Abstract
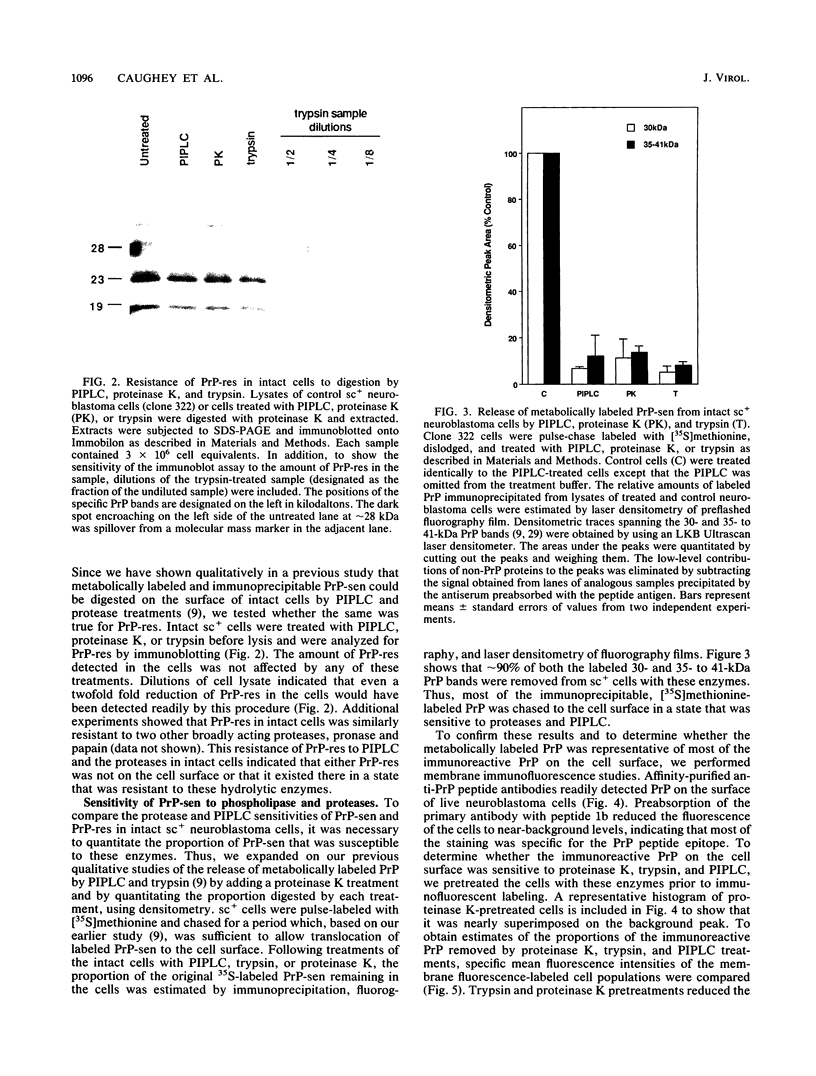
Previous studies have indicated that scrapie infection results in the accumulation of a proteinase K-resistant form of an endogenous brain protein generally referred to as prion protein (PrP). The molecular nature of the scrapie-associated modification of PrP accounting for proteinase K resistance is not known. As an approach to understanding the cellular events associated with the PrP modification in brain tissue, we sought to identify proteinase K-resistant PrP (PrP-res) in scrapie-infected neuroblastoma cells in vitro and to compare properties of PrP-res with those of its normal proteinase K-sensitive homolog, PrP-sen. PrP-res was detected by immunoblot in scrapie-infected but not uninfected neuroblastoma clones. Densitometry of immunoblots indicated that there was two- to threefold more PrP-res than PrP-sen in one infected clone. Metabolic labeling and membrane immunofluorescence experiments indicated that PrP-sen was located on the cell surface and could be removed from intact cells by phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C and proteases. In contrast, PrP-res was not removed after reaction with these enzymes. Thus, either the scrapie-associated PrP-res was not on the cell surface or it was there in a form that is resistant to these hydrolytic enzymes. Attempts to detect intracellular PrP-res by immunofluorescent staining of fixed and permeabilized cells revealed that PrP was present in discrete perinuclear Golgi-like structures. However, the staining pattern was similar in both scrapie-infected and uninfected clones, and thus the intracellular staining may have represented only PrP-sen. Analysis of scrapie infectivity in cells treated with extracellular phospholipase, proteinase K, and trypsin indicated that, like PrP-res, the scrapie agent was not removed from the infected cells by any of these enzymes.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alper T., Cramp W. A., Haig D. A., Clarke M. C. Does the agent of scrapie replicate without nucleic acid? Nature. 1967 May 20;214(5090):764–766. doi: 10.1038/214764a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basler K., Oesch B., Scott M., Westaway D., Wälchli M., Groth D. F., McKinley M. P., Prusiner S. B., Weissmann C. Scrapie and cellular PrP isoforms are encoded by the same chromosomal gene. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):417–428. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90662-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton D. C., Bendheim P. E., Marmorstein A. D., Potempska A. Isolation and structural studies of the intact scrapie agent protein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Nov 1;258(2):579–590. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90380-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton D. C., McKinley M. P., Prusiner S. B. Identification of a protein that purifies with the scrapie prion. Science. 1982 Dec 24;218(4579):1309–1311. doi: 10.1126/science.6815801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton D. C., McKinley M. P., Prusiner S. B. Molecular characteristics of the major scrapie prion protein. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 4;23(25):5898–5906. doi: 10.1021/bi00320a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton D. C., Meyer R. K., Prusiner S. B. Scrapie PrP 27-30 is a sialoglycoprotein. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):596–606. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.596-606.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler D. A., Scott M. R., Bockman J. M., Borchelt D. R., Taraboulos A., Hsiao K. K., Kingsbury D. T., Prusiner S. B. Scrapie-infected murine neuroblastoma cells produce protease-resistant prion proteins. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1558–1564. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1558-1564.