Abstract
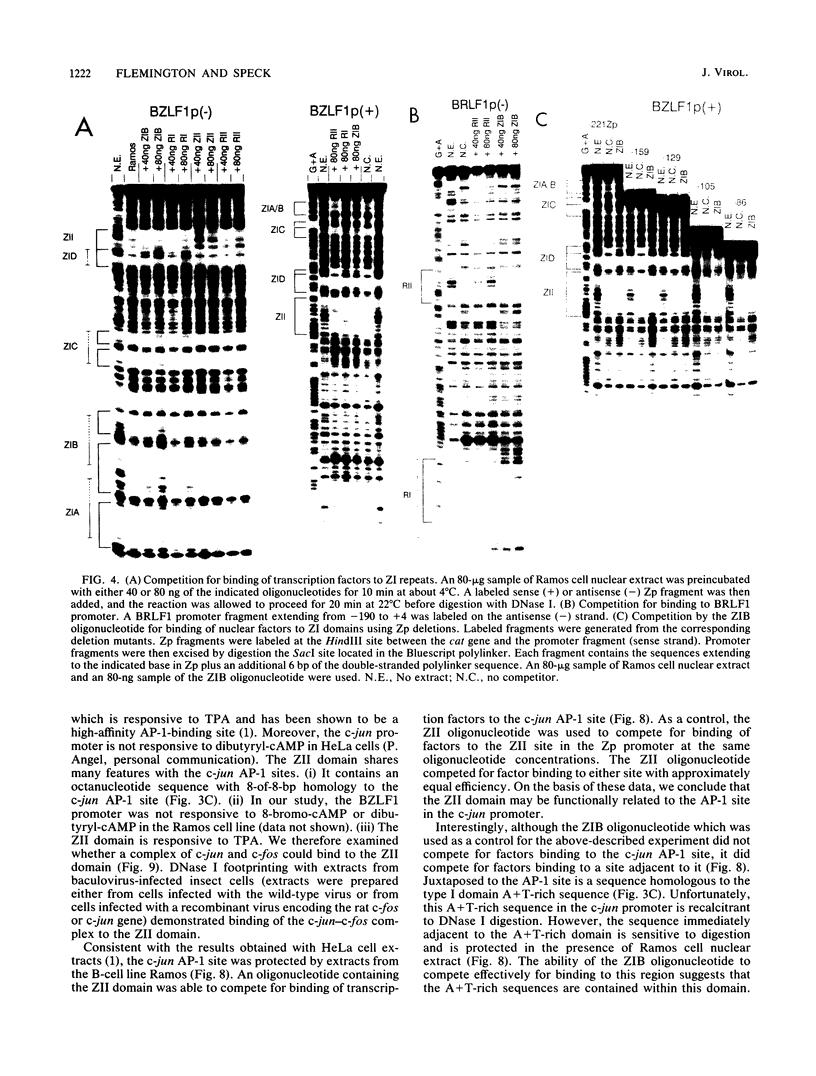
The product of the Epstein-Barr virus BZLF1 gene encodes a protein which is related to c-fos, it has been shown to bind specifically to a consensus AP-1 site, and its expression in latently Epstein-Barr virus-infected lymphocytes is sufficient to trigger the viral lytic cycle. We identified several elements within the BZLF1 promoter (Zp) which are responsive to the phorbol ester 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA), an inducer of the viral lytic cycle. These elements fall into two classes based on the factors which bind to these sequences and their resulting functional behavior. Four of the elements are homologous (ZI elements) and share homology to a protein-binding domain in the promoter region of the coordinately expressed BRLF1 gene. When cloned upstream of heterologous promoters, the ZI elements function as silencers which exhibit TPA-inducible enhancer activity. A distinct TPA-responsive element (ZII) is located near the TATA box and shares homology with the AP-1-binding site in the c-jun promoter. A synthetic oligonucleotide with a sequence corresponding to the ZII element effectively competes for binding of nuclear factors to the c-jun AP-1 site. Furthermore, we found that a complex of c-jun and c-fos bound to the ZII domain.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Hattori K., Smeal T., Karin M. The jun proto-oncogene is positively autoregulated by its product, Jun/AP-1. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):875–885. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90143-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold H. H., Tannich E., Paterson B. M. The promoter of the chicken cardiac myosin light chain 2 gene shows cell-specific expression in transfected primary cultures of chicken muscle. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(6):2411–2429. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.6.2411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austin P. J., Flemington E., Yandava C. N., Strominger J. L., Speck S. H. Complex transcription of the Epstein-Barr virus BamHI fragment H rightward open reading frame 1 (BHRF1) in latently and lytically infected B lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3678–3682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer G., Höfler P., Zur Hausen H. Epstein-Barr virus induction by a serum factor. I. Induction and cooperation with additional inducers. Virology. 1982 Aug;121(1):184–194. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90128-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M., Bodescot M., Perricaudet M., Farrell P. Epstein-Barr virus gene expression in P3HR1-superinfected Raji cells. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3120–3132. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3120-3132.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodescot M., Brison O., Perricaudet M. An Epstein-Barr virus transcription unit is at least 84 kilobases long. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2611–2620. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodescot M., Chambraud B., Farrell P., Perricaudet M. Spliced RNA from the IR1-U2 region of Epstein-Barr virus: presence of an open reading frame for a repetitive polypeptide. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1913–1917. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02067.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodescot M., Perricaudet M., Farrell P. J. A promoter for the highly spliced EBNA family of RNAs of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3424–3430. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3424-3430.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chevallier-Greco A., Manet E., Chavrier P., Mosnier C., Daillie J., Sergeant A. Both Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-encoded trans-acting factors, EB1 and EB2, are required to activate transcription from an EBV early promoter. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3243–3249. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04635.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen L. K., Speck S. H., Roberts B. E., Strominger J. L. Identification and mapping of polypeptides encoded by the P3HR-1 strain of Epstein-Barr virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4183–4187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Countryman J., Jenson H., Seibl R., Wolf H., Miller G. Polymorphic proteins encoded within BZLF1 of defective and standard Epstein-Barr viruses disrupt latency. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3672–3679. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3672-3679.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Countryman J., Miller G. Activation of expression of latent Epstein-Barr herpesvirus after gene transfer with a small cloned subfragment of heterogeneous viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4085–4089. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschamps J., Meijlink F., Verma I. M. Identification of a transcriptional enhancer element upstream from the proto-oncogene fos. Science. 1985 Dec 6;230(4730):1174–1177. doi: 10.1126/science.3865371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donoghue M., Ernst H., Wentworth B., Nadal-Ginard B., Rosenthal N. A muscle-specific enhancer is located at the 3' end of the myosin light-chain 1/3 gene locus. