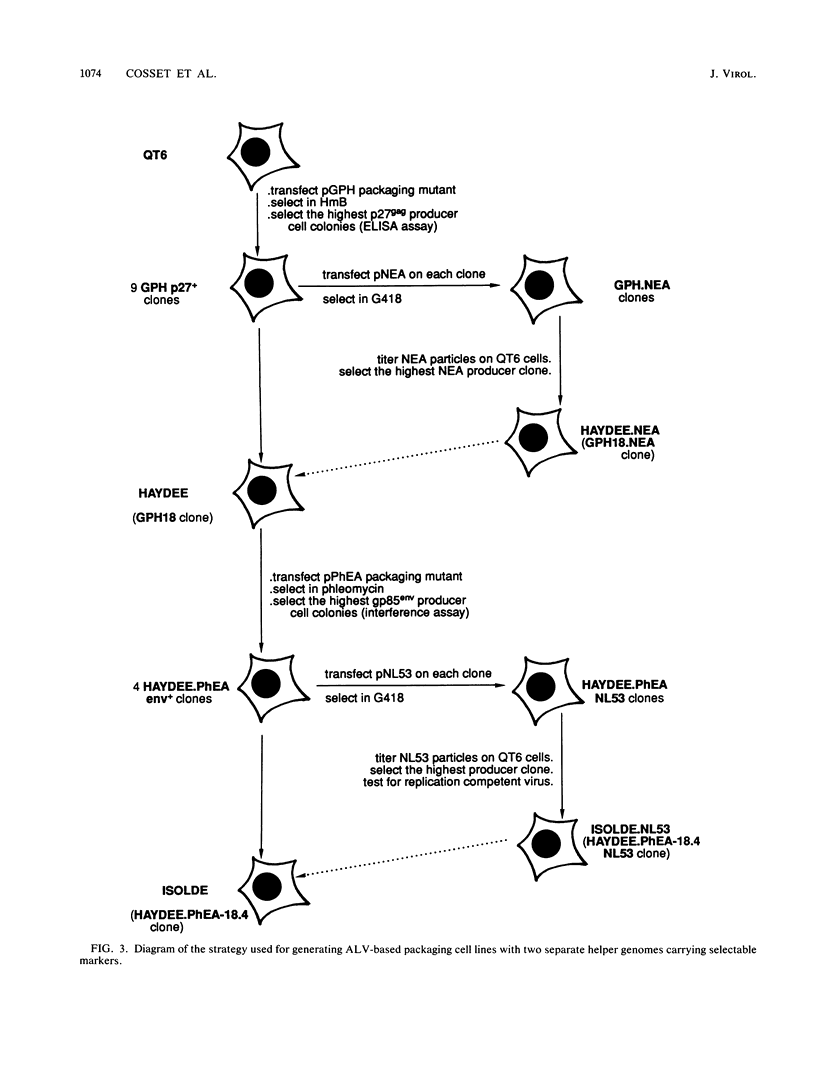
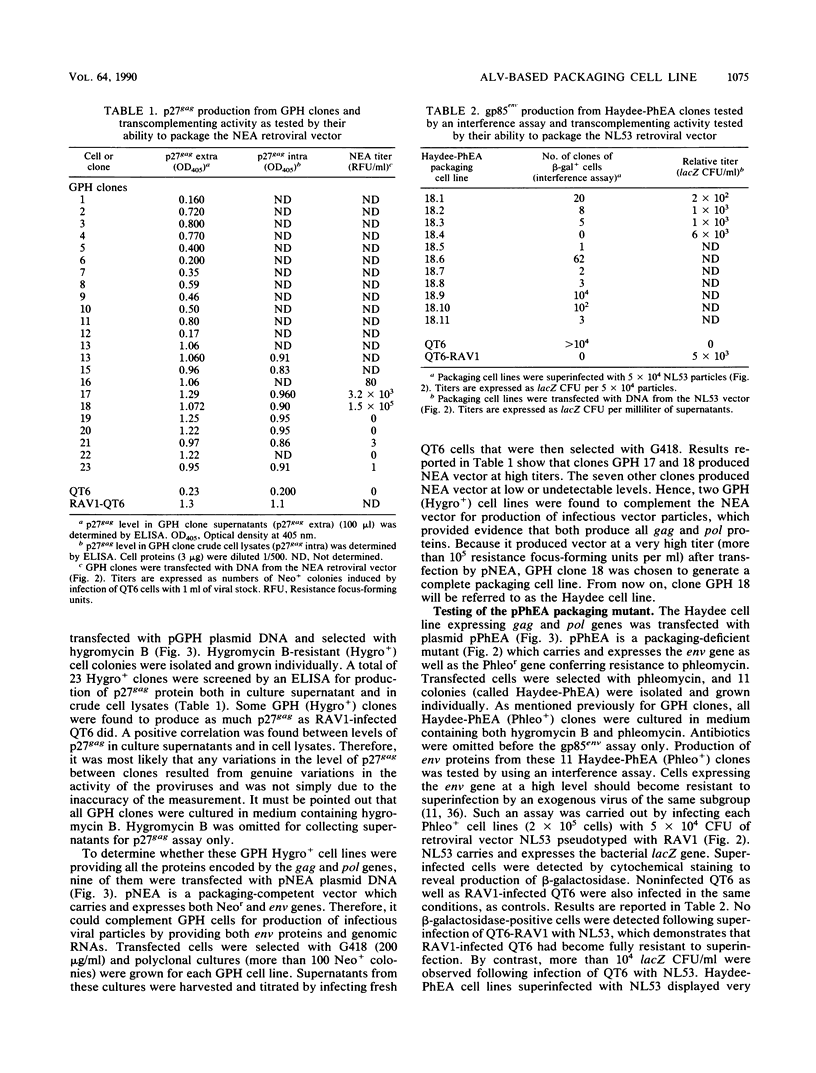



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benchaibi M., Mallet F., Thoraval P., Savatier P., Xiao J. H., Verdier G., Samarut J., Nigon V. Avian retroviral vectors derived from avian defective leukemia virus: role of the translational context of the inserted gene on efficiency of the vectors. Virology. 1989 Mar;169(1):15–26. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bestwick R. K., Kozak S. L., Kabat D. Overcoming interference to retroviral superinfection results in amplified expression and transmission of cloned genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5404–5408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosselman R. A., Hsu R. Y., Boggs T., Hu S., Bruszewski J., Ou S., Souza L., Kozar L., Martin F., Nicolson M. Replication-defective vectors of reticuloendotheliosis virus transduce exogenous genes into somatic stem cells of the unincubated chicken embryo. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2680–2689. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2680-2689.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosselman R. A., Hsu R. Y., Bruszewski J., Hu S., Martin F., Nicolson M. Replication-defective chimeric helper proviruses and factors affecting generation of competent virus: expression of Moloney murine leukemia virus structural genes via the metallothionein promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1797–1806. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. W., Robinson H. L. Influence of env and long terminal repeat sequences on the tissue tropism of avian leukosis viruses. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4828–4831. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4828-4831.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. P., Dougherty R. M. Detection of avian oncovirus group-specific antigens by the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Gen Virol. 1980 Apr;47(2):283–291. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-47-2-283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone R. D., Mulligan R. C. High-efficiency gene transfer into mammalian cells: generation of helper-free recombinant retrovirus with broad mammalian host range. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6349–6353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Kopchick J. J., Stacey D. W. Effect of intron size on splicing efficiency in retroviral transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 11;10(19):6177–6190. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.19.6177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danos O., Mulligan R. C. Safe and efficient generation of recombinant retroviruses with amphotropic and ecotropic host ranges. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6460–6464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delwart E. L., Panganiban A. T. Role of reticuloendotheliosis virus envelope glycoprotein in superinfection interference. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):273–280. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.273-280.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty J. P., Wisniewski R., Yang S. L., Rhode B. W., Temin H. M. New retrovirus helper cells with almost no nucleotide sequence homology to retrovirus vectors. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):3209–3212. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.3209-3212.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandrillon O., Jurdic P., Benchaibi M., Xiao J. H., Ghysdael J., Samarut J. Expression of the v-erbA oncogene in chicken embryo fibroblasts stimulates their proliferation in vitro and enhances tumor growth in vivo. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):687–697. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90545-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray G. E., Glover J. C., Majors J., Sanes J. R. Radial arrangement of clonally related cells in the chicken optic tectum: lineage analysis with a recombinant retrovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7356–7360. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang L. S., Park J., Gilboa E. Role of intron-contained sequences in formation of moloney murine leukemia virus env mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2289–2297. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz R. A., Terry R. W., Skalka A. M. A conserved cis-acting sequence in the 5' leader of avian sarcoma virus RNA is required for packaging. J Virol. 1986 Jul;59(1):163–167. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.1.163-167.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai S., Nishizawa M. New procedure for DNA transfection with polycation and dimethyl sulfoxide. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1172–1174. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R., Baltimore D. Varying the position of a retrovirus packaging sequence results in the encapsidation of both unspliced and spliced RNAs. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):401–407. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.401-407.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R., Mulligan R. C., Baltimore D. Construction of a retrovirus packaging mutant and its use to produce helper-free defective retrovirus. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90344-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz D., Goff S., Bank A. A safe packaging line for gene transfer: separating viral genes on two different plasmids. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1120–1124. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1120-1124.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Buttimore C. Redesign of retrovirus packaging cell lines to avoid recombination leading to helper virus production. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2895–2902. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Law M. F., Verma I. M. Generation of helper-free amphotropic retroviruses that transduce a dominant-acting, methotrexate-resistant dihydrofolate reductase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):431–437. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. K., Temin H. M. Insertion of several different DNAs in reticuloendotheliosis virus strain T suppresses transformation by reducing the amount of subgenomic mRNA. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):75–80. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.75-80.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscovici C., Moscovici M. G., Jimenez H., Lai M. M., Hayman M. J., Vogt P. K. Continuous tissue culture cell lines derived from chemically induced tumors of Japanese quail. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugatsch T., Stacey D. W. Identification of a sequence likely to be required for avian retroviral packaging. Virology. 1983 Jul 30;128(2):505–511. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90279-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savatier P., Bagnis C., Thoraval P., Poncet D., Belakebi M., Mallet F., Legras C., Cosset F. L., Thomas J. L., Chebloune Y. Generation of a helper cell line for packaging avian leukosis virus-based vectors. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):513–522. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.513-522.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoker A. W., Bissell M. J. Development of avian sarcoma and leukosis virus-based vector-packaging cell lines. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):1008–1015. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.1008-1015.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoltzfus C. M., Fogarty S. J. Multiple regions in the Rous sarcoma virus src gene intron act in cis to affect the accumulation of unspliced RNA. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1669–1676. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1669-1676.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swartz W. J., Domm L. V. A study on division of primordial germ cells in the early chick embryo. Am J Anat. 1972 Sep;135(1):51–70. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001350106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe S., Temin H. M. Construction of a helper cell line for avian reticuloendotheliosis virus cloning vectors. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2241–2249. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe S., Temin H. M. Encapsidation sequences for spleen necrosis virus, an avian retrovirus, are between the 5' long terminal repeat and the start of the gag gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5986–5990. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C., Reitz M. S., Okayama H., Eiden M. V. Formation of infectious hybrid virions with gibbon ape leukemia virus and human T-cell leukemia virus retroviral envelope glycoproteins and the gag and pol proteins of Moloney murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2374–2378. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2374-2378.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