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caughey B., Race R. E., Chesebro B. Detection of prion protein mRNA in normal and scrapie-infected tissues and cell lines. J Gen Virol. 1988 Mar;69(Pt 3):711–716. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-3-711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caughey B., Race R. E., Ernst D., Buchmeier M. J., Chesebro B. Prion protein biosynthesis in scrapie-infected and uninfected neuroblastoma cells. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):175–181. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.175-181.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caughey B., Race R. E., Vogel M., Buchmeier M. J., Chesebro B. In vitro expression in eukaryotic cells of a prion protein gene cloned from scrapie-infected mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4657–4661. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Race R., Wehrly K., Nishio J., Bloom M., Lechner D., Bergstrom S., Robbins K., Mayer L., Keith J. M. Identification of scrapie prion protein-specific mRNA in scrapie-infected and uninfected brain. Nature. 1985 May 23;315(6017):331–333. doi: 10.1038/315331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho H. J. Antibody to scrapie-associated fibril protein identifies a cellular antigen. J Gen Virol. 1986 Feb;67(Pt 2):243–253. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-2-243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diringer H., Gelderblom H., Hilmert H., Ozel M., Edelbluth C., Kimberlin R. H. Scrapie infectivity, fibrils and low molecular weight protein. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):476–478. doi: 10.1038/306476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith J. S. Self-replication and scrapie. Nature. 1967 Sep 2;215(5105):1043–1044. doi: 10.1038/2151043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay B., Barry R. A., Lieberburg I., Prusiner S. B., Lingappa V. R. Biogenesis and transmembrane orientation of the cellular isoform of the scrapie prion protein [published errratum appears in Mol Cell Biol 1987 May;7(5):2035]. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):914–920. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope J., Morton L. J., Farquhar C. F., Multhaup G., Beyreuther K., Kimberlin R. H. The major polypeptide of scrapie-associated fibrils (SAF) has the same size, charge distribution and N-terminal protein sequence as predicted for the normal brain protein (PrP). EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2591–2597. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04539.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope J., Multhaup G., Reekie L. J., Kimberlin R. H., Beyreuther K. Molecular pathology of scrapie-associated fibril protein (PrP) in mouse brain affected by the ME7 strain of scrapie. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Mar 1;172(2):271–277. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13883.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamoto T., Tateishi J., Tashima T., Takeshita I., Barry R. A., DeArmond S. J., Prusiner S. B. Amyloid plaques in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease stain with prion protein antibodies. Ann Neurol. 1986 Aug;20(2):204–208. doi: 10.1002/ana.410200205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Stiernberg J., Waneck G. L., Flavell R. A., Kincade P. W. Cell-specific heterogeneity in sensitivity of phosphatidylinositol-anchored membrane antigens to release by phospholipase C. J Immunol Methods. 1988 Oct 4;113(1):101–111. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90386-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L., Valley S., Manuelidis E. E. Specific proteins associated with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and scrapie share antigenic and carbohydrate determinants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4263–4267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinley M. P., Bolton D. C., Prusiner S. B. A protease-resistant protein is a structural component of the scrapie prion. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90207-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz P. A., Somerville R. A., Wisniewski H. M., Manuelidis L., Manuelidis E. E. Scrapie-associated fibrils in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):474–476. doi: 10.1038/306474a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. K., McKinley M. P., Bowman K. A., Braunfeld M. B., Barry R. A., Prusiner S. B. Separation and properties of cellular and scrapie prion proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2310–2314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesch B., Westaway D., Wälchli M., McKinley M. P., Kent S. B., Aebersold R., Barry R. A., Tempst P., Teplow D. B., Hood L. E. A cellular gene encodes scrapie PrP 27-30 protein. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):735–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90333-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattison I. H., Jones K. M. The possible nature of the transmissible agent of scrapie. Vet Rec. 1967 Jan 7;80(1):2–9. doi: 10.1136/vr.80.1.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B. Novel proteinaceous infectious particles cause scrapie. Science. 1982 Apr 9;216(4542):136–144. doi: 10.1126/science.6801762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Race R. E., Caughey B., Graham K., Ernst D., Chesebro B. Analyses of frequency of infection, specific infectivity, and prion protein biosynthesis in scrapie-infected neuroblastoma cell clones. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2845–2849. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2845-2849.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Race R. E., Fadness L. H., Chesebro B. Characterization of scrapie infection in mouse neuroblastoma cells. J Gen Virol. 1987 May;68(Pt 5):1391–1399. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-5-1391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. L., Kim B. H., Rosenberry T. L. Differences in the glycolipid membrane anchors of bovine and human erythrocyte acetylcholinesterases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7817–7821. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein R., Kascsak R. J., Merz P. A., Papini M. C., Carp R. I., Robakis N. K., Wisniewski H. M. Detection of scrapie-associated fibril (SAF) proteins using anti-SAF antibody in non-purified tissue preparations. J Gen Virol. 1986 Apr;67(Pt 4):671–681. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-4-671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklaviadis T., Manuelidis L., Manuelidis E. E. Characterization of major peptides in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and scrapie. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6146–6150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl N., Borchelt D. R., Hsiao K., Prusiner S. B. Scrapie prion protein contains a phosphatidylinositol glycolipid. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):229–240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90150-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessel D., Flügge U. I. A method for the quantitative recovery of protein in dilute solution in the presence of detergents and lipids. Anal Biochem. 1984 Apr;138(1):141–143. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90782-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley C. A., Burrola P. G., Buchmeier M. J., Wooddell M. K., Barry R. A., Prusiner S. B., Lampert P. W. Immuno-gold localization of prion filaments in scrapie-infected hamster brains. Lab Invest. 1987 Dec;57(6):646–656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







