Abstract
It has been established that the surface of poliovirus type 1 can be extensively modified to incorporate antigenic domains from other poliovirus serotypes and from unrelated viruses. The fact that the modified (chimeric) viruses exhibit dual antigenicity and immunogenicity led us to explore the possibility of using the Sabin vaccine strain of poliovirus type 1 as a vector for the presentation of antigenic domains from human papillomavirus type 16 (HPV-16), a virus associated with the development of cervical carcinoma. We report here the construction and characterization of a chimeric poliovirus containing a 16-residue sequence derived from the major capsid protein (L1) of HPV-16. This virus chimera stimulated the production in rabbits of antibodies which recognized the HPV-16-derived peptide and an L1 fusion protein synthesized in Escherichia coli and detected HPV-16 in human biopsy material by immunoperoxidase staining. The possibility that poliovirus-HPV chimeras could be used as vaccines against HPV-16 is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banks L., Spence P., Androphy E., Hubbert N., Matlashewski G., Murray A., Crawford L. Identification of human papillomavirus type 18 E6 polypeptide in cells derived from human cervical carcinomas. J Gen Virol. 1987 May;68(Pt 5):1351–1359. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-5-1351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Gissmann L., Ikenberg H., Kleinheinz A., Scheurlen W., zur Hausen H. A new type of papillomavirus DNA, its presence in genital cancer biopsies and in cell lines derived from cervical cancer. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1151–1157. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01944.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke K. L., Dunn G., Ferguson M., Minor P. D., Almond J. W. Antigen chimaeras of poliovirus as potential new vaccines. Nature. 1988 Mar 3;332(6159):81–82. doi: 10.1038/332081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke K. L., Evans D. J., Jenkins O., Meredith J., D'Souza E. D., Almond J. W. A cassette vector for the construction of antigen chimaeras of poliovirus. J Gen Virol. 1989 Sep;70(Pt 9):2475–2479. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-9-2475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cason J., Patel D., Naylor J., Lunney D., Shepherd P. S., Best J. M., McCance D. J. Identification of immunogenic regions of the major coat protein of human papillomavirus type 16 that contain type-restricted epitopes. J Gen Virol. 1989 Nov;70(Pt 11):2973–2987. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-11-2973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. E., Jenkins D., McCance D. J. Detection of human papillomavirus DNA sequences by in situ DNA-DNA hybridisation in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and invasive carcinoma: a retrospective study. J Clin Pathol. 1988 Mar;41(3):289–295. doi: 10.1136/jcp.41.3.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürst M., Gissmann L., Ikenberg H., zur Hausen H. A papillomavirus DNA from a cervical carcinoma and its prevalence in cancer biopsy samples from different geographic regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3812–3815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earle J. A., Skuce R. A., Fleming C. S., Hoey E. M., Martin S. J. The complete nucleotide sequence of a bovine enterovirus. J Gen Virol. 1988 Feb;69(Pt 2):253–263. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-2-253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., McKeating J., Meredith J. M., Burke K. L., Katrak K., John A., Ferguson M., Minor P. D., Weiss R. A., Almond J. W. An engineered poliovirus chimaera elicits broadly reactive HIV-1 neutralizing antibodies. Nature. 1989 Jun 1;339(6223):385-8, 340. doi: 10.1038/339385a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M., Minor P. D., Magrath D. I., Qui Y. H., Spitz M., Schild G. C. Neutralization epitopes on poliovirus type 3 particles: an analysis using monoclonal antibodies. J Gen Virol. 1984 Jan;65(Pt 1):197–201. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-1-197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
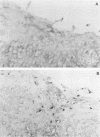
- Jenkins D., Tay S. K., McCance D. J., Campion M. J., Clarkson P. K., Singer A. Histological and immunocytochemical study of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) with associated HPV 6 and HPV 16 infections. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Nov;39(11):1177–1180. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.11.1177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathe R., Kieny M. P., Gerlinger P., Clertant P., Guizani I., Cuzin F., Chambon P. Tumour prevention and rejection with recombinant vaccinia. 1987 Apr 30-May 6Nature. 326(6116):878–880. doi: 10.1038/326878a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin A., Wychowski C., Couderc T., Crainic R., Hogle J., Girard M. Engineering a poliovirus type 2 antigenic site on a type 1 capsid results in a chimaeric virus which is neurovirulent for mice. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2839–2847. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03140.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCance D. J., Campion M. J., Clarkson P. K., Chesters P. M., Jenkins D., Singer A. Prevalence of human papillomavirus type 16 DNA sequences in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and invasive carcinoma of the cervix. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1985 Nov;92(11):1101–1105. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1985.tb03019.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melnick J. L. Poliomyelitis vaccines: an appraisal after 25 years. Compr Ther. 1980 Jan;6(1):6–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor P. D., Ferguson M., Evans D. M., Almond J. W., Icenogle J. P. Antigenic structure of polioviruses of serotypes 1, 2 and 3. J Gen Virol. 1986 Jul;67(Pt 7):1283–1291. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-7-1283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor P. D., Pipkin P. A., Hockley D., Schild G. C., Almond J. W. Monoclonal antibodies which block cellular receptors of poliovirus. Virus Res. 1984;1(3):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(84)90039-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. G., Bradley J., Yang X. F., Wimmer E., Moss E. G., Racaniello V. R. Poliovirus host range is determined by a short amino acid sequence in neutralization antigenic site I. Science. 1988 Jul 8;241(4862):213–215. doi: 10.1126/science.2838906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. G., Kuhn R. J., Arita M., Kawamura N., Nomoto A., Wimmer E. Poliovirus type 1/type 3 antigenic hybrid virus constructed in vitro elicits type 1 and type 3 neutralizing antibodies in rabbits and monkeys. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3203–3207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogra P. L., Ogra S. S. Local antibody response to poliovaccine in the human female genital tract. J Immunol. 1973 May;110(5):1307–1311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D., Shepherd P. S., Naylor J. A., McCance D. J. Reactivities of polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies raised to the major capsid protein of human papillomavirus type 16. J Gen Virol. 1989 Jan;70(Pt 1):69–77. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-1-69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rico-Hesse R., Pallansch M. A., Nottay B. K., Kew O. M. Geographic distribution of wild poliovirus type 1 genotypes. Virology. 1987 Oct;160(2):311–322. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90001-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smotkin D., Wettstein F. O. Transcription of human papillomavirus type 16 early genes in a cervical cancer and a cancer-derived cell line and identification of the E7 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4680–4684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhaori G., Sun M., Ogra P. L. Characteristics of the immune response to poliovirus virion polypeptides after immunization with live or inactivated polio vaccines. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jul;158(1):160–165. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.1.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Werf S., Bradley J., Wimmer E., Studier F. W., Dunn J. J. Synthesis of infectious poliovirus RNA by purified T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]