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1779–1790. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan C. M., Maniatis T. Two different virus-inducible elements are required for human beta-interferon gene regulation. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):101–110. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03353.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Rowe D. T., Rooney C. M., Kouzarides T. Epstein-Barr virus BZLF1 trans-activator specifically binds to a consensus AP-1 site and is related to c-fos. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):127–132. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03356.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fennewald S., van Santen V., Kieff E. Nucleotide sequence of an mRNA transcribed in latent growth-transforming virus infection indicates that it may encode a membrane protein. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):411–419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.411-419.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flemington E., Speck S. H. Autoregulation of Epstein-Barr virus putative lytic switch gene BZLF1. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1227–1232. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1227-1232.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foss K., McClain W. H. Rapid site-specific mutagenesis in plasmids. Gene. 1987;59(2-3):285–290. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90336-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossett L. A., Kelvin D. J., Sternberg E. A., Olson E. N. A new myocyte-specific enhancer-binding factor that recognizes a conserved element associated with multiple muscle-specific genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5022–5033. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grogan E., Jenson H., Countryman J., Heston L., Gradoville L., Miller G. Transfection of a rearranged viral DNA fragment, WZhet, stably converts latent Epstein-Barr viral infection to productive infection in lymphoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1332–1336. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardwick J. M., Lieberman P. M., Hayward S. D. A new Epstein-Barr virus transactivator, R, induces expression of a cytoplasmic early antigen. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2274–2284. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2274-2284.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III in DNA sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:156–165. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallin B., Luka J., Klein G. Immunochemical characterization of Epstein-Barr virus-associated early and late antigens in n-butyrate-treated P3HR-1 cells. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):710–716. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.710-716.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney S., Kamine J., Holley-Guthrie E., Lin J. C., Mar E. C., Pagano J. The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) BZLF1 immediate-early gene product differentially affects latent versus productive EBV promoters. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1729–1736. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1729-1736.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laux G., Perricaudet M., Farrell P. J. A spliced Epstein-Barr virus gene expressed in immortalized lymphocytes is created by circularization of the linear viral genome. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):769–774. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02874.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Mitchell P., Tjian R. Purified transcription factor AP-1 interacts with TPA-inducible enhancer elements. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90612-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman P. M., Hardwick J. M., Hayward S. D. Responsiveness of the Epstein-Barr virus NotI repeat promoter to the Z transactivator is mediated in a cell-type-specific manner by two independent signal regions. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):3040–3050. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.3040-3050.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman P. M., O'Hare P., Hayward G. S., Hayward S. D. Promiscuous trans activation of gene expression by an Epstein-Barr virus-encoded early nuclear protein. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):140–148. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.140-148.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luka J., Kallin B., Klein G. Induction of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) cycle in latently infected cells by n-butyrate. Virology. 1979 Apr 15;94(1):228–231. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90455-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magrath I., Freeman C., Novikovs L. Induction of complement receptor expression cell lines derived from human undifferentiated lymphomas. I. Mode of action of theophylline and inhibition by certain purines. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1034–1038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manet E., Gruffat H., Trescol-Biemont M. C., Moreno N., Chambard P., Giot J. F., Sergeant A. Epstein-Barr virus bicistronic mRNAs generated by facultative splicing code for two transcriptional trans-activators. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1819–1826. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03576.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan J. H., Pagano J. S. Enchancement of the infectivity of simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid with diethylaminoethyl-dextran. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Aug;41(2):351–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Rabson M., Heston L. Epstein-Barr virus with heterogeneous DNA disrupts latency. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):174–182. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.174-182.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Sevarino K. A., Wagner J. A., Mandel G., Goodman R. H. Identification of a cyclic-AMP-responsive element within the rat somatostatin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6682–6686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson G. R., Luka J., Petti L., Sample J., Birkenbach M., Braun D., Kieff E. Identification of an Epstein-Barr virus early gene encoding a second component of the restricted early antigen complex. Virology. 1987 Sep;160(1):151–161. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90055-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfitzner A. J., Tsai E. C., Strominger J. L., Speck S. H. Isolation and characterization of cDNA clones corresponding to transcripts from the BamHI H and F regions of the Epstein-Barr virus genome. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2902–2909. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2902-2909.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabson M., Heston L., Miller G. Identification of a rare Epstein-Barr virus variant that enhances early antigen expression in Raji cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2762–2766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. T., Farrell P. J., Miller G. Novel nuclear antigens recognized by human sera in lymphocytes latently infected by Epstein-Barr virus. Virology. 1987 Jan;156(1):153–162. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90446-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sample J., Hummel M., Braun D., Birkenbach M., Kieff E. Nucleotide sequences of mRNAs encoding Epstein-Barr virus nuclear proteins: a probable transcriptional initiation site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5096–5100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck S. H., Pfitzner A., Strominger J. L. An Epstein-Barr virus transcript from a latently infected, growth-transformed B-cell line encodes a highly repetitive polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9298–9302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck S. H., Strominger J. L. Analysis of the transcript encoding the latent Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen I: a potentially polycistronic message generated by long-range splicing of several exons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8305–8309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada K., Ono Y. Synchronous and sequential activation of latently infected Epstein-Barr virus genomes. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):445–449. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.445-449.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada K., Shimizu N., Sakuma S., Ono Y. trans activation of the latent Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) genome after transfection of the EBV DNA fragment. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):1016–1022. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.1016-1022.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tovey M. G., Lenoir G., Begon-Lours J. Activation of latent Epstein-Barr virus by antibody to human IgM. Nature. 1978 Nov 16;276(5685):270–272. doi: 10.1038/276270a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trask R. V., Strauss A. W., Billadello J. J. Developmental regulation and tissue-specific expression of the human muscle creatine kinase gene. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):17142–17149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urier G., Buisson M., Chambard P., Sergeant A. The Epstein-Barr virus early protein EB1 activates transcription from different responsive elements including AP-1 binding sites. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1447–1453. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03527.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. M., Levine A. J. Identification and mapping of Epstein-Barr virus early antigens and demonstration of a viral gene activator that functions in trans. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):149–156. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.149-156.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H., O'Neill F. J., Freese U. K., Hecker E. Persisting oncogenic herpesvirus induced by the tumour promotor TPA. Nature. 1978 Mar 23;272(5651):373–375. doi: 10.1038/272373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]