Abstract
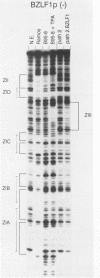
Expression of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) BZLF1 gene in latently infected lymphocytes is sufficient to trigger the viral lytic cycle. As shown in the accompanying report (E. Flemington and S.H. Speck, J. Virol. 64:1217-1226, 1990), the promoter for the BZLF1 gene (Zp) contains two distinct types of elements (ZI and ZII [an AP-1-like domain]) which are responsive to the phorbol ester 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA), an inducer of the viral lytic cycle. Although Zp can be activated with TPA in an EBV-negative Burkitt's lymphoma cell line (Ramos), its activity is considerably lower than in EBV-positive cell lines which can be induced with TPA. Here we show that the protein product of the BZLF1 gene (ZEBRA) can transactivate its own promoter by a mechanism which involves direct binding to a region distinct from the ZI and ZII element. Moreover, we show that this region is composed of two distinct ZEBRA-binding-transactivation domains. Interestingly, these two domains are not homologous, and while one domain (ZIIIA) is similar to previously described ZEBRA-binding domains, the second (ZIIIB) is a higher-affinity site which bears no detectable homology to the consensus ZEBRA recognition sequence. We also show that transactivation is independent of the otherwise essential ZII domain, suggesting that ZEBRA binding may functionally replace or supercede the need for a functional ZII domain. This observation supports a model for activation of the lytic cycle whereby synthesis of a critical level of ZEBRA signals commitment to BZLF1 transcription and initiation of the lytic cascade.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biggin M., Bodescot M., Perricaudet M., Farrell P. Epstein-Barr virus gene expression in P3HR1-superinfected Raji cells. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3120–3132. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3120-3132.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chevallier-Greco A., Manet E., Chavrier P., Mosnier C., Daillie J., Sergeant A. Both Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-encoded trans-acting factors, EB1 and EB2, are required to activate transcription from an EBV early promoter. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3243–3249. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04635.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Countryman J., Jenson H., Seibl R., Wolf H., Miller G. Polymorphic proteins encoded within BZLF1 of defective and standard Epstein-Barr viruses disrupt latency. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3672–3679. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3672-3679.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dieckmann C. L., Tzagoloff A. Assembly of the mitochondrial membrane system. CBP6, a yeast nuclear gene necessary for synthesis of cytochrome b. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1513–1520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Rowe D. T., Rooney C. M., Kouzarides T. Epstein-Barr virus BZLF1 trans-activator specifically binds to a consensus AP-1 site and is related to c-fos. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):127–132. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03356.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flemington E., Speck S. H. Identification of phorbol ester response elements in the promoter of Epstein-Barr virus putative lytic switch gene BZLF1. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1217–1226. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1217-1226.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foss K., McClain W. H. Rapid site-specific mutagenesis in plasmids. Gene. 1987;59(2-3):285–290. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90336-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardwick J. M., Lieberman P. M., Hayward S. D. A new Epstein-Barr virus transactivator, R, induces expression of a cytoplasmic early antigen. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2274–2284. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2274-2284.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney S., Kamine J., Holley-Guthrie E., Lin J. C., Mar E. C., Pagano J. The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) BZLF1 immediate-early gene product differentially affects latent versus productive EBV promoters. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1729–1736. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1729-1736.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Mitchell P., Tjian R. Purified transcription factor AP-1 interacts with TPA-inducible enhancer elements. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90612-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman P. M., Hardwick J. M., Hayward S. D. Responsiveness of the Epstein-Barr virus NotI repeat promoter to the Z transactivator is mediated in a cell-type-specific manner by two independent signal regions. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):3040–3050. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.3040-3050.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman P. M., O'Hare P., Hayward G. S., Hayward S. D. Promiscuous trans activation of gene expression by an Epstein-Barr virus-encoded early nuclear protein. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):140–148. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.140-148.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck S. H., Strominger J. L. Analysis of the transcript encoding the latent Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen I: a potentially polycistronic message generated by long-range splicing of several exons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8305–8309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spindler K. R., Rosser D. S., Berk A. J. Analysis of adenovirus transforming proteins from early regions 1A and 1B with antisera to inducible fusion antigens produced in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):132–141. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.132-141.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada K., Ono Y. Synchronous and sequential activation of latently infected Epstein-Barr virus genomes. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):445–449. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.445-449.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada K., Shimizu N., Sakuma S., Ono Y. trans activation of the latent Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) genome after transfection of the EBV DNA fragment. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):1016–1022. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.1016-1022.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urier G., Buisson M., Chambard P., Sergeant A. The Epstein-Barr virus early protein EB1 activates transcription from different responsive elements including AP-1 binding sites. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1447–1453. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03527.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt P. K., Bos T. J., Doolittle R. F. Homology between the DNA-binding domain of the GCN4 regulatory protein of yeast and the carboxyl-terminal region of a protein coded for by the oncogene jun. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3316–3319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]